As organizations prepare for the challenges and opportunities of 2024, the critical importance of cybersecurity preparedness is increasingly apparent. In an era characterized by rapid digital transformation and continuous innovation, cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, presenting substantial risks to businesses across all sectors.
Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) play a crucial role in this dynamic environment. They are responsible for proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber risks to secure their organizations’ assets and ensure operational resilience. This report explores the top 10 cyber threats that CISOs will face in 2024, offering insights and strategic recommendations to help them anticipate and counter emerging threats, thereby protecting their organizations’ digital infrastructure and data assets.
1) Ransomware

Ransomware Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
Ransomware continues to pose a major security risk as incidents increase in both frequency and complexity. Active ransomware groups such as LockBit, ALPHV Blackcat and Cl0p are particularly notorious for their attacks on essential services. These groups often utilize sophisticated strategies, including Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), which enables them to enhance their capabilities and expand the scope of their attacks.
Top Takeaways:
- The year 2023 marked a notable escalation in ransomware activities, with a 55.5% increase in the number of affected organizations, totaling 5,070 worldwide.
- Prominent ransomware entities such as LockBit3.0, ALPHV, and Cl0p were highly active, showcasing advanced tactics that challenge traditional security frameworks.
- The significant MOVEit campaign prominently affected major entities, illustrating critical vulnerabilities in supply chains and emphasizing the importance of rigorous version control and surface attack management.
- The total ransom payments made in 2023 soared to over $1 billion, the highest ever, signifying severe financial impacts on enterprises beyond the immediate costs of response and recovery.
- The United States remained the most targeted country, experiencing nearly half (47.74%) of all reported ransomware attacks.
- The increase in double extortion methods, where attackers both encrypt and threaten to leak data, highlights the evolving tactics used by threat actors to pressure organizations into paying ransoms.
- The trend towards targeting larger organizations for substantial ransoms, known as “big game hunting,” underscores the need for these entities to deploy sophisticated detection and response mechanisms.
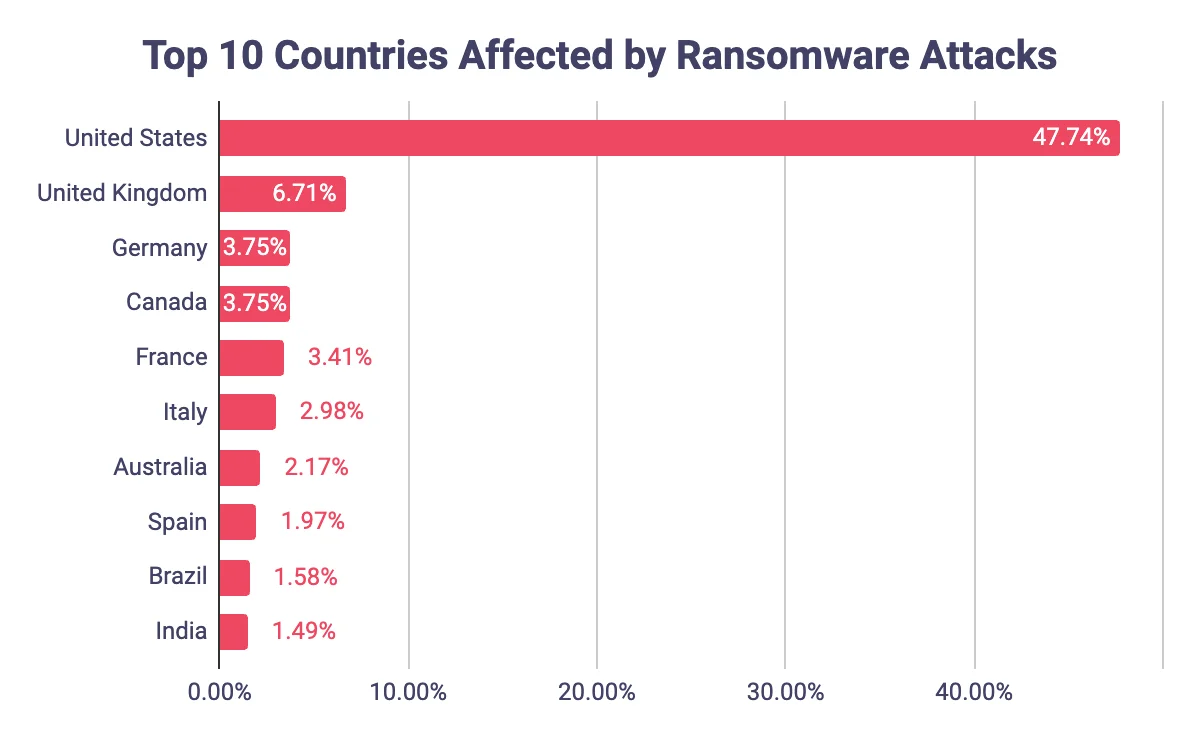
Distribution of ransomware attacks by target country
In 2023, according to SOCRadar, the United States was the most frequently targeted nation in ransomware attacks, comprising 47.74% of the incidents identified. It was followed by the United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, and France in terms of the frequency of attacks.
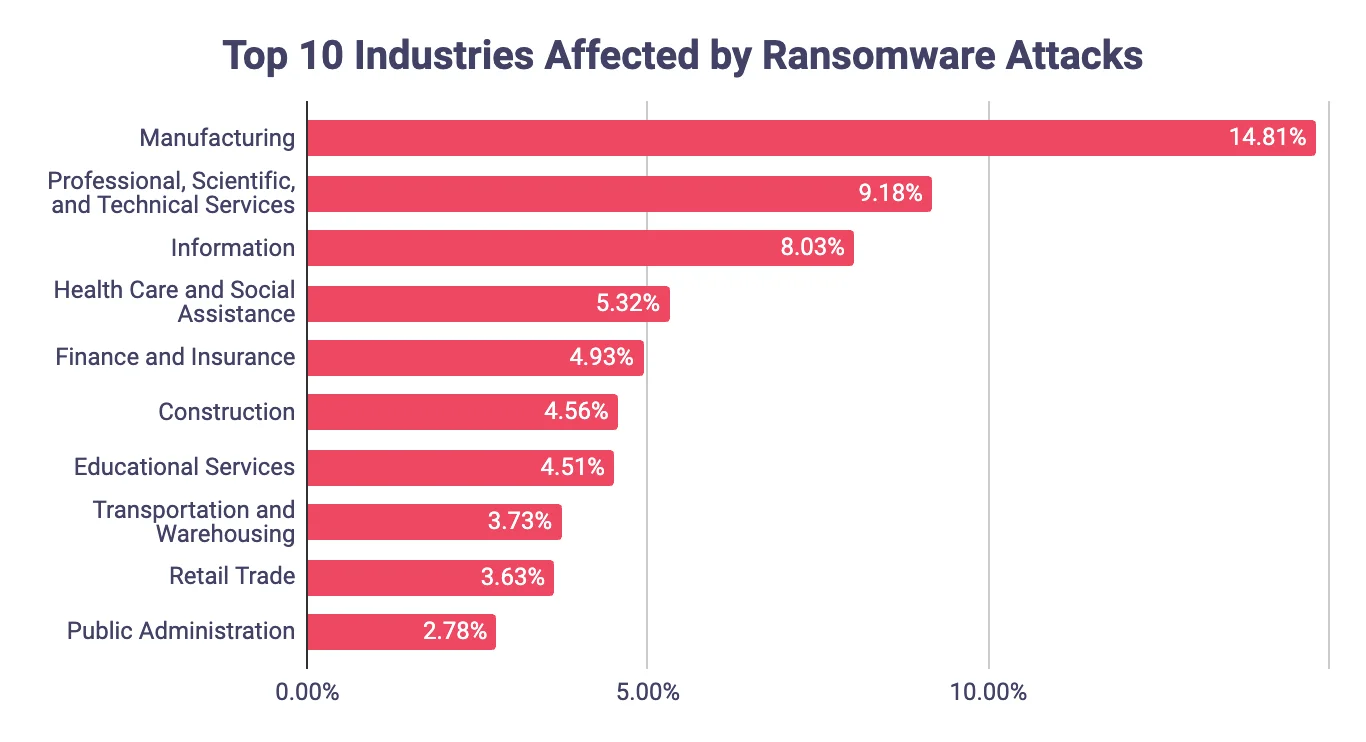
Distribution of ransomware attacks by target industry
In 2023, according to SOCRadar, the manufacturing industry was identified as the primary target of ransomware attacks, comprising 14.81% of all incidents. It was closely followed by the professional, scientific, and technical services industry and the information industry.
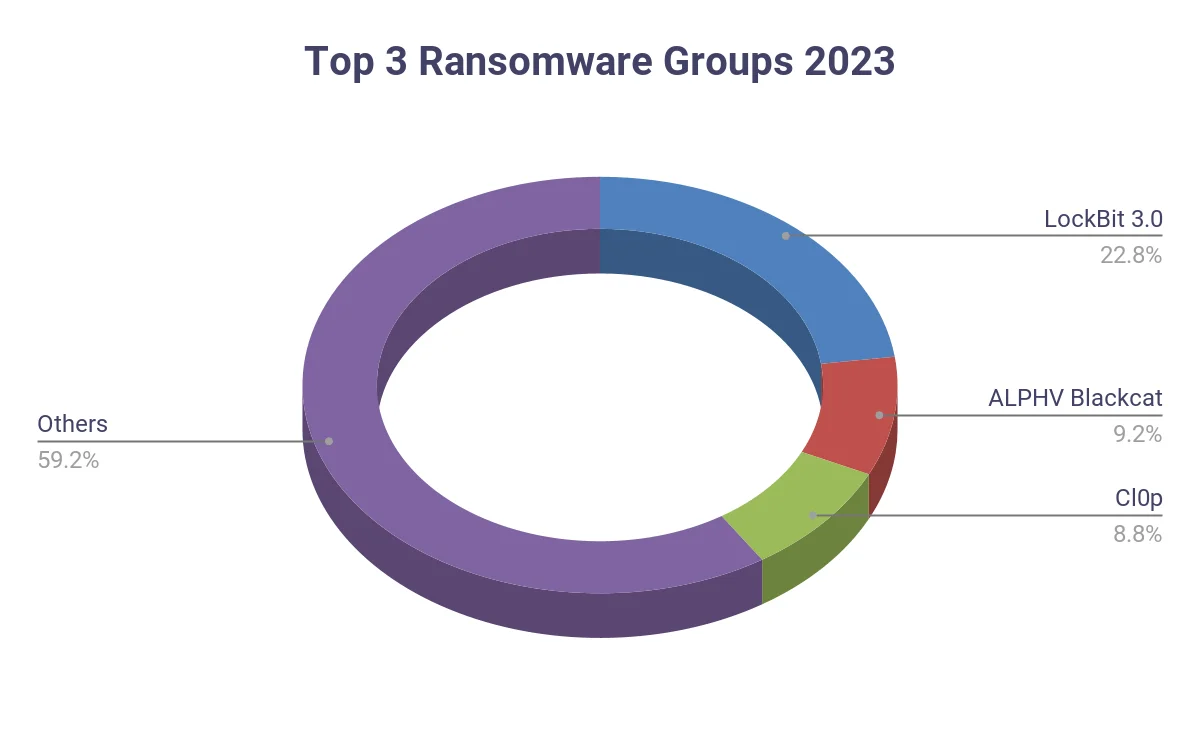
Top 3 ransomware groups in 2023
In 2023, SOCRadar reported that Lockbit 3.0 was the most active ransomware group, accounting for 22.8% of documented attacks. ALPHV Blackcat and Cl0p were also prominent, ranking next in terms of their operational frequency.
Top Ransomware Attacks in 2023:
Cl0p Ransomware’s Exploit of MOVEit Transfer:
The Cl0p ransomware group identified and leveraged a previously unknown vulnerability in the MOVEit Transfer system in May 2023. This software is commonly used for secure file transfers within cloud frameworks. The attackers managed to insert a webshell on servers, enabling them to steal data from both local and cloud-based storage. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with vulnerabilities in commonly used cloud applications and the importance of early detection and rapid response to emerging threats.
Cl0p Ransomware Exploits GoAnywhere MFT:
Cl0p ransomware capitalized on a zero-day flaw in Fortra’s GoAnywhere MFT software, impacting numerous enterprises. This strategic attack highlighted Clop’s approach to exploiting significant vulnerabilities within essential business software, affecting a broad range of organizations worldwide.
VMware ESXi Servers Targeted by ESXiArgs:
The ESXiArgs ransomware exploited a known vulnerability in VMware ESXi servers affecting thousands of servers globally. Many victims had not implemented an available patch, leading to extensive encryption of server data and subsequent ransom demands, predominantly requested in Bitcoin.
Key Considerations for Ransomware Negotiations:
Ransomware incidents have seen a rise in occurrence within the contemporary digital realm. Over recent years, the nature of this threat has progressed beyond mere file encryption to encompass data theft, leading to substantial losses for businesses as they grapple with the compromise of sensitive information and the necessity to pay substantial sums for data recovery.
Consequently, the importance of engaging in negotiation with threat actors has grown significantly, underscoring the critical need for organizations to adeptly navigate such negotiations.
- Role Presentation: Avoid presenting yourself as a manager or authority figure during negotiations.
- Extending Negotiations: Strategically extend the negotiation timeline. This can make the ransomware group more eager to settle, potentially leading to a better deal.
- Verification of Claims: Request a list of files that were compromised and verify a sample to ensure the group can actually decrypt the data, confirming their claims.
- Engaging Authorities: Report the incident to local authorities before the ransomware group can leverage it as a threat. This step protects your legal standing and integrity.
- Price Justification: Always ask the ransomware group to justify the ransom amount. They typically demand a ransom based on a percentage of annual revenue, allowing room for negotiation on more reasonable terms.
- Avoid Provocation: Maintain a professional demeanor without making accusations that could provoke or escalate tensions.
- Honest Communication: Be honest and straightforward in your communication. Avoid cliché excuses which are ineffective and could undermine the negotiation process.
- System Access Checks: Confirm whether the threat actors still have access to your systems to prevent further damage or additional breaches.
- Pre-Negotiation Planning: Determine your limits on operational interruptions and financial expenditure before negotiations start. This helps in making informed and strategic decisions during the negotiation process.
- Data Deletion Verification: After any payment, ensure the data is deleted by requesting proof, such as a video, to confirm the action.
By integrating these strategies, you can effectively navigate the complexities of ransomware negotiations, reducing potential damages and improving outcomes
For more in-depth analysis and additional insights, refer to the full article by Huzeyfe Önal, CEO of SOCRadar, on Medium.
Think Like a Hacker, Defend Like a Professional – Request Free Access
2) Identity-based Attacks

