Short Summary:
The analysis of the Latrodectus malware infrastructure revealed a command-and-control (C2) server and a malicious DLL file named MeDExt.dll, which functions as a downloader and backdoor. The research identified various associated domains and IP addresses, highlighting the malware’s ability to impersonate legitimate software and evade detection.
Key Points:
- Discovered a C2 server at IP address 103.144.139.189.
- Identified MeDExt.dll as a downloader, functioning as a backdoor for remote command execution.
- Common entry points for the malware include phishing and malicious ads.
- The DLL mimics a legitimate AhnLab product, enhancing its stealth.
- Communication with C2 infrastructure revealed multiple suspicious domains and IPs.
- Malware uses familiar techniques, such as Windows COM for persistence.
- Effective defense requires continuous monitoring and detailed network analysis.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs – created by AI
- Initial Access – Phishing
- Phishing campaigns likely serve as entry points for Latrodectus malware.
- Execution – Malicious DLL
- MeDExt.dll acts as a downloader and backdoor.
- Persistence – Scheduled Task
- Utilizes Windows COM to set scheduled tasks for persistence.
- Command and Control – Web Service
- Communicates with multiple C2 domains and IP addresses.
During a recent analysis of known Latrodectus infrastructure, our research team encountered a command-and-control (C2) server at 103.144.139.]189 after pivoting on the TLS certificates. Communicating with this server was a file named MeDExt.dll, detected as the downloader by multiple vendors in VirusTotal.
Leveraging this discovery, we were able to identify additional IP addresses and domains associated with the distribution of Latrodectus malware.
Latrodectus is a downloader that functions as a backdoor, allowing threat actors to execute remote commands, gather information from compromised machines, and deploy additional malicious payloads, the most recent being Brute Ratel C4.
In this blog post, we will examine the malicious DLL and then dive into the C2 infrastructure we uncovered, including the certificate pivot and the associated domains identified during our research.
MeDExt.dll
Unfortunately, we don’t have the initial access method for this attack campaign, but as past reports suggest, phishing and malicious ads are likely entry points into networks.
The DLL file that caught our attention, “MeDExt.dll,” mimics the legitimate MeD Engine Extension from AhnLab Smart Defense. Given that this malicious file is a DLL, it’s plausible that the legitimate parent executable was bundled with the Latrodectus malware or that this was a targeted attack aimed at a victim known to use AhnLab’s services.
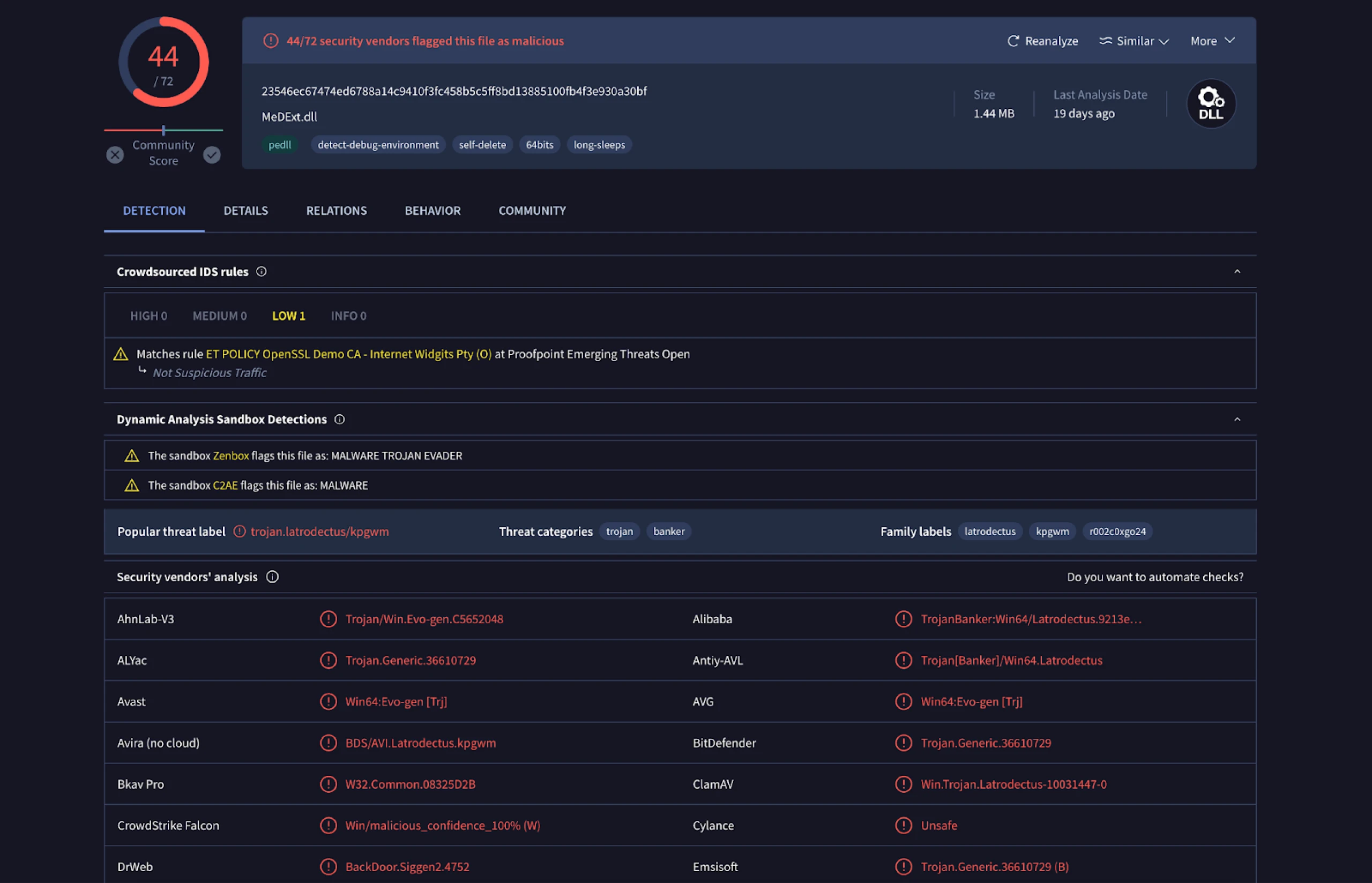
Spoofing a well-known anti-virus vendor increases the malware’s stealth and the likelihood of bypassing security measures, reinforcing the importance of scrutinizing renamed files.
