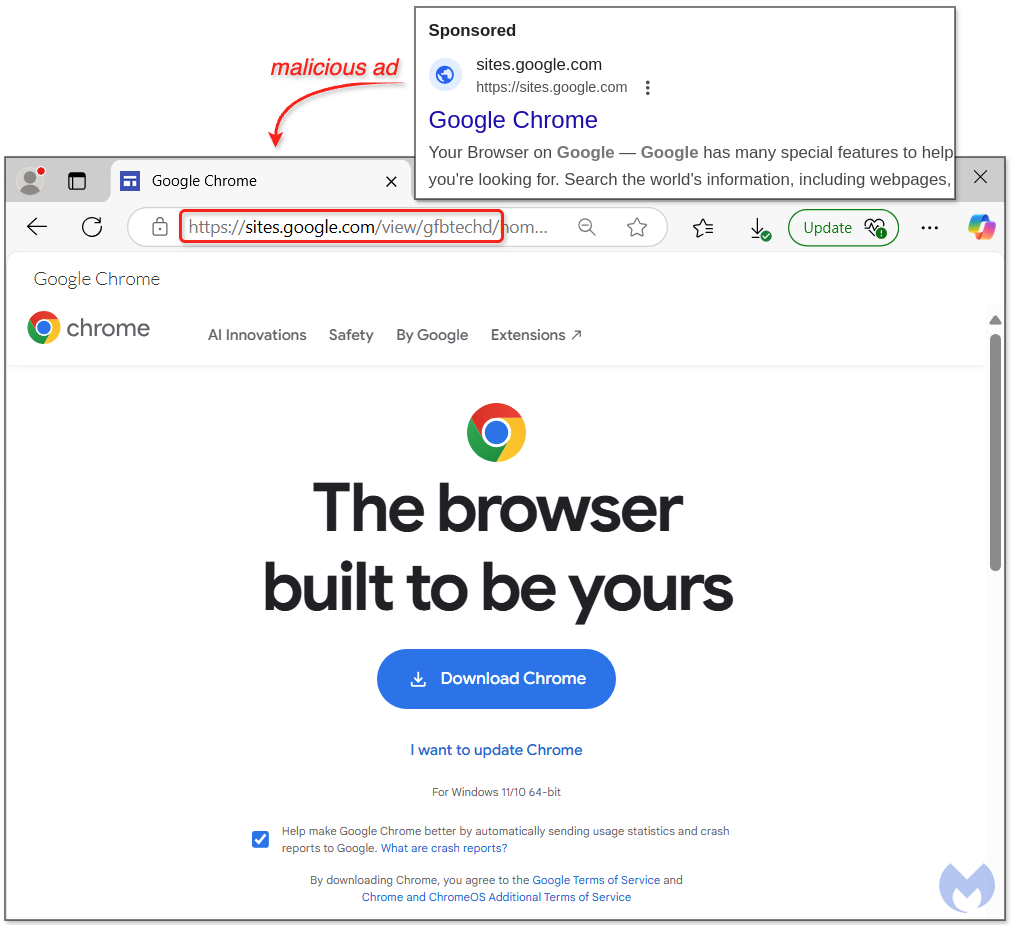
This article discusses a new scheme where criminals abuse Google Ads to entice users into downloading malware disguised as Google Chrome. The malicious ad leads victims to a fraudulent Google Sites page, ultimately infecting their systems with SecTopRAT. The attackers effectively exploit trust in search engines to distribute their malicious software. Affected: Google users, online security sector, cybersecurity industry
Keypoints :
- Criminals use Google Ads to trick users into downloading malware.
- The bait is a false advertisement for Google Chrome.
- Victims are redirected to a fraudulent Google Sites page.
- The malware payload is SecTopRAT, a remote access Trojan.
- Malicious downloads dynamically retrieve payloads from remote sites.
- Malware includes a fake Chrome installer that installs legitimate Google Chrome to mislead users.
- Malwarebytes protects users from this attack via Browser Guard and Antivirus.
MITRE Techniques :
- T1071.001 – Application Layer Protocol: The malware communicates with command and control using HTTP.
- T1218.011 – Signed Binary Proxy Execution: Malicious code is injected into the legitimate MSBuild.exe process.
- T1203 – Exploitation for Client Execution: Users are tricked into executing the downloaded malware.
- T1060 – Resource Hijacking: The payload masquerades as legitimate software to ensure execution without detection.
Indicator of Compromise :
- [Domain] launchapps[.]site
- [URL] hxxps[://]launchapps[.]site/getCode[.]php
- [URL] hxxps[://]launchapps[.]site/3[.]php?uuid={}_uuid
- [File] decrypted.exe
- [File] waterfox.exe
- [IP Address] 45.141.84[.]208
- [URL] sites[.]google[.]com/view/gfbtechd/
- [Malicious URL] chrome[.]browser[.]com[.]dechrome[.]browser[.]com[.]de/GoogleChrome.exe48fdfbe23eef7eddff071d3eda1bc654b94cf86036ca1cca9c73b0175e168a55