Phishing Illustrative Image – Source: SOCRadar
The prevalence of identity-related threats, such as phishing, social engineering, and credential stuffing, is rising, often facilitated by advances in generative AI. Threat actors employ techniques like SIM-swapping and MFA bypass to gain unauthorized access.
Additionally, stealer malware enables covert extraction of sensitive data, including login credentials, financial information, and personal identifiers. Deployed through phishing campaigns and malicious downloads, this malware allows attackers to infiltrate networks and escalate privileges. The stolen data is typically sold on dark web markets or used for identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage. The evolving sophistication of these threats, including advanced evasion techniques, underscores their persistent and formidable risk to cybersecurity.
Top Takeaways:
- In 2023, the United States was targeted in 31% of phishing attacks, followed by the United Kingdom with 15% and Canada with 13%.
- The financial services industry was targeted in 35% of phishing attacks, followed by the healthcare industry with 30% and public institutions with 25%.
- Despite the rise of messaging apps, email remains the top channel for phishing, accounting for 92% of cases.
- In 2023, India was the most affected country by stealer malware, accounting for 20.4% of total incidents, followed by Brazil with 19.4% and the United States with 11.7%.
- The financial services industry, healthcare and pharmaceutical industry, and manufacturing industry were the most heavily targeted by stealer malware, reflecting their high-value data and critical operational roles.
- In 2023, global data leaks caused by stealer malware were predominantly due to Redline, accounting for approximately 76.96% of incidents, followed by Raccoon with 14.42%, and Meta with 8.65%.
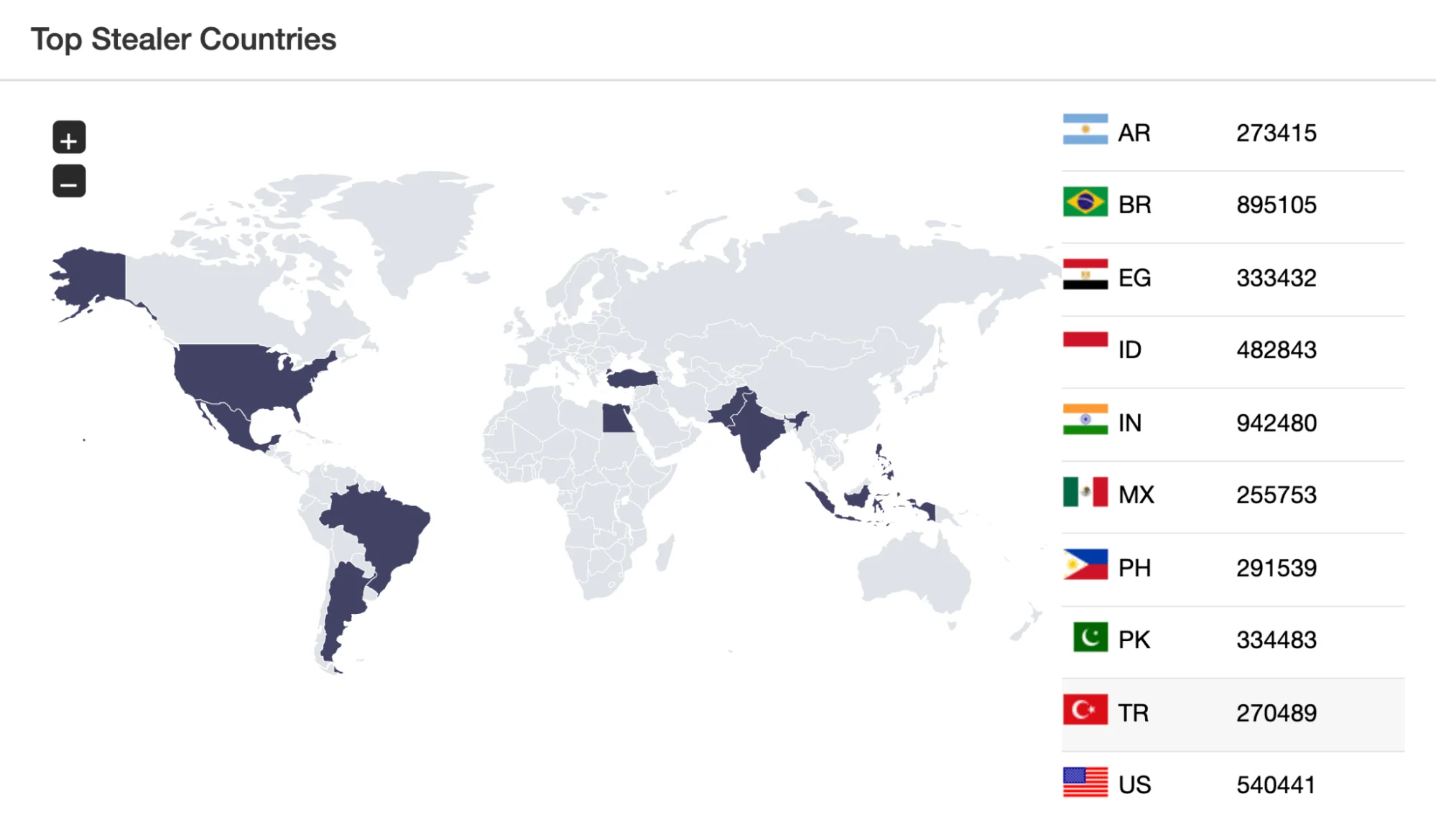
Countries affected by stealer malware – Source: SOCRadar
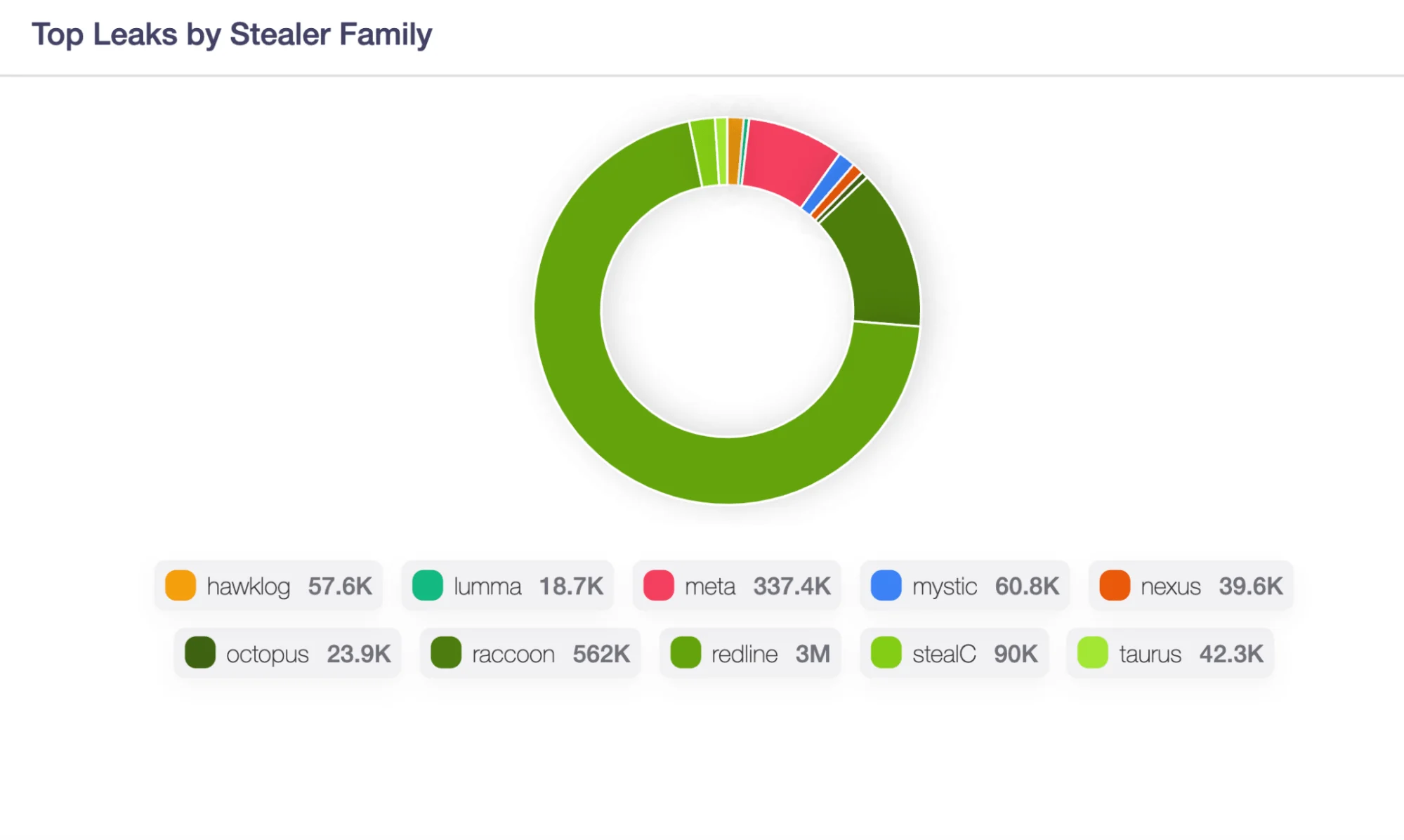
Data leaks caused by stealer malware family – Source: SOCRadar
Top Identity-based Attacks in 2023:
Microsoft Brand Phishing Campaign:
In 2023, there was a marked uptick in phishing attacks directed at Microsoft-associated entities such as OneDrive and SharePoint. These endeavors demonstrated a high level of sophistication, utilizing phishing kits obtained from illicit markets to circumvent security protocols like multi-factor authentication (MFA). The primary countries subjected to these attacks included the United States, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Russia, and Canada.
Microsoft Office Malware Phishing:
In the course of 2023, cyber attackers frequently embedded malware within Microsoft Office attachments, with Word documents emerging as the predominant vehicle, employed in roughly 40% of these instances. These deceptive phishing emails often masqueraded as originating from credible sources, enhancing their deceitful nature. The prevalence of such attacks highlights the ongoing risk posed by seemingly harmless email attachments as conduits for advanced cyber threats.
Microsoft Credential Harvesting Campaign:
In the beginning of 2023, a phishing scheme capitalized on the Microsoft name to gather user credentials. Threat actors compromised a legitimate website and utilized it as a platform to host a credential harvesting tool. The phishing emails contained a hyperlinked JPEG image resembling a Microsoft Office 365 login page, seemingly harmless at first glance but engineered to redirect unsuspecting victims to the malicious website upon interaction. This method leveraged the trusted Microsoft brand to dupe victims and evade email security protocols.
3) Denial of Service (DoS)

