This article discusses the proactive detection of cyber threats through automated pivoting on known indicators, showcasing three case studies involving phishing campaigns. It highlights the use of a graph neural network (GNN) to uncover new malicious domains and emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring of threat actors’ evolving indicators. Affected: phishing campaigns, web skimmer campaigns, financial services phishing campaigns
Keypoints :
- Threat actors leave traces of information when launching large-scale attacks.
- Automated pivoting can help defenders uncover new attack infrastructure.
- Three case studies illustrate the effectiveness of this approach: postal services phishing, credit card skimmer campaign, and financial services phishing.
- Palo Alto Networks provides advanced security measures to protect against these threats.
- Continuous monitoring of threat actors’ indicators can lead to proactive defense strategies.
MITRE Techniques :
- T1071.001 – Application Layer Protocol: Threat actors use various domains to communicate with command-and-control (C2) servers.
- T1070.001 – Indicator Removal on Host: Threat actors may rotate domains to evade detection.
- T1071.003 – Application Layer Protocol: Use of malware delivery URLs to distribute malicious binaries.
- T1046 – Network Service Discovery: Identifying co-hosted domains to map out infrastructure.
- T1583.001 – Acquire Infrastructure: Threat actors register numerous domains to support phishing campaigns.
Indicator of Compromise :
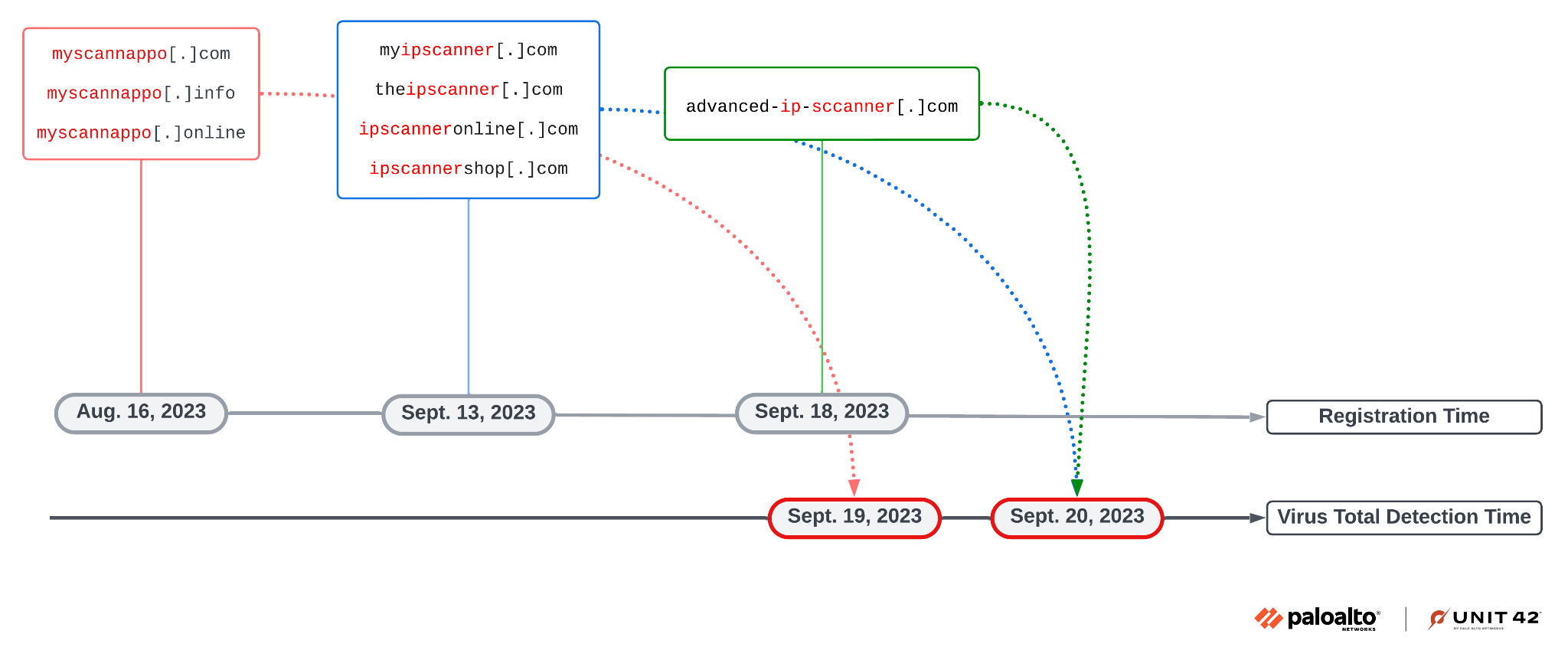
- [domain] advanced-ip-sccanner[.]com
- [domain] myipscanner[.]com
- [domain] myscannappo[.]com
- [domain] correosespana[.]top
- [domain] apple.com-ticket[.]info
- Check the article for all found IoCs.
Full Research: https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/graph-neural-networks/