Key Takeaways
- TA402, a likely Palestinian-aligned advance persistent threat actor, has recently engaged in campaigns leveraging a new implant, dubbed by Proofpoint analysts as NimbleMamba.
- NimbleMamba is likely a replacement for the group’s previously used LastConn implant.
- These campaigns have a complex attack chain that leverages geofencing and URL redirects to legitimate sites in order to bypass detection efforts.
Overview
In late 2021, Proofpoint analysts identified a complex attack chain targeting Middle Eastern governments, foreign policy think tanks, and a state-affiliated airline. Over three months, Proofpoint observed three subtle variations of this attack chain. Proofpoint attributes these campaigns to TA402, an actor commonly tracked as Molerats and believed to be operating in the interest of the Palestinian Territories. Based on Proofpoint’s research, TA402 is a persistent threat to organizations and governments in the Middle East, routinely updating not only their malware implants, but also their delivery methods. After publication of Proofpoint’s TA402 research in June 2021, TA402 appeared to halt its activities for a short period of time, almost certainly to retool. Proofpoint researchers believe they used that time to update their implants and delivery mechanisms, using malware dubbed NimbleMamba and BrittleBush. TA402 also regularly uses geofencing techniques and varied attack chains which complicate detection efforts for defenders.
Campaign Details
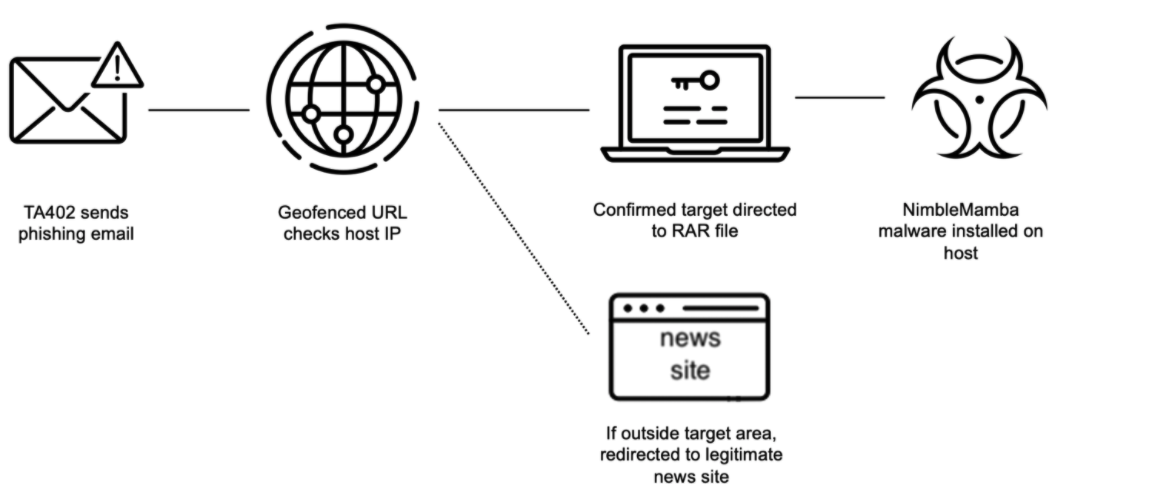
Figure 1. TA402 attack chain November 2021 to January 2022.
In the recently observed campaigns, TA402 used spear phishing emails containing links that often lead to malicious files. Proofpoint observed three different URL types in those campaigns.
Variation 1: Actor-Controlled Domain (November 2021)
In a November 2021 campaign, TA402 masqueraded as the Quora website while using an actor-controlled Gmail account with an actor-controlled domain. The malicious URL, such as https[:]//www[.]uggboots4sale[.]com/news15112021.php, in the phishing email was geofenced to the targeted countries. If the target’s IP address fits into the targeted region, the user would be redirected to the RAR file download containing the latest TA402 implant, NimbleMamba. If outside the target area, the user would be redirected to a legitimate news site, Figure 2.

Figure 2. Benign redirect to legitimate news site https[:]www[.]emaratalyoum[.]com.