Denial of Service Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
Throughout 2023, there was a 63% surge in global DDoS attack incidents compared to the prior year, significantly influenced by geopolitical tensions. This increase reflects how online conflicts often parallel real-world geopolitical disputes, affecting global internet security and stability. These trends underscore the escalating complexity and regularity of cyber threats, highlighting the critical need for enhanced security protocols to protect vital infrastructure and maintain uninterrupted business activities.
Top Takeaways:
- In 2023, 31% of organizations reported experiencing at least one DDoS attack.
- The most significant DDoS attack recorded in 2023 peaked at over 2.3 terabits per second.
- The financial sector and IT services were the most frequently targeted, accounting for 40% of all DDoS incidents.
- The financial impact of downtime resulting from a successful application DDoS attack averages at $6,130 per minute for large scale organizations.
- The average duration of severe DDoS attacks extended up to 17 hours.
- On average, DDoS mitigation and response per incident cost approximately $500,000.
Top DDoS Attacks in 2023:
KillNet DDoS Attack on NATO:
In February 12, 2023, NATO’s public-facing websites, including the Special Operations Headquarters homepage, were disrupted by a significant DDoS attack from the Russian hacktivist group, Killnet. This cyber assault, announced on an encrypted Telegram channel, temporarily hampered the availability of several NATO sites as the organization’s cyber defense teams implemented enhanced protective measures. The attack notably coincided with NATO’s coordination efforts for the Turkish-Syrian earthquake relief, underlining the critical timing and impact of the disruption. Although some sites remained down temporarily, NATO’s classified networks were confirmed secure, and no breach occurred.
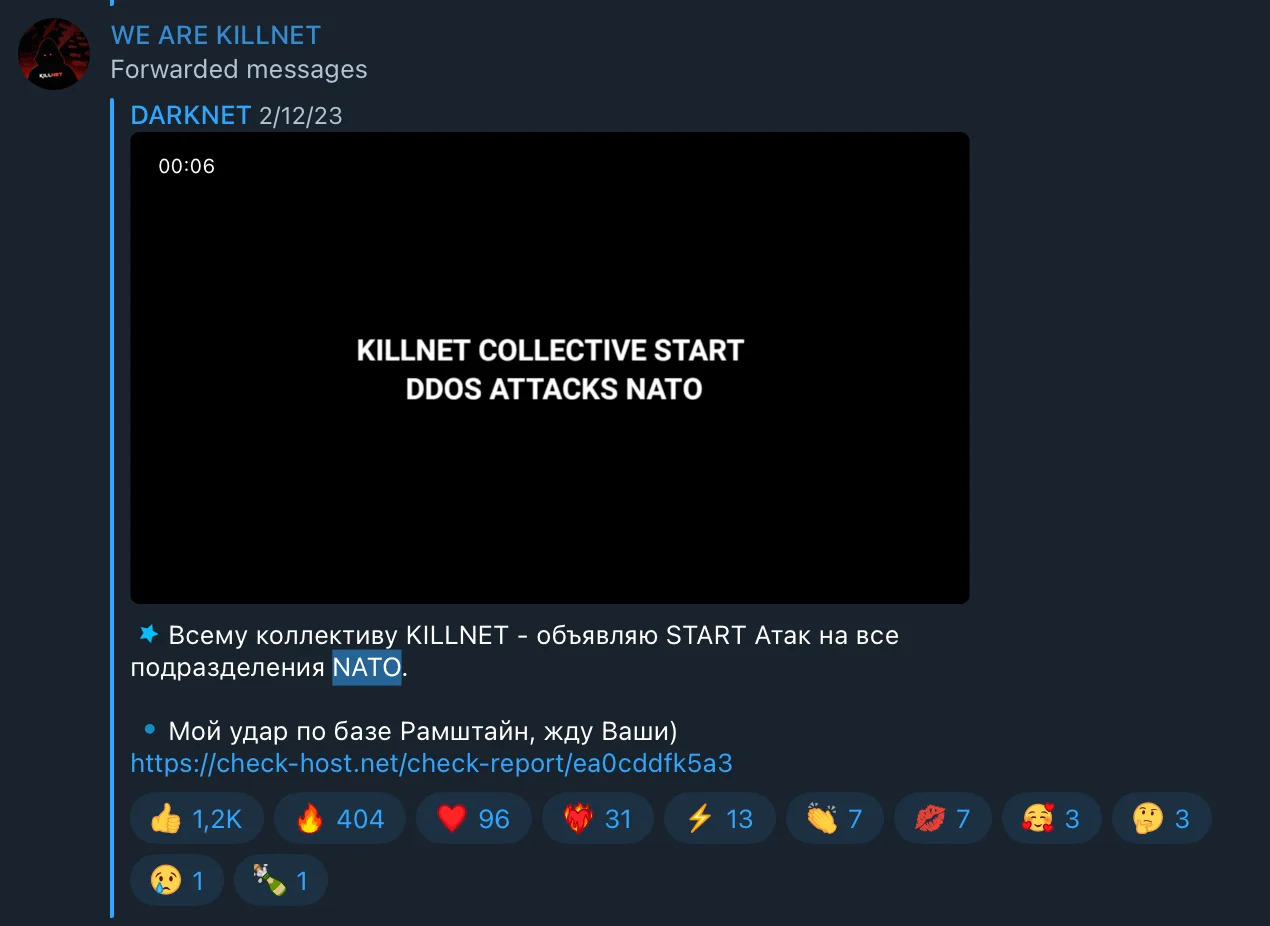
Official Announcement of DDoS Attacks by KillNet on NATO Websites – Screenshot from KillNet Telegram Channel
The screenshot above captures a message from Killnet’s Telegram channel, declaring the commencement of coordinated DDoS attacks targeting NATO member states’ websites, signaling a significant escalation in cyber hostilities.
Translation: “To the entire KILLNET team – I announce START Attacks on all NATO units. 
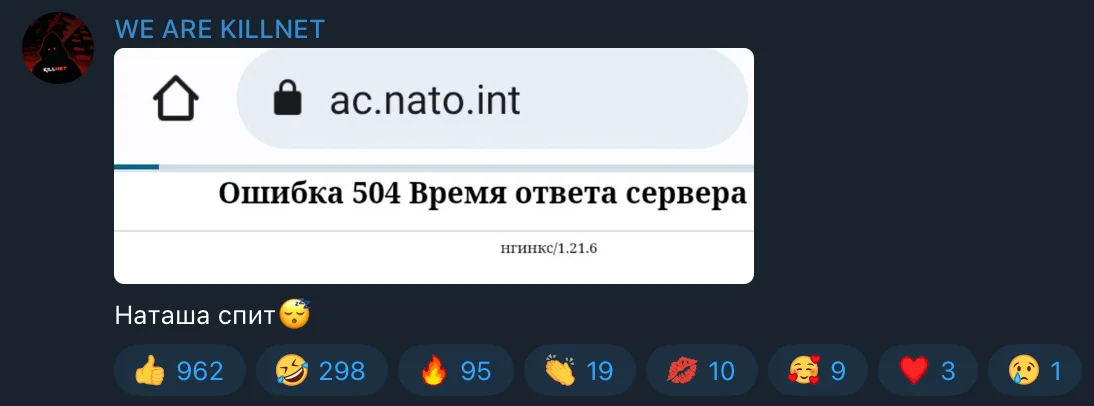
Screenshot from KillNet Telegram Channel
Translation: “Natasha is sleeping”
The screenshot above captures a message from Killnet’s Telegram channel, sarcastically stating that the targeted site is out of service.
Cloudflare’s 201 Million RPS Attack:
Cloudflare detected an extraordinarily powerful DDoS attack that achieved a rate of 201 million requests per second. Unlike typical large-scale botnet attacks, this one was carried out by a relatively small number of 20,000 compromised devices, showcasing a highly efficient attack strategy that still managed to exploit the same HTTP/2 protocol vulnerability.
Amazon’s 155 Million RPS Attack:
Over a span of two days, Amazon Web Services was hit by a series of DDoS attacks, with the most severe peaking at 155 million requests per second. These attacks employed a rapid request strategy, targeting a known vulnerability in HTTP/2, illustrating the potential for significant disruption even among robustly secured infrastructures.
To effectively safeguard against DDoS attacks, it is imperative to grasp their operational mechanisms and analyze the prevailing tactics. You can use the SOCRadar Labs-DOS Resiliency tool for free to measure your strength in this situation. The DoS Resilience Service allows you to check your domain’s or subnet’s resilience against DoS attacks. After determining your strengths and weaknesses from DOS Resiliency, you can use the SOCRadar Attack Surface Management module, no matter what action you must take.