Below is the file signature info. Note the DLL is not signed.
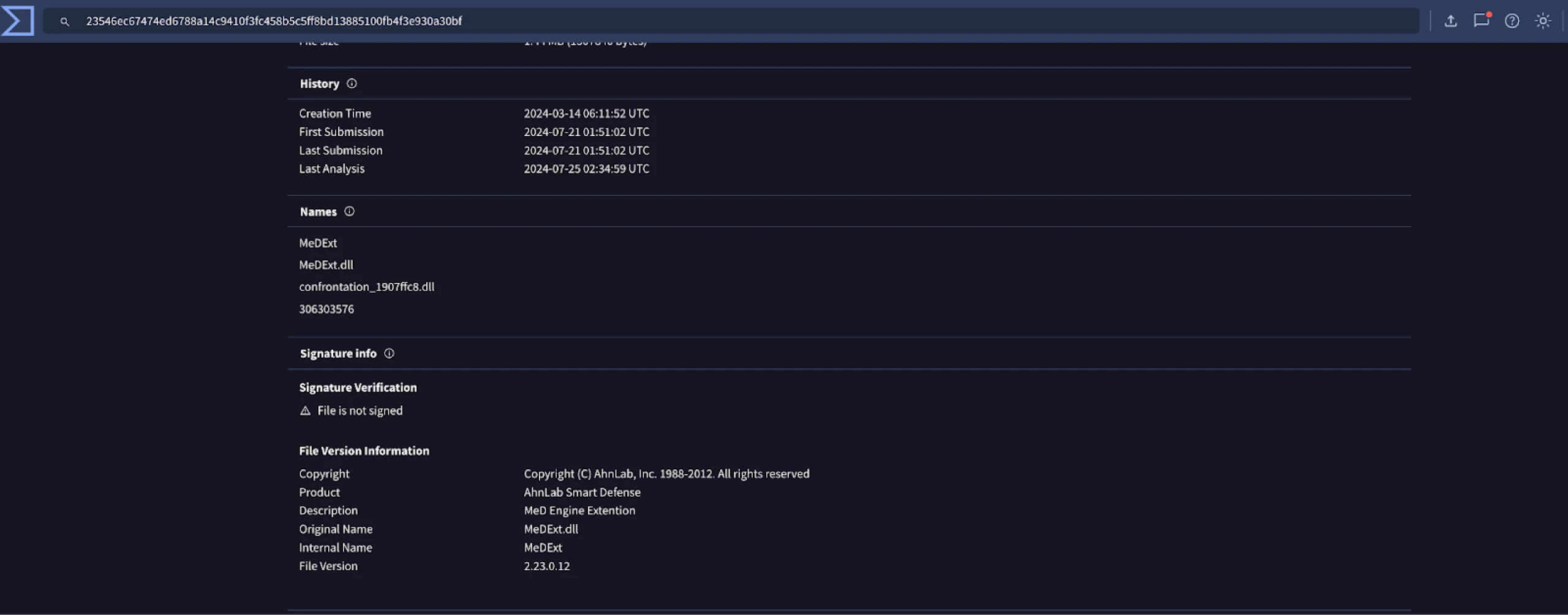
Figure 2: VirusTotal Signature Info for the suspect DLL
The PDB path (provided below) within the MeDExt.dll file offers a glimpse into the environment used by the threat actor(s)
C:BuildProjectMedicineEngine2.0_MainTrunkbuildingbuildProjectMedicineEngine2.0TrunkBuildAMD64freeMeDExt.pdb
The DLL has four exports with differing addresses, all following similar naming paths beginning with “MeDExt..”