Variation 2: Dropbox URL (December 2021)
In December 2021, TA402 used multiple phishing pretenses, including clickbait medical lures and ones allegedly sharing confidential geopolitical information. TA402 continued to use an actor-controlled Gmail account but shifted to Dropbox URLs to deliver the malicious RAR files containing NimbleMamba. This shift away from actor-controlled domains meant that TA402 could no longer geofence their payloads. Proofpoint discovered that TA402 is not only abusing Dropbox services for delivery of NimbleMamba, but also for malware command and control (C2). Proofpoint has shared our investigation and analysis with Dropbox prior to publication, and they took the needed actions for neutralizing the activity within their organization.
Variation 3: WordPress Redirect Actor-Controlled Domain (December 2021/January 2022)
In their latest campaigns, TA402 continued to use lure content customized for each of their targets but slightly adjusted their attack chain by inserting an additional actor-controlled WordPress URL. That WordPress site (Figure 3), which impersonates a news aggregator of the legitimate news site from Variation 1, likely redirects to the download site of the malicious RAR files containing NimbleMamba if the visitor is coming from an IP within the targeted region. If the source IP address does not align with the target region, the URL will redirect the recipient to a benign website, typically an Arabic language news website (Figure 2).
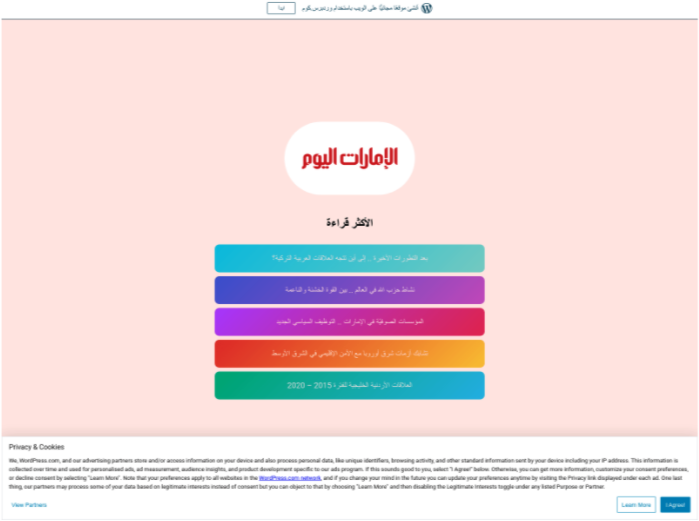
Figure 3. Example WordPress site (https[:]//emaratalyoumcom[.]wordpress[.]com/) impersonating an Arabic language news aggregator.
The use of geofenced URLs, Dropbox URLs and then redirect URLs demonstrate TA402’s determination to blend in with legitimate email traffic and infect targets with NimbleMamba.
Malware Analysis: NimbleMamba
Each variant of TA402’s attack chain led to a RAR file containing one or multiple malicious compressed executables. These executables include a TA402 implant Proofpoint dubbed NimbleMamba and oftentimes an additional trojan Proofpoint named BrittleBush. NimbleMamba is almost certainly meant to replace LastConn, which Proofpoint reported about in June 2021. LastConn was likely an updated version of the SharpStage malware, reported by Cybereason in December 2020. While NimbleMamba and LastConn have some similarities, such as being written in C#, base64 encoding within the C2 framework, and use of the Dropbox API for C2 communication, there appears to be little code overlap between the two.
NimbleMamba uses guardrails to ensure that all infected victims are within TA402’s target region. NimbleMamba uses the Dropbox API for both command and control as well as exfiltration. The malware also contains multiple capabilities designed to complicate both automated and manual analysis. Based on this, Proofpoint assesses NimbleMamba is actively being developed, is well-maintained, and designed for use in highly targeted intelligence collection campaigns.
For this malware analysis, Proofpoint researchers analyzed the following two samples:
| SHA256 | Compile time | Activity |
Sample 1 | c61fcd8bed15414529959e8b5484b2c559ac597143c1775b1cec7d493a40369d
| 2021-11-07 00:02:28 | Used in an email-based campaign in November 2021
|
Sample 2 | 430c12393a1714e3f5087e1338a3e3846ab62b18d816cc4916749a935f8dab44
| 2021-11-20 23:13:29 | Used in email-based campaigns in December 2021 and January 2022
|
NimbleMamba is written in C# and delivered as an obfuscated .NET executable using third-party obfuscators. Both samples analyzed used the SmartAssembly obfuscator. Additionally, the malware does basic virtual machine checks to avoid detection by looking for common strings that indicate a sample is running in a virtual environment.