SOCRadar DoS Resilience Module
You can visit our blog post for more information on DDoS attacks and mitigation methods.
4) Cloud Attacks

Cloud Attacks Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
With the accelerated adoption of cloud computing, threats targeting cloud environments have significantly increased. Threat actors are taking advantage of vulnerabilities in cloud management interfaces and other cloud-related weaknesses. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to infiltrate cloud systems and navigate laterally within these environments, posing substantial risks to data security.
Top Takeaways:
- Cloud security incidents saw a 75% increase in 2023 compared to the previous year.
- Misconfigured cloud storage led to unauthorized access in 24% of organizations.
- In 2023, 54% of all records stolen were from cloud-based assets.
- The average financial impact of a cloud breach was estimated to exceed $4.3 million.
- Only 45% of enterprises reported feeling very confident in their cloud security posture.
Top Cloud Attacks in 2023:
BMW Cloud Misconfiguration Incident:
In 2023, a misconfigured cloud storage bucket led to the inadvertent exposure of sensitive information belonging to BMW. This security oversight allowed unrestricted access to critical data stored in the cloud, impacting the confidentiality of vast amounts of proprietary information. The incident highlights the crucial need for stringent cloud configuration and regular security audits to prevent data exposure. Such vulnerabilities underscore the challenges organizations face in securing cloud environments against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
You can visit our blog post for more information about BMW Cloud Misconfiguration Incident.
Increase in Cloud Infostealers:
The frequency of cloud infostealers has increased steadily over the past year, with tools like AlienFox gaining prominence. These software are commonly available on platforms such as Telegram and are utilized for extracting credentials from improperly configured or susceptible cloud services. For example, AlienFox has been employed to pilfer API keys and other confidential data from platforms like AWS SES and Microsoft Office 365.
Exploitation of AWS CloudFormation:
In a significant security incident, perpetrators targeted a flaw within AWS CloudFormation, a service integral to resource management in cloud platforms, to carry out unauthorized activities. This exploitation highlighted critical vulnerabilities in the management of cloud resources, emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive security measures and constant monitoring of cloud management tools to prevent data breaches and ensure the integrity of cloud infrastructure
SOCRadar Cloud Security Module
SOCRadar has expanded its External Attack Surface Management (EASM) services by introducing the Cloud Security Module (CSM), tailored to bolster the security of clients’ cloud storage infrastructure. This innovative module facilitates the identification of new cloud buckets, enabling classification into “public,” “private,” or “protected” categories. Upon the discovery of new cloud storage, SOCRadar promptly issues a “Cloud Bucket Detected” alert, seamlessly integrating it into the roster of digital assets.
The SOCRadar CSM Module ensures ongoing vigilance over the status of buckets, promptly notifying stakeholders of any alterations through a “Cloud Bucket Status Change” alert, including transitions from “private” to “public” configurations.
Request Your Demo Now!
5) Supply Chain Attacks