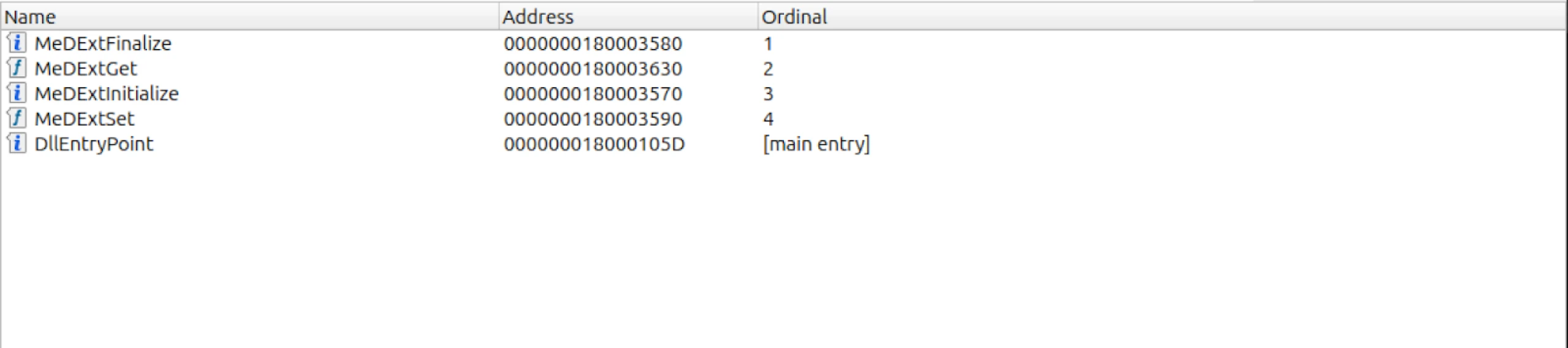
Figure 3: Obligatory IDA screenshot showing the DLL’s exports
We could not identify any new TTPs during the analysis of the malicious file. This sample of Latrodectus employed familiar techniques, such as using the Windows Component Object Model (COM) to set a scheduled task for persistence.
Next, we’ll examine the communication with the command and control infrastructure.
Command & Control Infrastructure Analysis
After running the file through multiple sandboxes, we observed Lactrodecuts attempting to communicate with the following domains + URLs:
- stripplasst.]com/live/
- coolarition.]com/live/
stripplasst.]com was registered through the OwnRegistrar, Inc. registrar, and coolarition[.]com through PDR Ltd. This consistent use of a single registrar should be used as a low-confidence indicator in tracking and attributing related malicious activity.
Both domains were unavailable during analysis, though we captured the first POST request to the C2 registering the victim’s details in a PCAP, as seen below.
The IP address, 103.144.139.]189 for a short period resolved to the domain riscoarchez[.]com, also identified in a Latrodecuts attack paired with Brute Ratel C4 by Rapid7.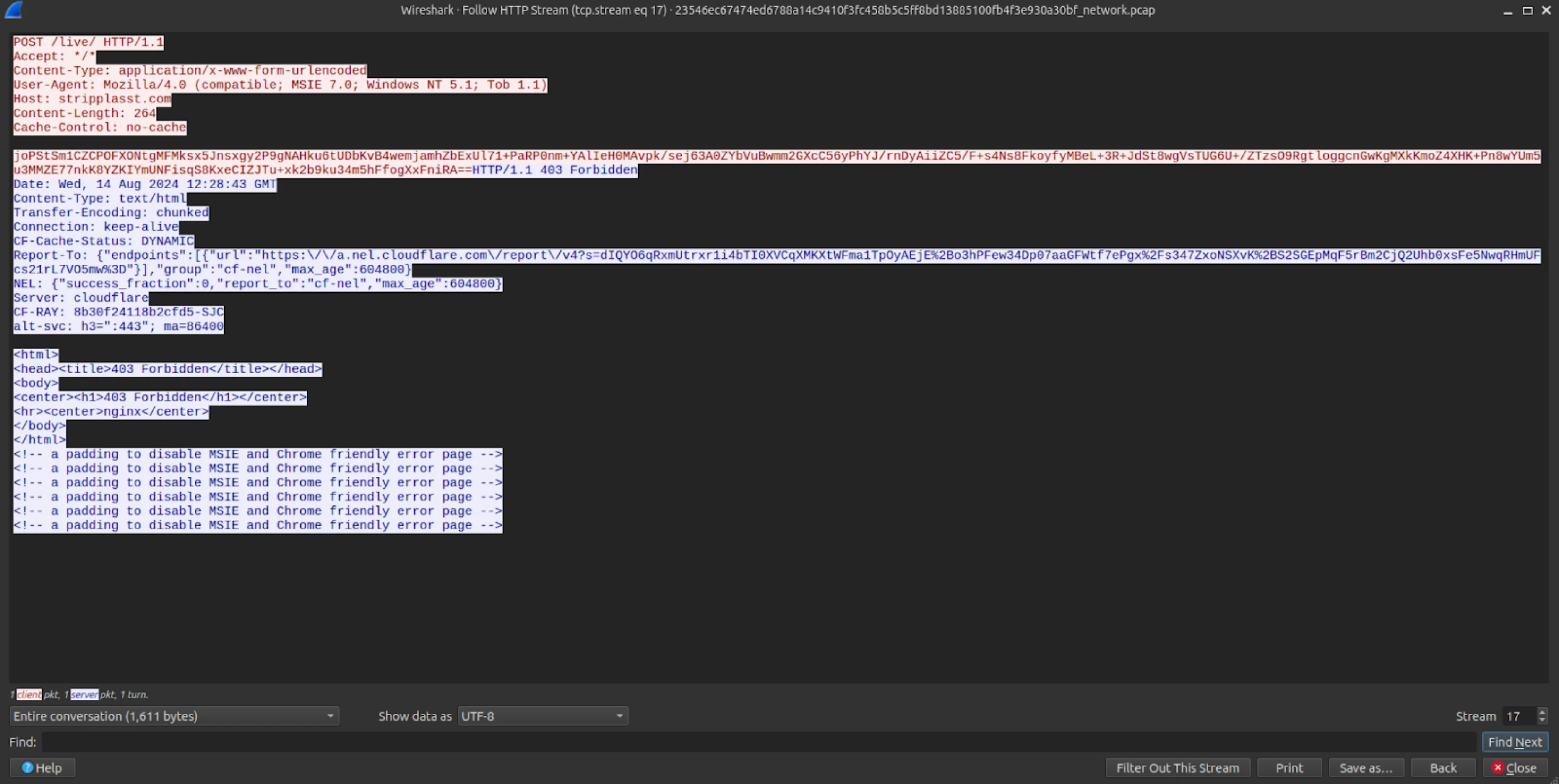
Figure 4: PCAP showing the initial registration request to one of the C2 domains.