Guardrails
NimbleMamba contains multiple guardrails to ensure that the malware only executes on targeted machines. It uses the following IP resolving web services to check the user’s IP address and determine if it fits into the target region. This is done to avoid detection and analysis.
If the machine is unable to connect to those services, the malware will keep calling the addresses in random order, thus putting the execution in an endless loop in closed network environments.
The malware will only continue executing if the country of the resolved IP address country code matches one from the following table or if the host computer has an Arabic language pack (code “AR”) installed.
Code | Country |
KW | Kuwait |
EG | Egypt |
IL | Israel |
SA | Saudi Arabia |
IR | Iran |
AE | United Arab Emirates |
TN | Tunisia |
DZ | Algeria |
SY | Syria |
QA | Qatar |
JO | Jordan |
OM | Oman |
PS | Palestine |
LB | Lebanon |
LY | Libya |
SS | South Sudan |
SSD | Soud Sudan (Alpha-3 code, probably added by accident) |
IQ | Iraq |
YE | Yemen |
MA | Morocco |
BH | Bahrain |
Configuration
NimbleMamba’s configuration is retrieved from a paste on the website JustPasteIt. NimbleMamba takes the current timestamp from an online real-time service to ensure that the timestamp matches the current time. Some computers may have modified time settings and this method ensures that the time is standardized across infections. The obtained timestamp is then used to generate a JustPasteIt URL with the algorithm in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Python implementation of NimbleMamba’s JustPasteIt algorithm.
When there is an active paste under the generated URL, it should look like this:
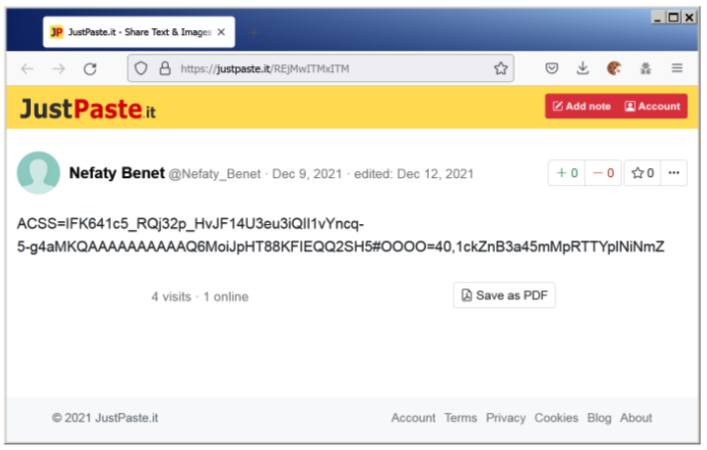
Figure 5. Example of JustePasteIt paste content.
The data taken from the paste service is split by “#” and then each split by “=” to form the following two key-value pairs.
Key | Value |
ACSS | IFK641c5_RQj32p_HvJF14U3eu3iQIl1vYncq-5-g4aMKQAAAAAAAAAAQ6MoiJpHT88KFIEQQ2SH5 |
OOOO | 40,1ckZnB3a45mMpRTTYplNiNmZ |
ACSS contains the obfuscated Dropbox account API auth key that is used for C2 communication. The malware then takes the external IP address, username and computer name retrieved earlier, writes them as comma-separated strings, base64 encodes them with stripped padding bytes and then reverses the string. The resulting string is used as a folder name that is created on the Dropbox account using their API with the API key deobfuscated (Figure 6) from the JustPasteIt post.
