Summary:
Keypoints:
MITRE Techniques
12/11/2024
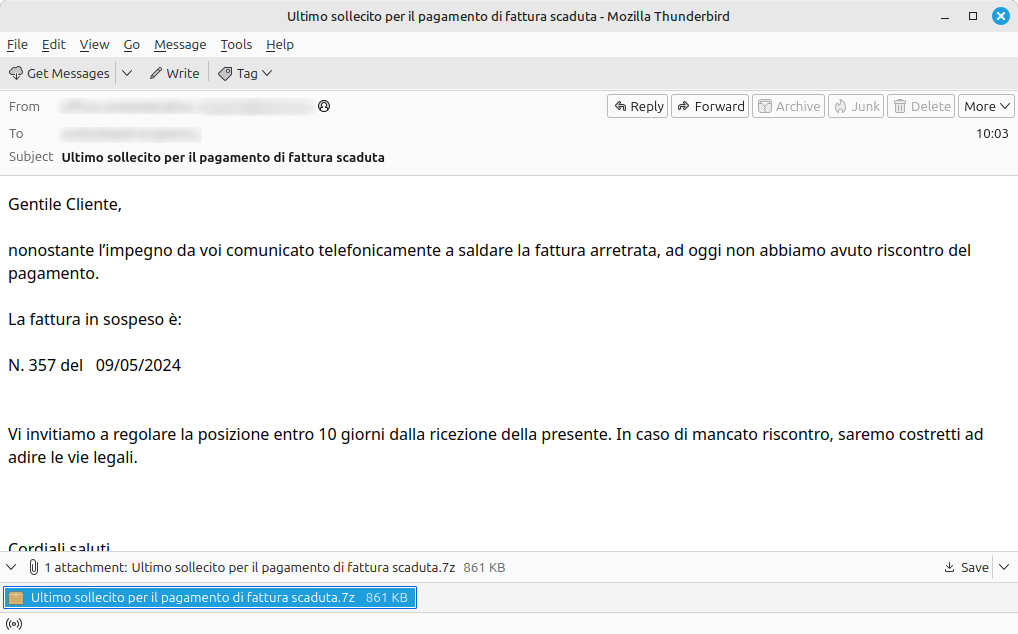
A malspam campaign is currently underway, written in correct Italian, spread nationwide, aimed at compromising victims with the Formbook malware, known for its infostealer capabilities.
The email presents itself as an urgent communication regarding unpaid invoices and prompts victims to react quickly in order to open the attached compressed 7Z archive, named: Last reminder for overdue invoice.7z. Inside this compressed archive, there is a VBS file with the same name.
Analysis of the VBS
Upon analyzing the VBS file, it can be observed that it is well-structured and commented throughout, with clear and descriptive variable names. This makes its analysis easier and allows for an understanding of its operation and the objectives it aims to achieve.
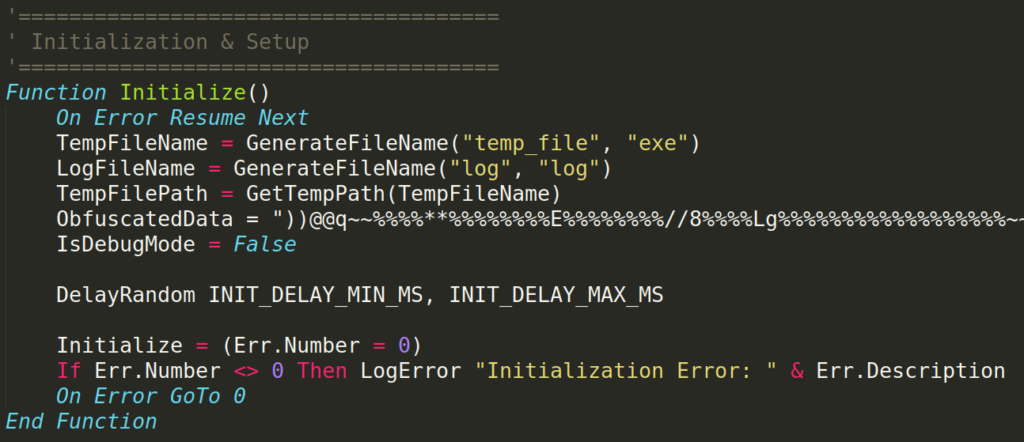
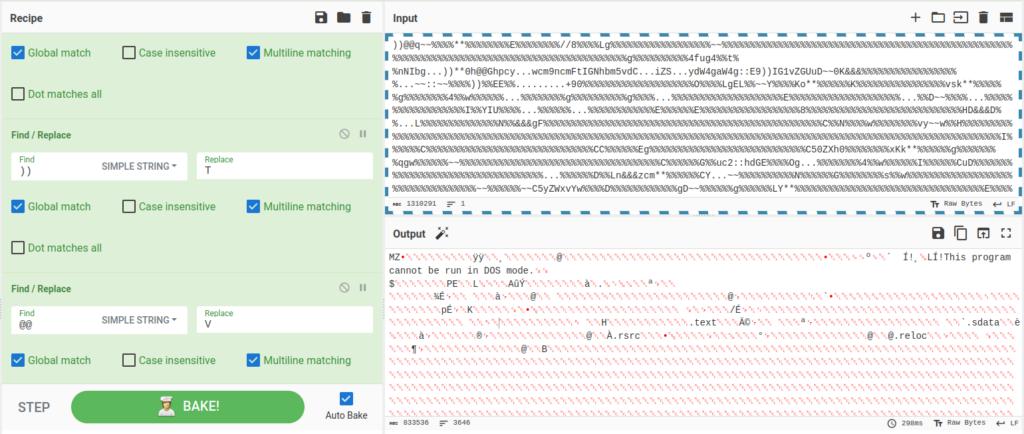
The code is designed to decode the content of the ObfuscatedData variable, replacing certain characters to obtain clean code, encoded in Base64, from which an EXE file can be extracted.