The server that initiated our investigation is hosted on the Gigabit Hosting Sdn Bhd ASN.
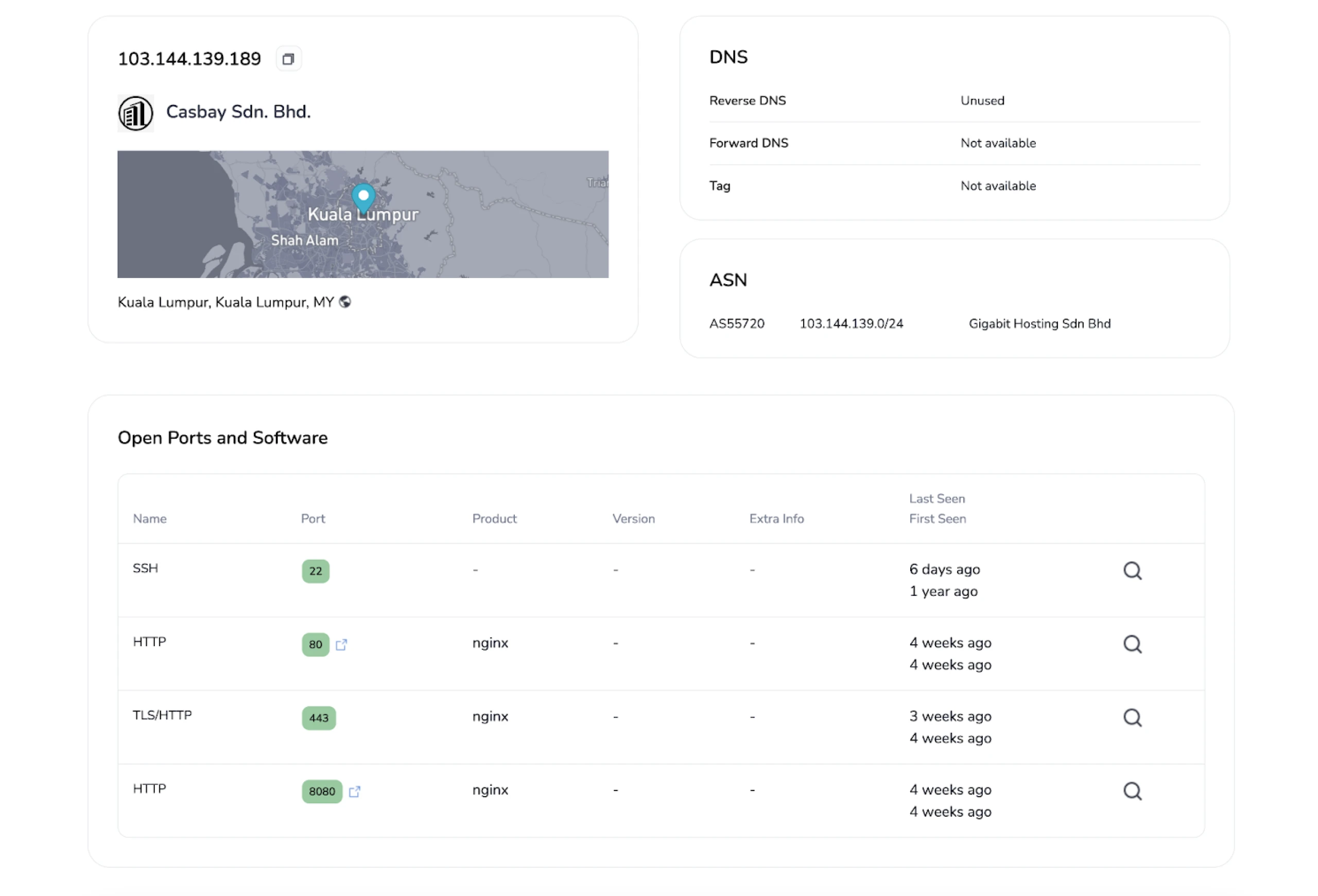
As reported by ProofPoint in their joint blog post with Team Cymru, we can see the server also has ports 443 and 8080 open, which were one of the criteria used to search for additional C2 servers in the article.
Moving to the SSL History, we noticed a semi-unique certificate on port 443. We say “semi” because many malware families use the “Internet Widgits Pty Ltd” Issuer Organization name in their self-signed certificates.