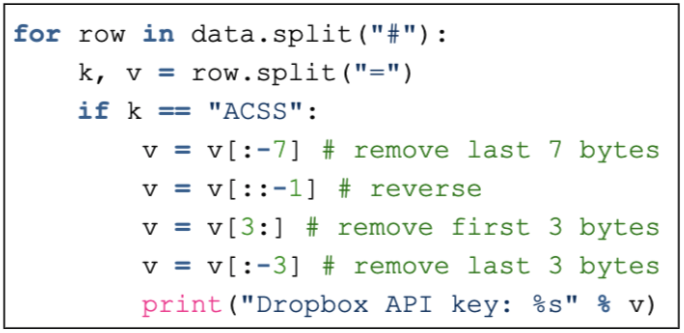
Figure 6. Dropbox API key deobfuscation.
From there, the malware starts communicating with Dropbox to obtain a RAR file and a decoy file that is immediately displayed to the user if present. The decoy file is often an office document or PDF. The RAR file is password-protected with a password stored as the second comma-separated value in the OOOO argument from the JustPasteIt paste and dropped to the folder pointed by the first parameter in OOOO. The downloaded RAR file contains two additional executables, an updated sample of NimbleMamba along with an executable that contains a screenshot of the functionality. This technique allows for TA402 to serve additional payloads to targeted NimbleMamba victims.
Pivoting on the JustPasteIt user “Nefaty Benet” (Researcher Note: This account is likely meant to impersonate the Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett) allows us to see that the NimbleMamba campaign likely started in August 2021, two months after Proofpoint’s previous research. This timeframe is consistent with the compile dates of the NimbleMamba samples identified in VirusTotal.
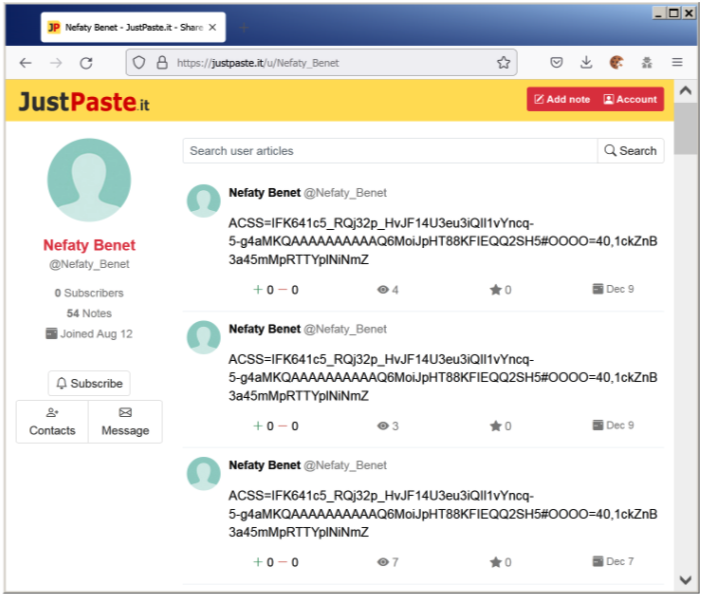
Figure 7. Pivot to all pastes created by user “Nefaty Benet.”
Functionality
NimbleMamba has the traditional capabilities of an intelligence-gathering trojan and is likely designed to be the initial access. Functionalities include capturing screenshots and obtaining process information from the computer. Additionally, it can detect user interaction, such as looking for mouse movement.
BrittleBush Trojan
Later versions of the RAR files that deliver NimbleMamba also included a small trojan application Proofpoint dubbed BrittleBush (2E4671C517040CBD66A1BE0F04FB8F2AF7064FEF2B5EE5E33D1F9D347E4C419F). This trojan communicated with easyuploadservice[.]com and received commands as base64 encoded JSON structure.

Figure 8. BrittleBush JSON structure.
Attribution
Proofpoint attributes the campaigns to TA402 based on both technical indicators and victimology. The observed attack chains mimic historical TA402 campaigns, some of which are discussed in Proofpoint’s June 2021 research. The phishing campaigns share thematic elements with historical Molerats campaigns. For example, the December 2021 campaign contained a title bearing significant similarities to a 2015 TA402 campaign reported by Kaspersky.
