The Kimsuky APT is a North Korea-based cyber espionage group operating since at least 2012. Initially, The group targeted South Korean government entities, think tanks, and individuals identified as experts in various fields.
Tracked as: APT43, Black Banshee, Velvet Chollima, THALLIUM, ARCHIPELAGO, and Emerald Sleet
Targets and Objectives: The group primarily targets South Korea, Japan, and the United States, focusing on sectors such as national defense, education, energy, government, healthcare, and think tanks. Their primary objective is intelligence gathering.
Tactics and Tools: Kimsuky employs a variety of tactics, including social engineering, spear-phishing emails, and watering hole attacks. They have developed unique malware for various operations.
Kimsuky began its campaign against significant targets in South Korea in January 2024. By January 24, we found that the compilation times for many samples dated back to December 2023. Based on these and other artifacts, our team at Dark Atlas initiated efforts to track these attacks and investigate the tools used.
Beyond our analysis, we discovered that the TA has registered their installer with digital signatures from “SGA Solutions CO., Ltd.” and “D2innovation CO., LTD.” This is the initial stage of the attack, where the installer is used to deliver and deploy another stage of the malware.
It drops a stealer called TrollAgent, a DLL file written in GoLang and protected using VMProtect3. Additionally, it drops a batch file to remove the initial installer upon dropping the DLL. An executable file named “NXTPKIENTS.exe” is also dropped, which serves as the main file for the SGA package installer.
Then, it writes a file named with the exported function in the TrollAgent DLL to the ProgramData path. The DLL later uses this file to check the execution method.
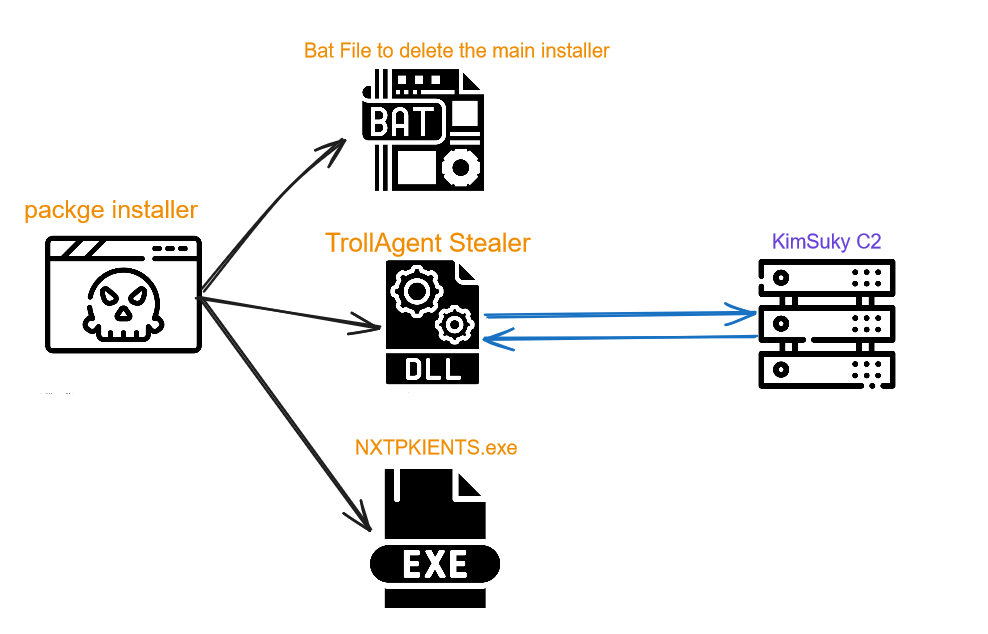
Figure 1- TrollAgent attack chain
We investigated one of the campaign samples used by Kimsuky, with hash “2e0ffaab995f22b7684052e53b8c64b9283b5e81503b88664785fe6d6569a55e,” and it has a digital signature from “D2innovation CO., LTD.”
