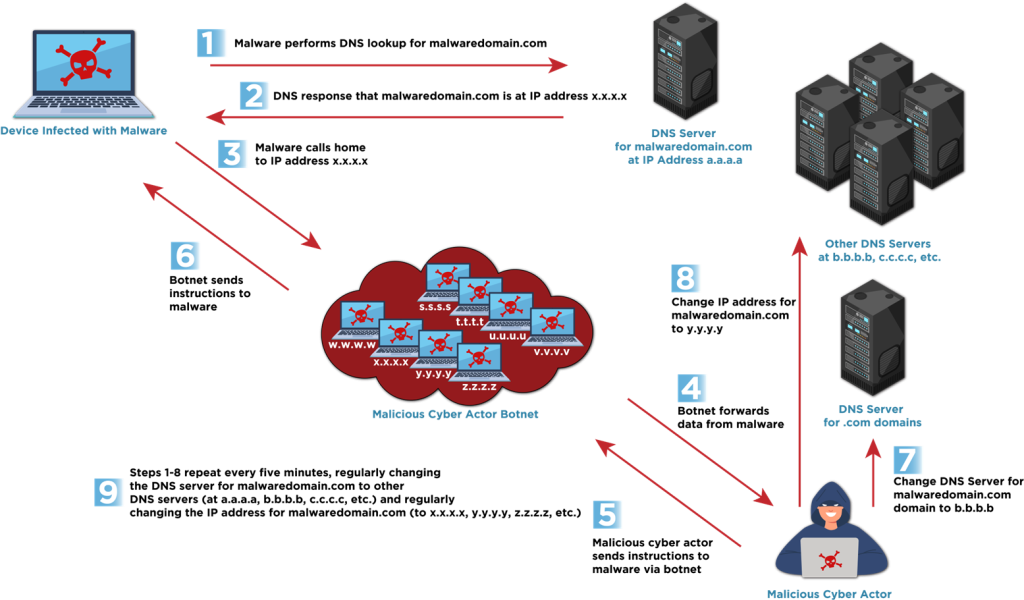
Summary: Law enforcement agencies across the US and Europe have successfully identified customers of the Smokeloader botnet and made five arrests as part of Operation Endgame, which disrupted multiple malware infrastructures. The operation relied on a seized database to connect online identities with actual individuals, leading to collaborations with several suspects.…
Read More