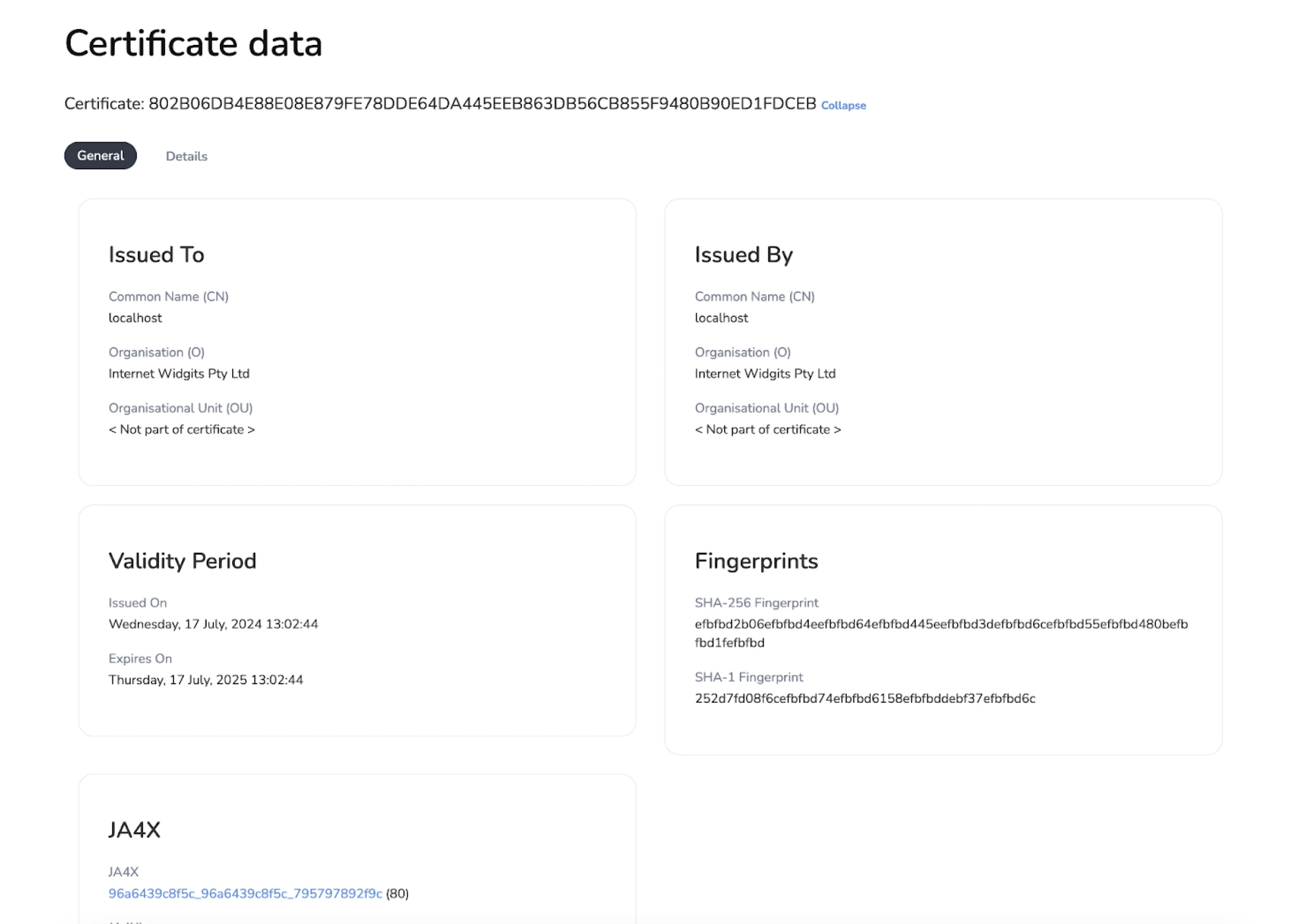
The complete certificate fields are below:
- Subject Common Name: localhost
- Subject Country: AU
- Subject Organization: Internet Widgits Pty Ltd
- Subject Organisational Unit: N/A
- Subject Locality: N/A
- Subject State: Some-State
We can use Hunt’s Advanced Search feature to craft a query that will assist us in identifying servers using similar certificates as the above.
In the case of the Latrodectus C2 certs, we came up with the following query based on the JA4X hash and Subject Common Name:
ja4x:”96a6439c8f5c_96a6439c8f5c_795797892f9c” AND subject.common_name:”localhost”
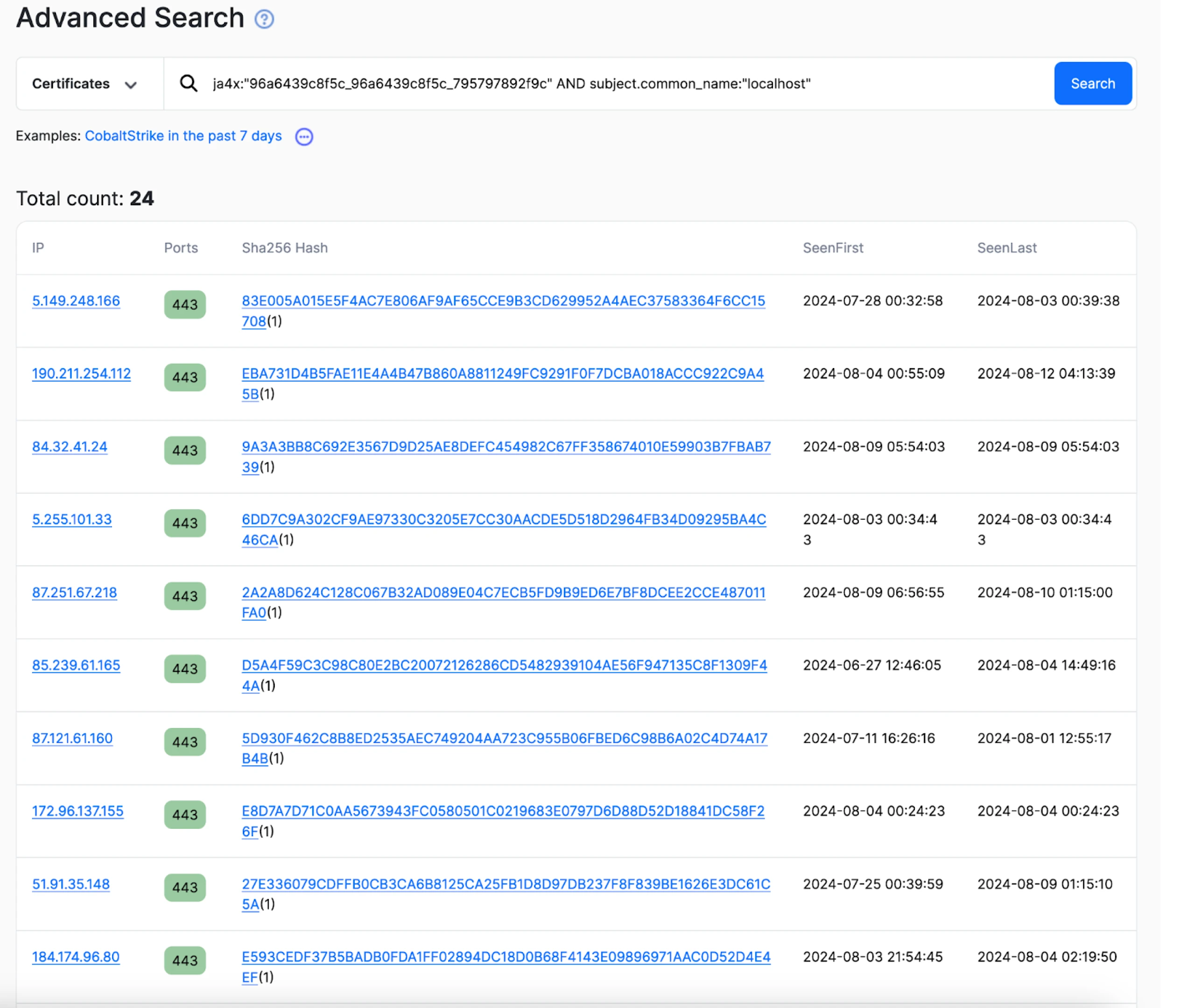