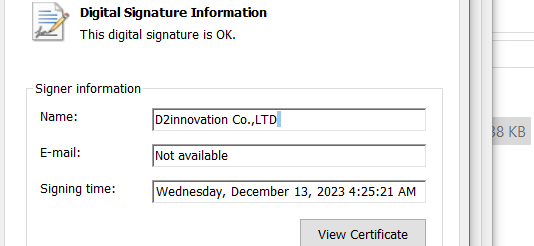
Figure 2- Digital Signature
This exe file is dropping a file named [4].tmp.bat in the TEMP directory

Figure 3- Created TEMP file
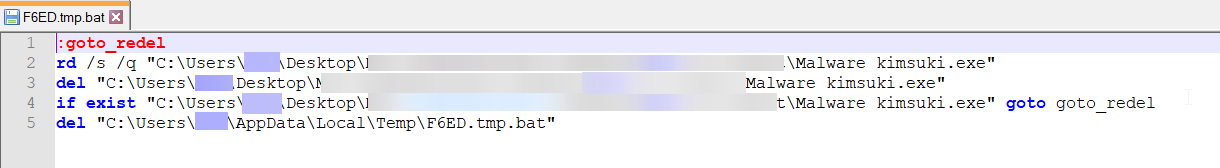
Figure 4- Bat file to delete main installer
This batch script is designed to repeatedly attempt to delete the main installer until it is successfully removed. After the target file is deleted, the script proceeds to delete itself from the system to ensure no residual files are left behind. This process ensures the complete removal of the specified file and cleans up any temporary files created during execution.
It then drop another PE file under C:Users<USER>AppDataRoamingMedia with the name win-[6].db
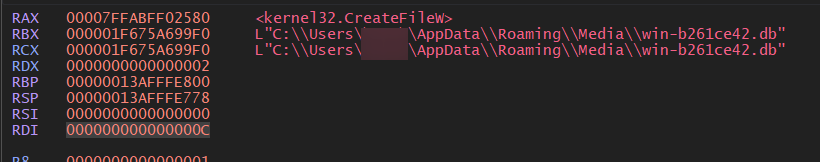
Figure 5- Dropped db file
It then drops the main installer, which is NXTPKIE.exe, in the same directory for this process.
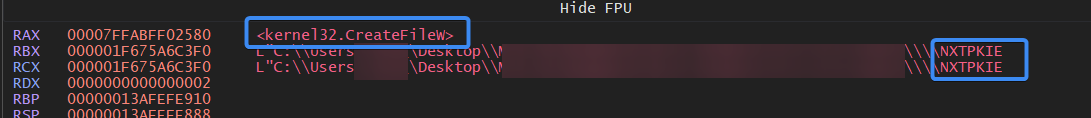
Figure 5- Dropped db file
In the ProgramData path, it drops another file with the name of the DLL exported function. The DLL uses this file later to check the execution method. If the file exists, it indicates that the DLL was executed by the main installer, not by a sandbox or analyst.
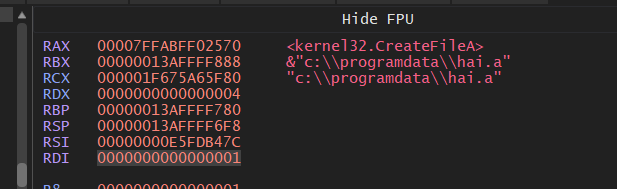
Figure 6- Dropped Config File
It then creates a process to launch the DLL file, and it calls a specific exported function within the DLL to be executed.