Supply Chain Attacks Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
Supply chain attacks exploit vulnerabilities within a trusted third-party to access a broader network of clients. This strategy allows attackers to impact multiple organizations across diverse sectors with a single intrusion. The growing risk associated with these attacks is driven by the deepening interdependencies between companies and their suppliers. Additionally, as digital connections within supply chains intensify, they introduce new vulnerabilities, thereby increasing both the potential and severity of these security incidents.
Top Takeaways:
- Supply chain attacks saw a 42% increase in 2023.
- On average, breaches originating from third-party vulnerabilities took 250 days to identify.
- The average cost of a supply chain attack surpassed $3 million.
- 29% of organizations were unable to determine the initial entry point of a supply chain attack.
- 34% of organizations affected by breaches were compromised through a software supplier.
Top Supply Chain Attacks in 2023:
MOVEit Transfer Attack:
The MOVEit Transfer software experienced a critical security breach due to a zero-day vulnerability that permitted remote code execution. This flaw allowed attackers to gain unauthorized access and control over the software, which is widely used for secure file transfers, impacting numerous organizations globally. The breach exposed sensitive data and underscored the importance of securing software against such vulnerabilities. It highlighted the ongoing challenge of protecting widely used enterprise applications from emerging cyber threats.
You can visit our blog post for more information about MOVEit Transfer Supply Chain Attack.
3CX VoIP Software Compromise:
In 2023, the 3CX VoIP software was compromised via malware that was inserted into software updates. This attack affected over 600,000 businesses by allowing threat actors to execute remote commands on infected systems. The compromised systems spanned various industries, disrupting communications and data integrity. This incident demonstrated the critical need for rigorous security protocols in software updates and distribution channels to prevent malware distribution through trusted applications.
You can visit our blog post for more information about 3CX VoIP Supply Chain Attack.
GoAnywhere MFT Attack:
The GoAnywhere managed file transfer software was exploited through a high-severity vulnerability that enabled unauthorized data access and exfiltration. This breach was significant, with attackers targeting and extracting sensitive data from numerous companies. The attack not only led to data theft but also raised concerns about the security of file transfer software used in critical infrastructure and sensitive industries. It emphasized the necessity for continuous vulnerability assessments and prompt patching of identified software flaws.
You can visit our blog post for more information about GoAnywhere MFT Supply Chain Attack.
Supply Chain Intelligence by SOCRadar – Your Vanguard in Cyber Warfare
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence module stands as a beacon of innovation in the cybersecurity landscape, offering a comprehensive suite of features designed to fortify the security posture of organizations globally.
By automating the mapping process and generating actionable recommendations, the SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence module ensures that organizations are informed and equipped to take decisive action.
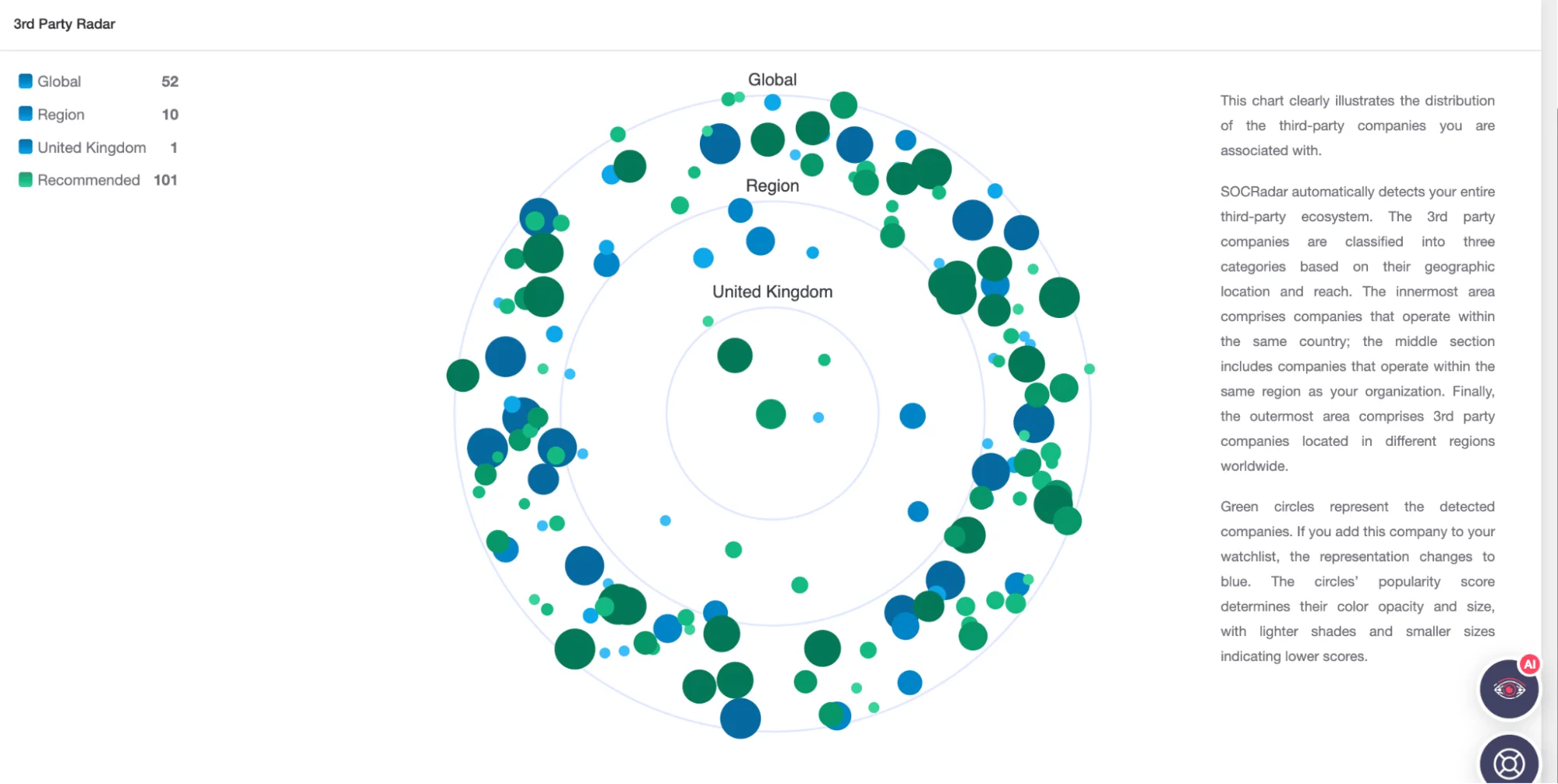
SOCRadar 3rd Party Radar
The Analytics Board, an advanced feature of the module, allows for effortless monitoring of third-party firms and in-depth analysis of global trends, ensuring that strategic decisions are informed by comprehensive data. Real-time updates and continuous monitoring are core to the module’s offering, keeping organizations abreast of the evolving threat landscape.
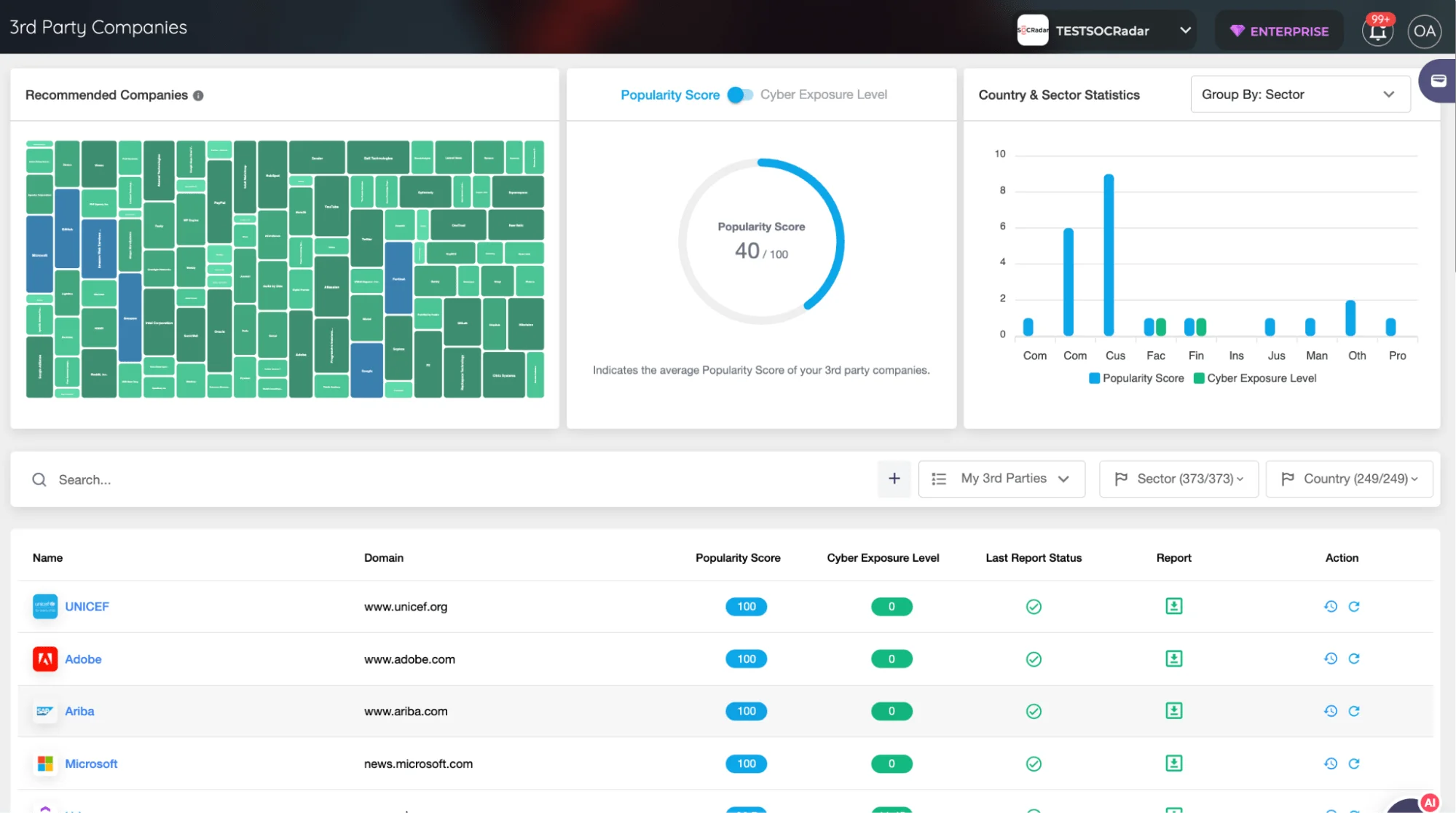
SOCRadar 3rd Party Companies
45% of organizations worldwide will experience software supply chain attacks by 2025 (Gartner). Secure your supply chain before it’s too late!
Request Your Demo Now!
6) Remote Code Execution / 0-Day Vulnerabilities