Analysis of the loader
The executable obtained is written in .NET and, as is usually the case with loaders used for Formbook, its analysis is not particularly complex.
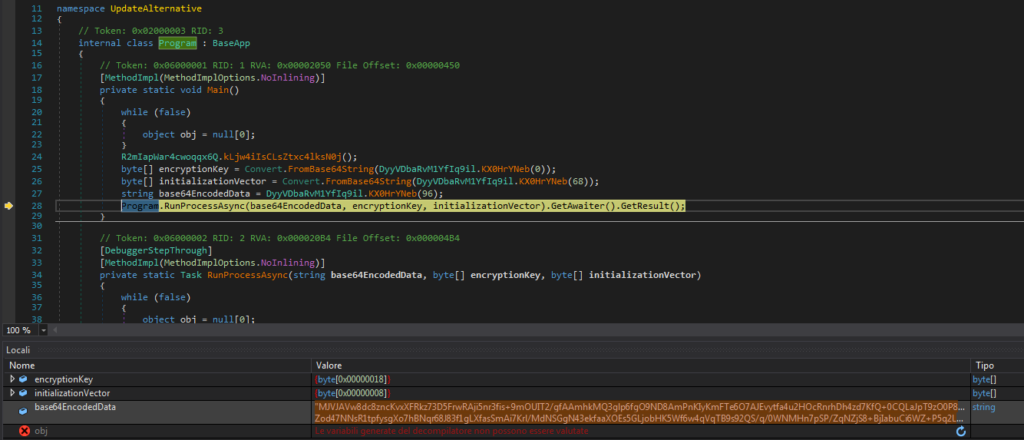
Again, the executable extracts a encrypted Base64 string, which it will then decode using an internal class AesUtilities with a static method DecryptData, which is specifically designed to decrypt encrypted data using a cryptographic algorithm. Despite the name AesUtilities, the decryption uses the TripleDES algorithm instead of AES.
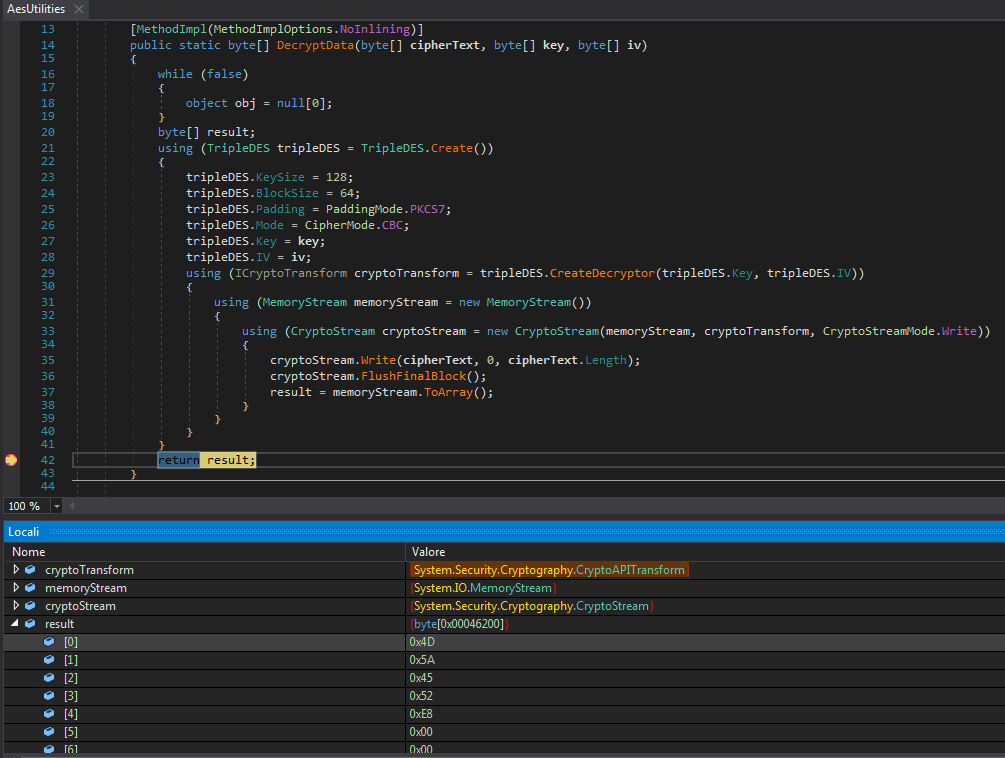
The final file generated at the end of this operation, intended to be executed on the victim’s machine, is indeed Formbook.
Indicators of Compromise
CERT-AGID has already shared the IoCs through its platforms to promote their dissemination.
In order to make public the details of this campaign, the following detected indicators are reported:
Link: Download IoC
Source: Original Post