The query returns just 24 results, suggesting we’re on the right track in identifying Latrodectus servers. However, it’s important to note that the certificate fields we’re analyzing are commonly used for legitimate purposes and by other threat actors.
We cannot confirm that all results are linked to the malware; further investigation is required.
Poking around for similar server + certificate combinations on the same ASN as our initial IP, we found a malicious file mimicking the Google Authenticator app, also associated with Latrodectus communicating with 103.144.139.]182.
The domain spikeliftall.]com resolves to the IP mentioned above, registered through PDR Ltd.
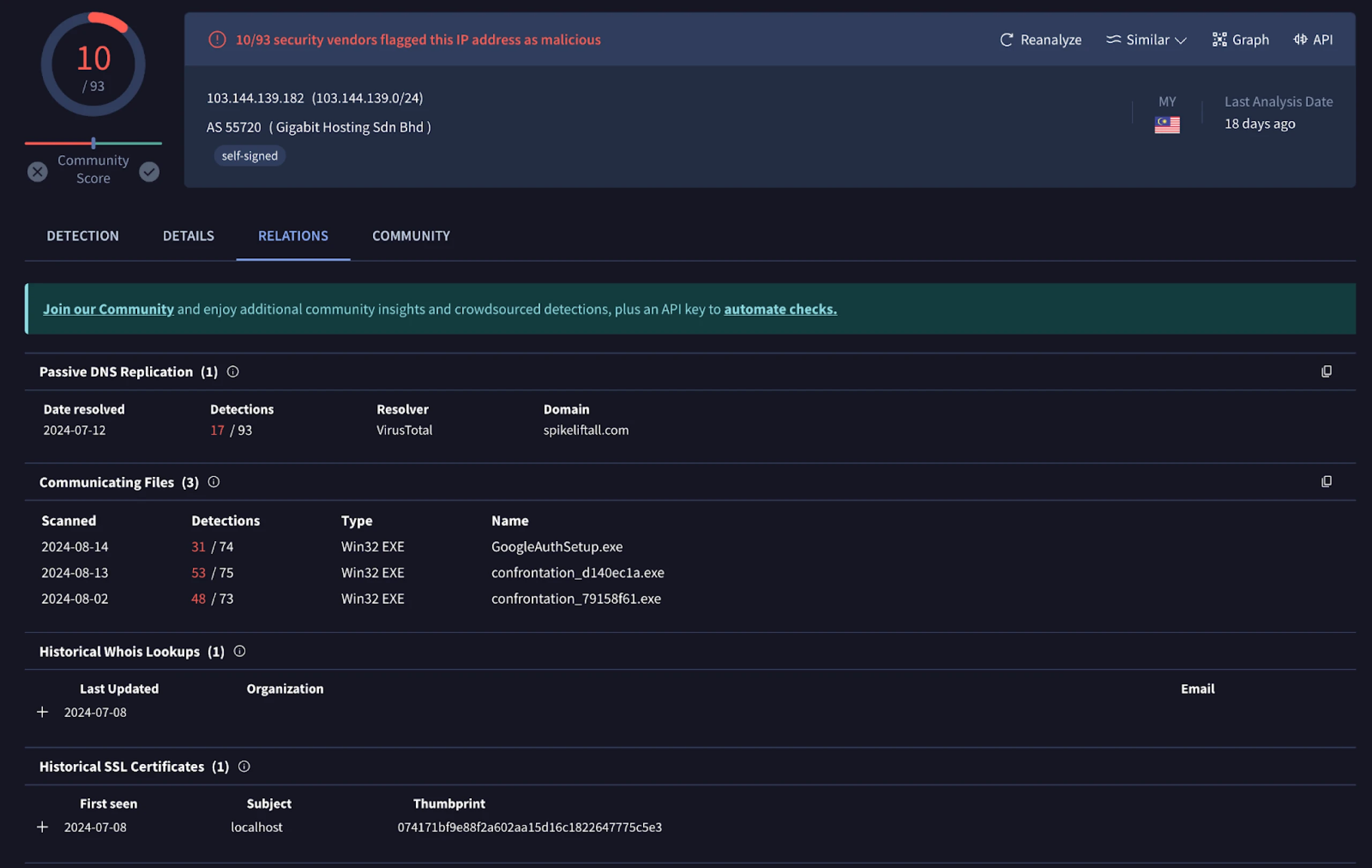
Again, this server also had port characteristics (443 & 8080) and a matching certificate seen with other command and control infrastructure.