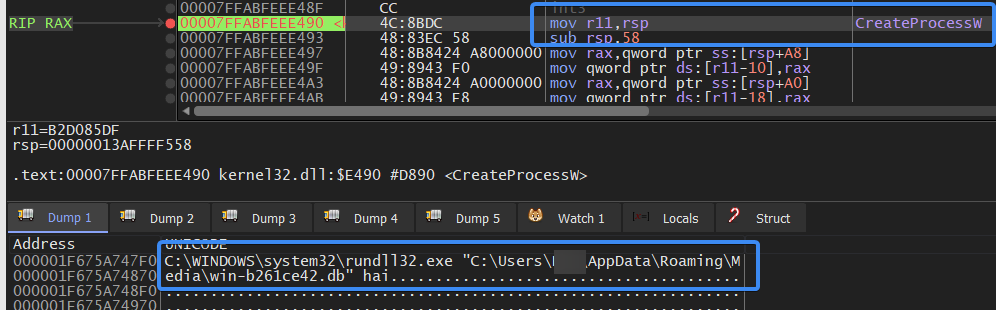
Figure 7- Create Process
TrollAgent Stealer (DLL Analysis)
The DLL file was protected using VMprotect. Unpacking this type of protection is challenging due to its anti-debugging techniques and code virtualization, which make it harder to unpack. However, our team successfully unpacked the sample by attaching a debugger to the process created earlier, editing the creation flags to set it in suspended mode, and then attaching the debugger again. Finding the code’s entry point was difficult due to control flow flattening and obfuscation. Nevertheless, we managed to obtain an unpacked specimen from this DLL file. This DLL was written using Golang and is named TrollAgent.
Figure 8- TrollAgent DLL
Anti-Analysis Techniques
The malware’s main function calls a function named main_anti. Initially, it deletes a scheduled task named “ChromeUpdateTaskMachineUAC” using schtasks.
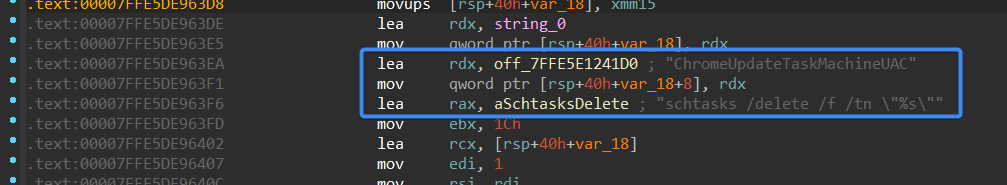
Figure 9- Deleting a scheduled task
It checks for the configuration file, and if “hai.a” or “oni.a” based on the DLL itself does not exist, it stops the process and deletes itself.
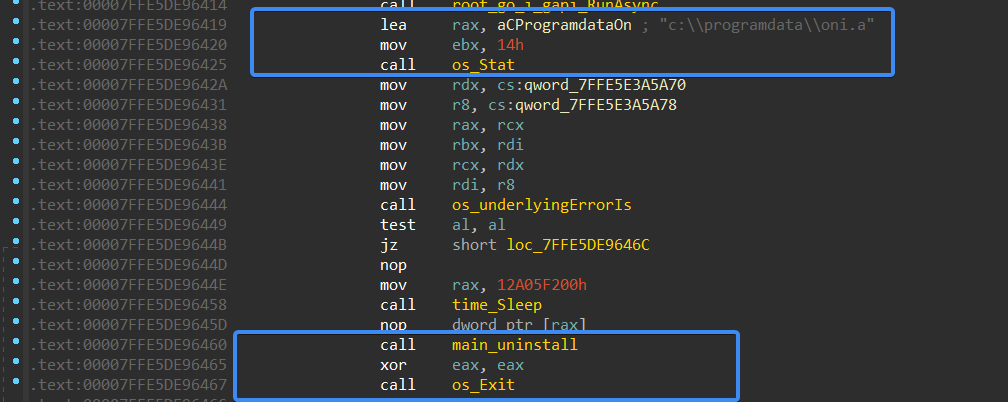
Figure 10- Anti Analysis Check
Then it creates a mutex named “chrome development kit 1.0”
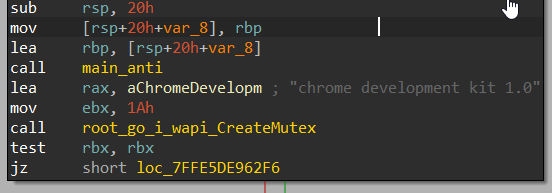
Figure 11- Mutex Creation