Campaign | Arabic Title | Translation |
2015 Kaspersky Campaign | “مكالمة مسربة بين القائد العام للقوات المسلحة المصرية صدقي صبحي.exe” | Leaked conversation with the Egyptian leader of military forces Sodqi Sobhi[.]exe |
December 2021 Campaign | لقاء سري بين بن سلمان واردوغان في قطر | Secret meeting between bin Salman and Erdogan in Qatar |
The campaigns observed by Proofpoint likely occurred concurrently to Zscaler’s recently published research on Molerats activity targeting individuals in Palestine & Turkey and demonstrate Molerats continued ability to modify their attack chain based on their intelligence targets.
The significant technical connections between the DropBox accounts used by the LastConn malware, the account used to deploy NimbleMamba, and the account used to store intelligence exfiltrated by NimbleMamba indicate that LastConn and NimbleMamba are almost certainly deployed by the same operators. This was based on the findings found during the investigation performed by Dropbox Security Team, which neutralized all the associated accounts.
Technical intelligence, including analysis of Molerats network activity from TeamCymru, indicates NimbleMamba developers operate in the interest of the Palestinian Territories. The guardrails employed by NimbleMamba demonstrate a clear focus on targeting Arabic speakers along with computers in the Middle East. Proofpoint observed campaigns targeting Middle Eastern governments, foreign policy think tanks, and a state-affiliated airline. Proofpoint assesses TA402 likely operates in support of Palestinian objectives, which is consistent with prior Proofpoint and the broader industry’s previously published assessments.
Conclusion
TA402 continues to be an effective threat actor that demonstrates its persistence with its highly targeted campaigns focused on the Middle East. Based on the variations between campaigns delivering NimbleMamba, along with the historical pattern of developing new malware post disclosure, Proofpoint judges with moderate confidence that TA402 will continue to update both their implants and infection chains to complicate defensive efforts.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
IOC | IOC Type | Description |
430c12393a1714e3f5087e1338a3e3846ab62b18d816cc4916749a935f8dab44 | SHA256 | NimbleMamba Sample 1 (Dec 2021 / Jan 2022) |
c61fcd8bed15414529959e8b5484b2c559ac597143c1775b1cec7d493a40369d | SHA256 | NimbleMamba Sample 2 (Nov 2021) |
uggboots4sale[.]com | Domain | Actor-owned domain used for NimbleMamba delivery |
925aff03ab009c8e7935cfa389fc7a34482184cc310a8d8f88a25d9a89711e86 | SHA256 | Additional NimbleMamba Sample found with retro hunt (Oct 2021) |
easyuploadservice[.]com | Domain | BrittleBush C2 |
2e4671c517040cbd66a1be0f04fb8f2af7064fef2b5ee5e33d1f9d347e4c419f | SHA256 | BrittleBush Sample |
ET Signatures
2035112 TA402/Molerats CnC Checkin
2035113 TA402/Molerats Payload Downloaded
2035120 TA402/Molerats CnC Activity
2035121 TA402/Molerats External IP Lookup Activity
2035122 TA402/Molerats Related Malware Domain in DNS Lookup
2035123 TA402/Molerats Related Malware Domain in DNS Lookup
YARA Signatures
rule Proofpoint_Molerats_TA402_NimbleMamba {
meta:
description = “Detects .NET written NimbleMamba malware used by TA402/Molereats”
author = “Proofpoint Threat Research”
disclaimer = “Yara signature created for hunting purposes – not quality controlled within enterprise environment”
hash1 = “430c12393a1714e3f5087e1338a3e3846ab62b18d816cc4916749a935f8dab44”
hash2 = “c61fcd8bed15414529959e8b5484b2c559ac597143c1775b1cec7d493a40369d”
strings:
$dotnet = “#Strings” ascii
$dropbox = “dropboxapi.com” ascii wide
$justpaste = “justpaste.it” wide
$ip_1 = “api.ipstack.com” wide
$ip_2 = “myexternalip.com” wide
$ip_3 = “ip-api.com” wide
$ip_4 = “api.ipify.com” wide
$vm_1 = “VMware|VIRTUAL|A M I|Xen” wide
$vm_2 = “Microsoft|VMWare|Virtual” wide
condition:
uint16be(0) == 0x4D5A and $dotnet and $dropbox and $justpaste and any of ($ip_*) and any of ($vm_*)
}