Zero Day Exploit Illustrative Image – Source: Contrast Security
Threat actors progressively leverage software vulnerabilities to access systems or enhance their privileges. In 2023, critical vulnerabilities identified as CVE-2023-0669 and CVE-2023-20887 have been notably prevalent among exploited security flaws. This trend underscores a growing risk in cybersecurity, as threat actors find and utilize these weaknesses more frequently, posing significant challenges for organizations striving to protect their digital environments. The continuous discovery of such vulnerabilities highlights the essential need for ongoing vigilance and timely updates in software security practices.
Top Takeaways:
- In 2023, more than 15,000 new software vulnerabilities were reported.
- Approximately 70% of attacks exploited vulnerabilities for which patches had been available for over a year.
- The average time required to patch critical vulnerabilities in 2023 was 60 days.
- 62% of the vulnerabilities exploited were classified as high or critical in severity.
- The average cost of breaches involving unpatched known vulnerabilities was $5.3 million.
Top Vulnerabilities in 2023:
CVE-2023-24489 – Citrix Content Collaboration:
Citrix Content Collaboration, particularly through its ShareFile service, faced a critical vulnerability identified as CVE-2023-24489. This security flaw, scoring a dire 9.8 on the CVSS scale, was discovered to permit unauthenticated arbitrary file uploads and enable remote code execution. Initially flagged in August 2023, exploitation activities surged following its disclosure. Cybersecurity entities observed and reported multiple exploitation attempts, which were characterized by unauthorized access attempts exploiting the cryptographic weaknesses in the application’s storage zones controller. This vulnerability served as a gateway for attackers to execute code remotely on the compromised systems, posing significant risks to data integrity and security.
CVE-2023-27997 – Fortinet FortiGate SSL-VPN:
In 2023, Fortinet’s FortiGate SSL-VPN appliances were compromised due to a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability, cataloged as CVE-2023-27997, which allowed unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary code through specially crafted requests. Even in configurations where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) was enabled, this vulnerability represented a critical threat. Fortinet proactively issued a patch in June 2023, prior to public disclosure, to mitigate this vulnerability. However, the widespread deployment of FortiGate appliances and delayed patch applications in various infrastructures made this vulnerability a focal point for significant malicious exploits, affecting numerous organizations globally.
CVE-2023-20887 – VMware Aria Operations for Networks:
VMware Aria Operations for Networks, previously known as vRealize Network Insight, was found to contain a severe command injection flaw, known as CVE-2023-20887, which enabled remote code execution. This vulnerability could be exploited by a remote attacker with access to the network, allowing them to inject commands and potentially take control of the affected systems. First identified in 2023, this vulnerability quickly became a target for threat actors, exploiting the flaw to gain unauthorized access and execute malicious operations within the networked environments. VMware responded with urgency, releasing patches to address this critical security issue, underscoring the need for rapid remedial action in the face of such high-risk exposures.
Unlock Your Cyber Defense Potential with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence Module
Stay ahead of cyber threats with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence Module. Our cutting-edge solution offers deep insights and real-time data to help you identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they are exploited. With comprehensive coverage and precise, actionable intelligence, you can streamline your security efforts, enhance your response capabilities, and protect your assets with confidence.
To explore the future of cybersecurity, visit our platform today to see how we can help fortify your defenses and safeguard your digital landscape.
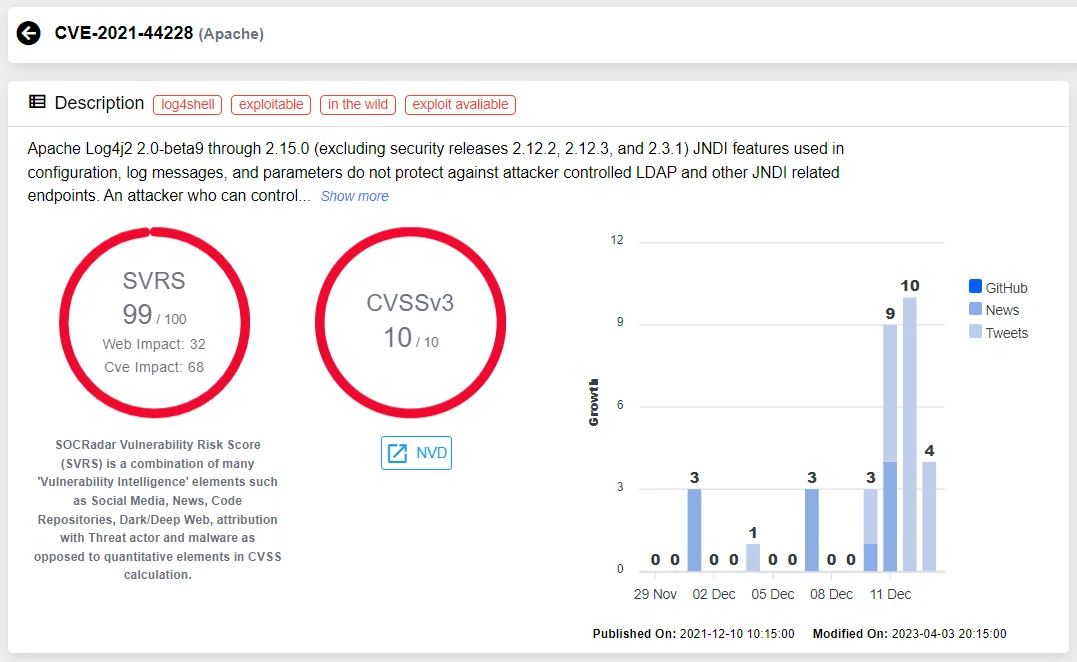
Vulnerability card of CVE-2021-44228 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Stay Secure with SOCRadar’s CVE Radar
Harness the power of real-time vulnerability tracking with SOCRadar’s CVE Radar, available for free to all users. This indispensable tool provides you with instant updates on the latest CVEs, empowering you to react swiftly to new threats and secure your systems effectively.
CVE Radar is designed to simplify your cybersecurity efforts, offering a user-friendly interface and comprehensive insights at no cost. Dive into the world of proactive defense and ensure your digital assets are always protected.
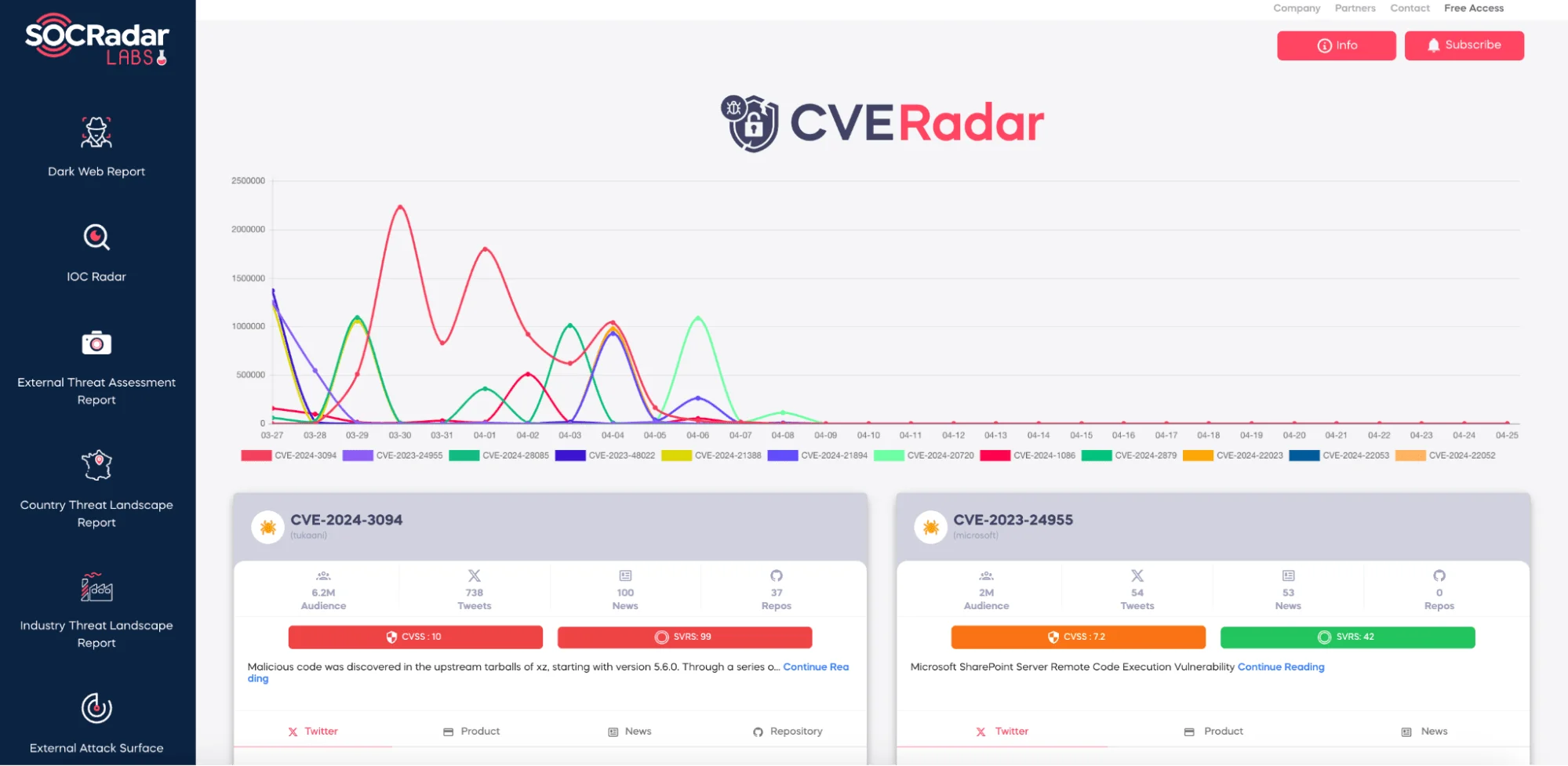
SOCRadar CVE Radar
7) Cyber Warfare and Espionage

Cyber Warfare and Espionage Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
Government-backed APT groups and politically motivated groups are intensifying their use of cyber strategies to pursue their objectives, primarily focusing on espionage and unauthorized control of resources. This escalation in cyber tactics reflects a growing trend where digital methods are employed for geopolitical leverage and intelligence gathering. The increasing sophistication of these cyber operations poses significant security risks, underscoring the need for robust defense mechanisms and international cooperation to mitigate these threats effectively.
Top Takeaways:
- Government-backed threat actors accounted for 23% of all cyber incidents in 2023.
- Nearly half (48%) of espionage attacks specifically targeted the government and defense sectors.
- On average, cyber espionage incidents led to the exfiltration of 2.6 terabytes of data per incident.
- Approximately 35% of all cyber espionage activities had connections to geopolitical conflicts.
- The average cost for recovery and mitigation from state-sponsored cyber attacks exceeded $7 million.
Top State-Sponsored APT Group Activities in 2023:
Russian APT29 Activities in Ukraine:

APT29 / Cozy Bear Dark Web Profile – SOCRadar
Known as Cozy Bear, APT29 executed an array of complex phishing operations against Ukrainian diplomatic and governmental agencies throughout the year. These operations typically involved fraudulent invitations to non-existent diplomatic events designed to disseminate malware. This was part of a wider strategy to exploit security vulnerabilities and deploy deceptive tactics for unauthorized data access within Ukrainian state systems.
You can visit our blog post for more information about Cozy Bear APT Group.
Sandworm Exploiting WinRAR Vulnerability:

Sandworm Threat Actor Profile – SOCRadar
The Russian military intelligence-associated group, Sandworm, capitalized on a known vulnerability in WinRAR (CVE-2023-38831) to launch attacks across multiple sectors, including the energy industry. The group distributed decoy documents laden with malware capable of extracting sensitive data and potentially causing significant disruptions to critical infrastructures.
You can visit our blog post for more information about Sandworm APT Group.
APT40’s Phishing Campaigns in Papua New Guinea:

APT40: Wanted by the FBI – Source: FBI
Attributed to Chinese government support, APT40 focused on Papua New Guinea through precise spear-phishing attacks. These attacks were characterized by emails embedded with harmful links that exploited system vulnerabilities to install spyware, reflecting China’s strategic interests and the operational use of cyber espionage to exert influence over regional matters.
Enhance Your Cybersecurity Awareness with SOCRadar’s Threat Actor Tracking
Elevate your security strategy with SOCRadar’s Threat Actor Tracking, an essential tool for organizations aiming to stay one step ahead of cyber adversaries. Our module provides in-depth insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of known threat actors, enabling you to understand and anticipate their next moves. With real-time tracking and detailed threat analysis, you can tailor your defenses to the specific risks facing your organization. Stay informed, stay secure, and turn the tables on cyber threats.
Learn more about how Threat Actor Tracking can protect your organization today.
8) Code Injection Attacks

Code Injection Attacks Illustrative Image – Source: Indusface
Code injection remains a prevalent threat in 2023, with attackers exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to execute malicious code. This cyber threat manipulates software to perform unintended actions that can severely compromise data integrity and security.
Top Takeaways:
- Code injection techniques continue to be a favored method among threat actors, exploiting security gaps in web applications to hijack user sessions and manipulate server behavior.
- E-commerce platforms and financial services are particularly vulnerable, often targeted due to their handling of sensitive customer data and financial transactions.
- SQL injection remains one of the most common forms of code injection attacks, consistently posing risks to databases by allowing attackers to bypass security measures and access or corrupt data.
Top Code Injection Attacks in 2023:
ResumeLooters’ Attack on Recruitment and Retail Websites:
Between November and December 2023, the hacking group known as ResumeLooters utilized SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) methods to breach a minimum of 65 websites, comprising recruitment and retail platforms. This breach led to the unauthorized acquisition of over two million email addresses and assorted personal data. The targets spanned various nations, including India, Taiwan, and Thailand, impacting sectors such as retail and recruitment.
GambleForce Attacks on APAC Companies:
Starting in September 2023, the GambleForce faction targeted 24 organizations across eight countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Employing sophisticated SQL injection tactics, they infiltrated websites operating within sectors such as gambling, government, retail, and travel, successfully absconding with sensitive information, including user credentials and hashed passwords.
QNAP Systems Command Injection Vulnerability:
In November 2023, vulnerabilities designated as CVE-2023-23368 and CVE-2023-23369 were disclosed within QNAP’s QTS operating system and affiliated applications. These security loopholes enabled remote assailants to remotely execute commands via network channels, posing grave risks to the integrity and security of network-attached storage systems.
9) Legacy Infrastructure Exploits

Legacy Infrastructure Exploits Illustrative Image – Generated by DALL-E
Legacy infrastructure exploits occur when threat actors target outdated systems that have not been updated or replaced. These systems often lack the advanced security features needed to defend against modern cyber threats, making them particularly vulnerable. The risk associated with using such outdated infrastructures is increasing, as they provide easier points of entry for attackers, posing serious security challenges and potential disruptions to business operations. Consequently, maintaining these systems without necessary updates poses escalating security threats to organizations.
Top Takeaways:
- 58% of attacks on critical infrastructure involved outdated systems or software.
- The average age of the software exploited in these attacks was 7 years.
- About 40% of the vulnerabilities exploited in legacy systems lacked an available patch.
- The average cost to update or replace legacy systems was $1.2 million per organization.
- Organizations using outdated systems reported twice as many security incidents compared to those with updated technology.
Top Legacy Infrastructure Exploits in 2023:
Exploitation of Citrix Systems (CVE-2023-3519):
A critical flaw in Citrix devices, essential for VPN connectivity and secure application delivery, was targeted by attackers who managed to execute arbitrary code remotely. This breach not only emphasized the importance of swift patch application but also showcased the strategic isolation of network devices to minimize breach impacts.
3CX VoIP Software Compromise:
This incident involved a supply chain attack by North Korean entities on the 3CX VoIP platform, affecting its global user base. Attackers inserted malicious code into software updates, highlighting the risks linked with third-party services and the necessity for vigilant update management.
You can visit our blog post for more information about 3CX VoIP Supply Chain Attack.
Targeted Ransomware Attacks on VMware ESXi and Linux Servers:
Numerous ransomware campaigns focused on exploiting older vulnerabilities in VMware ESXi and Linux servers. These attacks serve as a reminder of the critical need for maintaining security updates and defenses across all operating systems, particularly those managing critical data and infrastructure.
Optimize Your Cyber Defenses with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management
Transform your cybersecurity approach with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management, the ultimate tool for comprehensive visibility into your organization’s digital footprint. By identifying and evaluating exposed assets across the web, this powerful module enables you to pinpoint vulnerabilities and close security gaps efficiently. Leverage our advanced scanning technology to detect risks before they become breaches and maintain robust protection across all fronts.
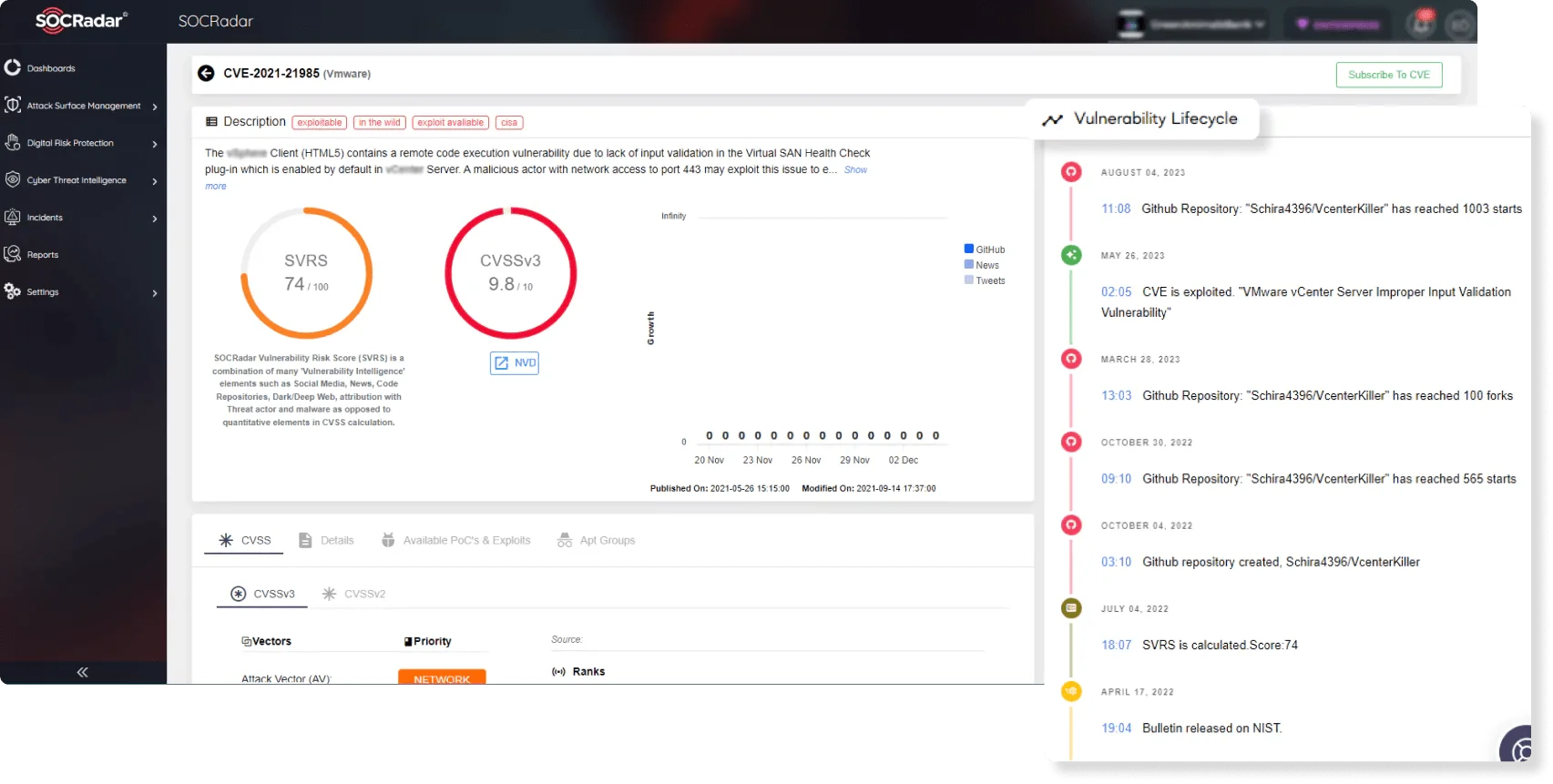
Vulnerability card of CVE-2021-21985 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Proactively Secure Your Network with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Management
Stay proactive in your cybersecurity efforts with SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Management. This module equips you with the tools necessary to detect, assess, and respond to vulnerabilities swiftly. With continuous monitoring and prioritized remediation recommendations, you can effectively manage vulnerabilities and mitigate potential threats. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Management ensures that you are always prepared to defend against evolving cyber threats.
Request Your Demo Now!
10) Cryptojacking