Building Stealer Configuration
Next, It delves into a function called root_go_s_troll_agent_config_Init which is responsible for Configuration initialization; it sets the version to “gt@2.0,” and it also gets the Mac address and then hash it or generates UID for the Mac address
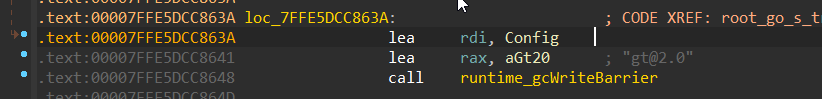
Figure 12- setting version to gt@2.0

Figure 13- Getting Mac address
Then, it sets the C&C servers to be used to communicate with TA; it uses two URLs for that
- http://sa[.]netup.p-e[.]kr/index.php
- http://dl[.]netup.p-e[.]kr/index.php
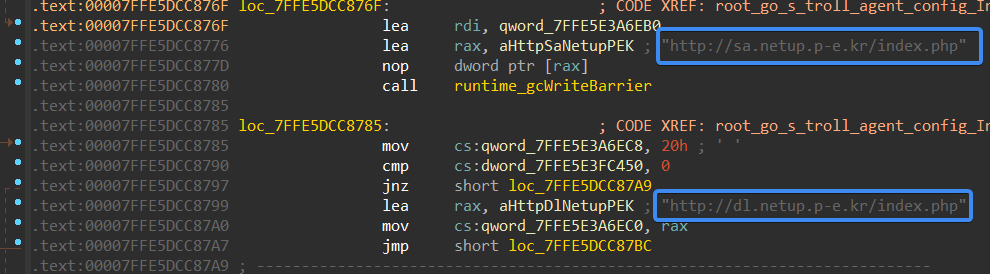
Figure 14- Command and Control servers
It then initiates a connection with C2 and marks the request with “init” which is relative to the initialization configuration; it then checks if the response is “ok”
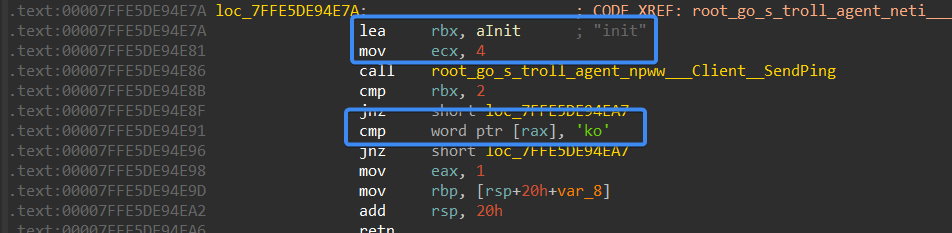
Figure 15– sending init data to C2
It then calls two functions, which indicate the core functionality of this stealer:
root_go_s_troll_agent_cmd___CmdGt2__doInfo , root_go_s_troll_agent_cmd___CmdGt2__doWork
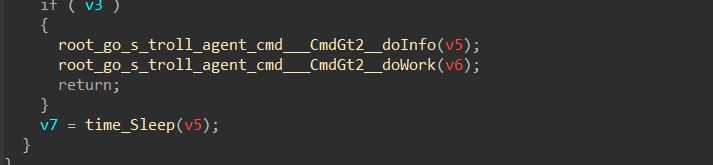
Figure 16- main functions
C2 Connection
It then creates an org file, this file contains the collected data about the victim like MAC address, version, used URLs, and some extra information, these data are RSA encrypted and then sent to the C2 followed by removing this file.