On Aug 13, 2024, Symantec also noticed this campaign releasing a Protection Bulletin identifying the initial access vector as phishing.
After submitting a few IP addresses to VirusTotal for analysis, another server with a file detected as Latrodectus caught our attention.
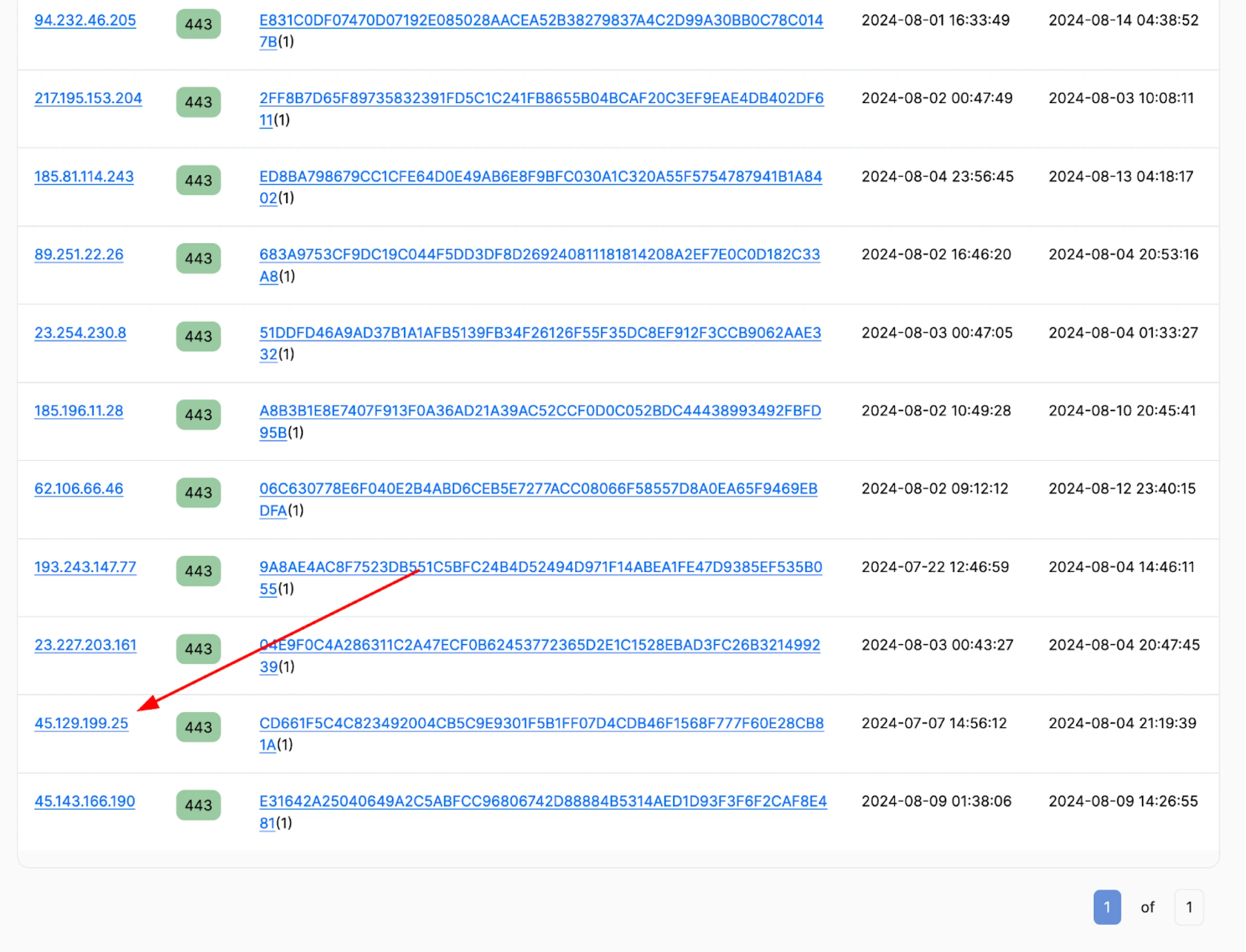
Figure 9: Additional suspicious IP associated with Latrodetus
The IP, hosted on BlueVPS OU, resolves to a single domain, worlpquano.]com registered through HOSTINGER, and used CloudFlare services in mid-July 2024.