Cryptojacking Illustrative Image – Source: Securus Communications
Cryptojacking continues to rise sharply in 2023, representing a significant and evolving threat across multiple sectors. This form of cyberattack, which illegally utilizes the computing resources of unsuspecting victims to mine cryptocurrency, has seen remarkable increases in frequency and sophistication.
Top Takeaways:
- In 2023, there was a staggering 399% increase in cryptojacking incidents in the first half of the year alone, with a total of 332 million incidents recorded, highlighting a dramatic escalation from previous years.
- The education sector experienced the most significant rise, with the number of cryptojacking incidents increasing by 320 times compared to the first half of 2022.
- Major targeted countries include the US, where incidents surged by 340%, and the UK, which saw a 479% increase in cryptojacking attacks.
Top Cryptojacking Threats in 2023:
Cloud Platform Exploitation:
In January 2023, threat actors exploited GitHub Actions workflows by creating around 130,000 free trial accounts on various cloud services. This attack utilized the cloud resources for illicit cryptocurrency mining, marking a significant misuse of legitimate cloud platforms.
Redis Server Campaigns:
Throughout 2023, there has been an increasing trend in cryptojacking attacks targeting Redis servers. These campaigns leveraged vulnerabilities in Redis server configurations to install crypto mining scripts, exploiting the servers’ computational resources to mine cryptocurrencies without authorization.
Record-breaking Cryptojacking Surge:
The first half of 2023 saw an alarming rise in cryptojacking activities, with incidents increasing by nearly 400%. During this period, the number of cryptojacking hits surged to 332 million, a significant jump from previous years, demonstrating the growing preference for this type of cyberattack over more traditional methods like ransomware.
11) Bonus: Cyber Threats Driven by AI
AI-Driven Cyber Threats (Illustrative Image) – Generated by DALL-E
Artificial intelligence (AI) has increasingly become a dual-edged sword in cybersecurity, facilitating both innovative defenses and sophisticated attacks. As AI technologies advance, so too do the methods by which they are exploited by threat actors.
Top AI-Powered Cyber Threats
Advanced Phishing Attacks
Malicious actors are leveraging AI to craft highly personalized and convincing phishing campaigns. By analyzing the communication styles of individuals or organizations, AI can generate phishing messages that are difficult to distinguish from legitimate communications. This sophistication increases the risk of sensitive information disclosure.
Adversarial Attacks
AI-driven adversarial techniques pose significant challenges to AI-powered security measures. By exploiting weaknesses in AI models, attackers can manipulate systems like image recognition or natural language processing to misinterpret inputs, allowing unauthorized access or incorrect actions.
AI-Generated Malware
AI capabilities enable malware to adapt and evolve, bypassing traditional security measures designed to detect and neutralize threats. This type of malware can autonomously modify its code to avoid detection, making it increasingly challenging to protect against.
Deepfake Technology in Cyber Attacks
Deepfake technology, powered by AI, facilitates the creation of audio and video forgeries convincing enough to impersonate individuals. These deepfakes can be used in sophisticated social engineering attacks, potentially leading to significant breaches and misinformation spread.
Automated Exploitation of Vulnerabilities
AI algorithms can rapidly identify and exploit vulnerabilities in software and networks, speeding up the attack process. This automation allows cybercriminals to efficiently target and compromise systems, escalating the scale and impact of cyber attacks.
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
In the rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, staying ahead of emerging threats is paramount for organizations to mitigate risks effectively. The comprehensive analysis presented in this report sheds light on the top 10 cyber threats encountered in 2023, serving as a strategic resource for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) in fortifying their defenses.
To augment our analysis of cyber threats, we reference the strategic recommendations from Verizon’s 17th annual Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) for 2024. This report, which examines data from over 30,458 incidents and 10,626 confirmed breaches between November 2022 and October 2023, delivers essential insights into the evolving threat landscape.
Please refer to our detailed blog post for strategic insights about the Verizon DBIR 2024 Report.
Below are the top ten takeaways for organizations worldwide.
Top Takeaways from Verizon DBIR 2024 Report
- Enhance Defenses Against Social Engineering:
- Develop targeted training programs to educate employees about the latest phishing techniques, including AI-generated voices and deepfake videos. Increasing awareness can reduce the risk of falling victim to these sophisticated social engineering attacks.
- Implement advanced email filtering solutions that can detect and block phishing attempts and pretexting emails, thereby reducing exposure to such attacks.
- SOCRadar’s Digital Risk Protection suite provides comprehensive VIP Protection and Brand Protection services, effectively addressing the challenges posed by identity-based attacks.
- Strengthen Ransomware Preparedness and Response:
- Invest in robust backup solutions and regular data backup practices to mitigate the impacts of ransomware attacks. Ensure that backups are stored securely and are easily recoverable.
- Develop and rehearse an incident response plan that includes procedures for ransomware attacks. This plan should also outline the steps for negotiation and recovery to ensure continuity in ransomware crisis situations.
- SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management solution offers advanced vulnerability detection and management tools, ensuring potential ransomware attack vectors are identified and addressed promptly. By continuously scanning for vulnerabilities across your digital footprint, SOCRadar enhances your organization’s resilience against ransomware threats, fortifying your preparedness and response strategies.
- Secure Web Applications Against Credential Theft:
- Employ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across all web applications to significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access due to credential theft.
- Regularly audit and rotate credentials, especially for high-privileged accounts, to minimize the risks associated with stolen credentials.
- SOCRadar’s Credentials and Data Leak Detection solution monitors the dark web platforms for exposed or stolen credentials. This proactive surveillance enables organizations to swiftly respond to potential security breaches, securing web applications against credential theft.
- Close Gaps in Patch Management:
- Implement a comprehensive vulnerability management program that ensures timely application of patches to critical systems, particularly those exposed to the internet.
- Utilize automated tools to continuously scan for and address vulnerabilities, particularly in software and applications that are commonly targeted by attackers.
- SOCRadar can assist vulnerability teams in maintaining an accurate inventory of externally-facing assets. To complete the life cycle of a vulnerability threat, the platform is equipped with additional capabilities to scan these assets and discover new critical vulnerabilities continually. SOCRadar offers worldwide monitoring of the surface, deep, and dark web to uncover vulnerabilities exploited by adversaries or in the wild.
- Mitigate Insider Threats Through Rigorous Controls:
- Adopt a zero-trust security model that requires verification at every step of digital interaction, which helps in mitigating risks from both insider threats and external actors.
- Enhance monitoring of user activities and behaviors to detect and respond to suspicious actions that could indicate data theft or unauthorized access.
- By adopting a proactive approach like SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence solutions to insider threat management, organizations can detect and respond to potential threats before they can cause significant damage.
- Address Supply Chain Vulnerabilities:
- Conduct regular security assessments of third-party vendors and integrate strict security requirements into all vendor contracts.
- Use advanced analytics to monitor the entire supply chain, enabling early detection of potential security breaches and vulnerabilities.
- SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence module provides an extensive overview of your supply chain, identifying and evaluating risks associated with third-party vendors. By leveraging real-time intelligence and advanced analytics, this service ensures that vulnerabilities within the supply chain are swiftly detected and managed, significantly enhancing your security posture.
- Protect IoT Devices from Breaches:
- Increase security measures for IoT devices by implementing strong authentication mechanisms, regular firmware updates, and encrypted communications.
- Leverage tools for continuous monitoring of IoT environments to detect anomalies and prevent potential breaches.
- Incorporating the IoT infrastructure into SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module and monitoring against existing vulnerabilities or zero-days will provide better visibility against cyber threats. This allows timely patch management and mitigation of various security misconfigurations.
- Focus on Financial Motives Behind Cyber Attacks:
- Prioritize the protection of financial information by employing data encryption, secure transaction processes, and fraud detection systems.
- Educate employees on the tactics used in BEC schemes and other financially motivated attacks to reduce susceptibility to such threats.
- SOCRadar’s Fraud Protection service enhances the security of financial information by integrating advanced fraud detection systems with continuous monitoring capabilities. This robust protection shields against BEC schemes and other financially motivated attacks, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and securing transaction processes across your organization.
- Enhance Resilience Against DDoS Attacks:
- Develop a comprehensive DDoS mitigation strategy that includes over-provisioning bandwidth, using anti-DDoS services, and implementing advanced network traffic analysis tools.
- Regularly test the resilience of your network against DDoS attacks to ensure that defensive measures are effective.
- SOCRadar Labs’ DoS Resilience module offers sophisticated solutions to bolster your defenses against DDoS attacks. By providing detailed analytics and continuous monitoring of network traffic, this module helps ensure that your DDoS mitigation strategies are both proactive and effective, safeguarding your infrastructure from disruptive cyber threats.
- Sector-Specific Security Enhancements:
- For sectors such as healthcare and retail trade, tailor cybersecurity strategies to address the most prevalent risks, such as insider threats in healthcare and credential theft in retail.
- Implement industry-specific security measures, such as secure handling of payment card information in retail and protecting patient data in healthcare.
- SOCRadar provides a wealth of resources, including Industry Reports, Country Reports, and Dark Web Reports, freely available to help organizations tailor their cybersecurity strategies according to specific sector risks.
As we consolidate the comprehensive analysis of the Top 10 Cyber Threats of 2023 and top takeaways from the Verizon DBIR report, the pivotal role of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) becomes apparent. CTI stands as a cornerstone in the strategic defense against evolving cyber threats, providing CISOs with invaluable insights into emerging actors, sophisticated tactics, and emerging vulnerabilities.
Building a culture of risk awareness and implementing proactive mitigation strategies are essential in fortifying defenses against these dynamic threats. By adopting a forward-thinking approach and harnessing the full potential of Cyber Threat Intelligence, CISOs empower their teams to navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape with enhanced resilience and confidence. This proactive stance is crucial, not only in responding to immediate threats but also in preparing for future challenges.
As we look towards the future, the collaboration among cybersecurity professionals, bolstered by robust CTI frameworks, will be critical in safeguarding digital assets. This collaborative effort is key to maintaining organizational resilience and ensuring the continuous protection of critical information systems against an ever-evolving array of cyber threats.

Source: Original Post
Views: 1