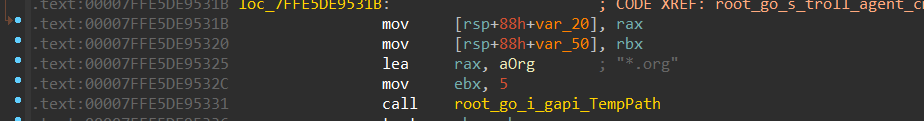
Figure 17- creating org file in .tmp path
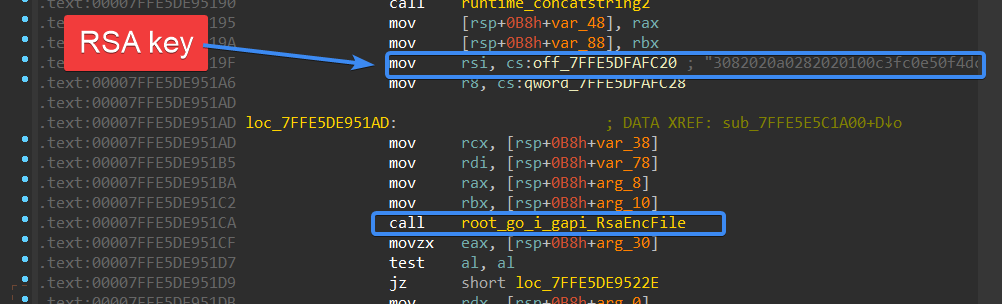
Figure 18- Encrypting file using RSA
This file then is sent to the C2 using root_go_s_troll_agent_npww___Client__FileUP function
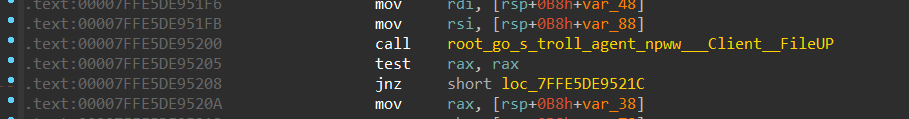
Figure 19- sending encrypted data to C2
Stealing function
Next, the malware will start collecting the victim’s data. It can collect SSH sessions and FileZilla, and it can steal sticky notes from the machine.
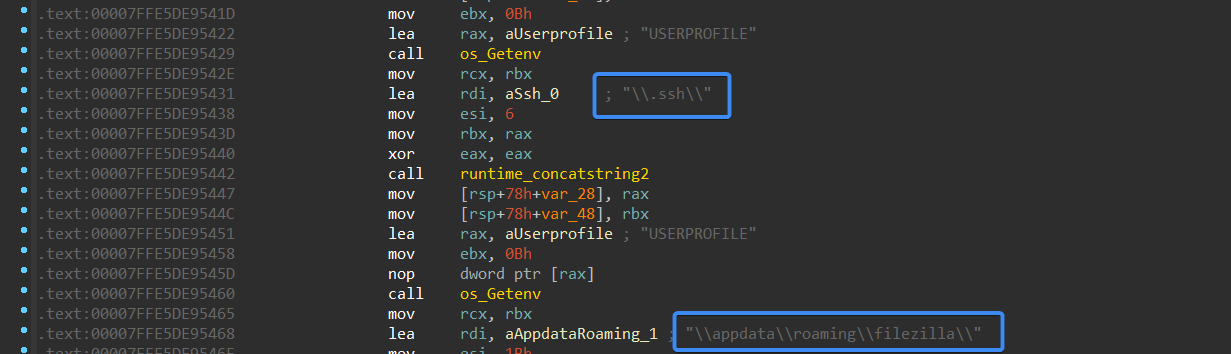
Figure 20- SSH and FileZilla session collection
After building the full file path it uses a function called io_ioutil_ReadDir to read this file, this function is wrapped with root_go_s_troll_agent_cmd___CmdGt2__getYes function.