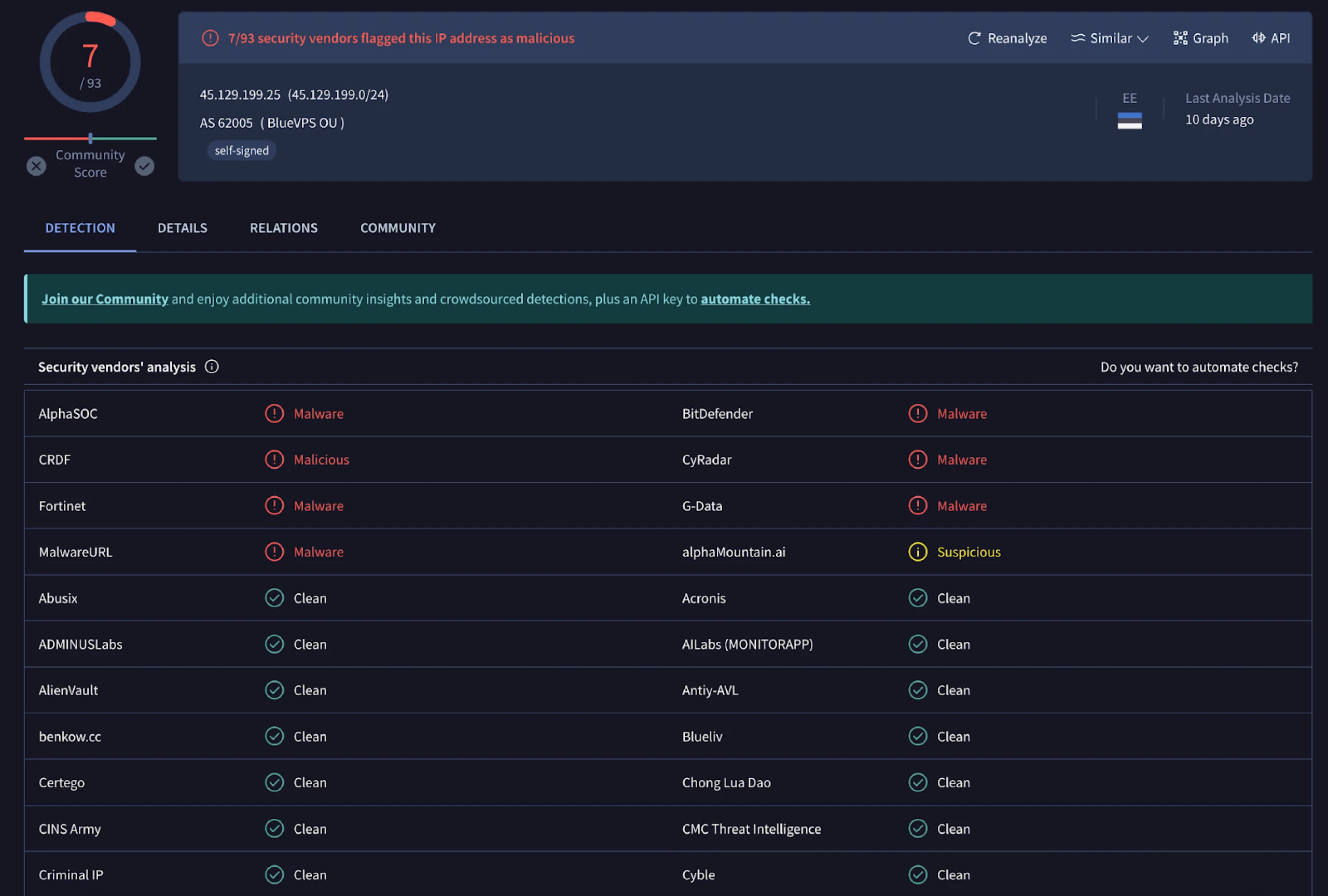
Conclusion
Latrodectus’ tactic of impersonating legitimate security software highlights the persistent challenge of distinguishing between trusted and malicious files. Effective defense against such threats requires continuous monitoring and detailed analysis of network activity.
Request a demo today to get a closer look at how the Hunt platform can strengthen your defenses.
Network Observables
| IP Address | Domain(s) | Domain Registrar | ASN | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 103.144.139.]189:443 | riscoarchez.]com | Own Registrar | Gigabit Hosting Sdn Bhd | Initial IP that started investigation. |
| 188.114.97.]7:443 | stripplasst.]com | Own Registrar | CloudFlare | C2 for MeDExt.dll |
| 188.114.97.]7:443, 84.32.41.]12:443 | coolarition.]com | PDR Ltd. | CloudFlare, Hostgnome Ltd | C2 for MeDExt.dll |
| 103.144.139.]182:443 | spikeliftall.]com | PDR Ltd. | Gigabit Hosting Sdn Bhd | Jarm fingerprint + HTML response hash |
| 45.129.199.]25:443 | worlpquano.]com | HOSTINGER | BlueVPS OU | Identified as a possible Latrodectus C2 by Symantec |
Host Observables
| File Name | SHA-256 Hash | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MeDExt.dll | 23546ec67474ed6788a14c9410f3fc458b5c5ff8bd13885100fb4f3e930a30bf | Seen communicating with riscoarchez.]com/live/ stripplasst.]com/live/ coolartiion.]com/live/ |
| GoogleAuthSetup.ex | 62536e1486be7e31df6c111ed96777b9e3f2a912a2d7111253ae6a5519e71830 | Seen communicating with steamcommunity.]com/profiles/76561199619773134 godfaetret.]com/live/ spikeliftall.]com/live/ |
| confrontation_d46a184c.exe | a459ce4bfb5d649410231bd4776c194b0891c8c5328bafc22184fe3111c0b3e7 | Seen communicating with worlpquano.]com/live/ carflotyup.]com/live/ |
Source: https://hunt.io/blog/latrodectus-malware-masquerades-as-ahnlab-security-software-to-infect-victims