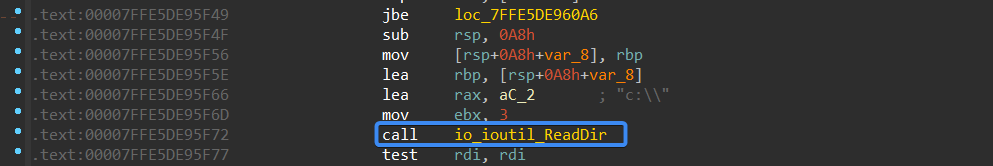
Figure 21- Reading files
It then executes a command that collects some information.
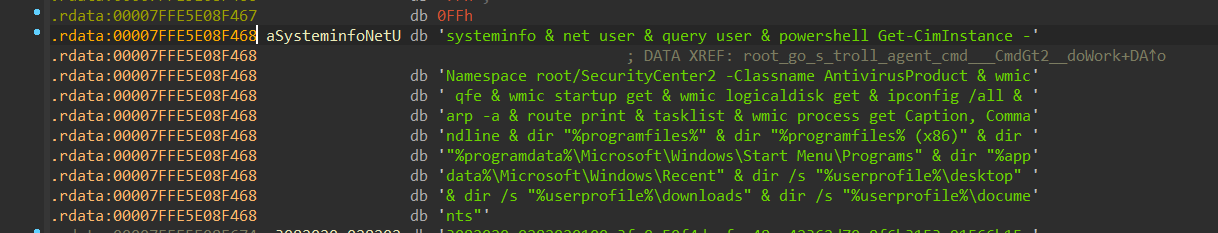
Figure 22- executed command
Commands explanation
| Command | Description | Output |
| systeminfo | Gathers detailed system information. | OS version, hardware specs, hostname, domain info |
| query user | Provides details on specific user accounts. | Usernames, privileges, account status. |
| net user | Lists local user accounts. | Usernames, groups, account status. |
| powershell Get-CimInstance -Namespace root/SecurityCenter2 -Classname AntivirusProduct | Queries Antivirus status (requires PowerShell). | Antivirus software name, status, configuration. |
| wmic qfe | Lists installed hotfixes (updates). | Hotfix IDs, installation dates. |
| wmic startup get | Shows programs configured to run at startup. | Program names, locations. |
| wmic process get Caption, CommandLine | Lists running processes with their details. | Process names, command-line arguments. |
| tasklist | Provides a simpler view of running processes | Process names, PIDs (process identifiers). |
| ipconfig /all | Displays detailed network adapter information | IP addresses, subnet masks, gateways, DNS servers. |
| arp -a | Shows the ARP cache (IP to MAC address mapping). | IP addresses, corresponding MAC addresses. |
| route print | Lists the routing table for network traffic. | Destination networks, gateways, metrics |
| dir “%programfiles%” | Lists contents of the “Program Files” directory | Installed program files and folders. |
| dir “%programfiles% (x86)” | Lists contents of “Program Files (x86)” (32-bit programs | Installed program files and folders. |
| dir “%programdata%MicrosoftWindowsStart MenuPrograms” | Lists contents of the Start Menu’s Programs folder | Installed application shortcuts. |
| dir “%appdata%MicrosoftWindowsRecent” | Shows recently accessed files and applications. | List of recently used files. |
| dir /s “%userprofile%desktop” | Lists all files and subfolders within the user’s Desktop. | Complete directory listing of the Desktop |
| dir /s “%userprofile%downloads” | Lists all files and subfolders within the user’s Downloads. | Complete directory listing of the Downloads folder. |
| dir /s “%userprofile%documents” | Lists all files and subfolders within the user’s Documents | Complete directory listing of the Documents folder |
So now, after collecting the above-mentioned data, each data type is zipped and then encrypted using an RSA key, followed by sending it to C2. It uses a function called root_go_i_gapi_ZipTo to compress the files.
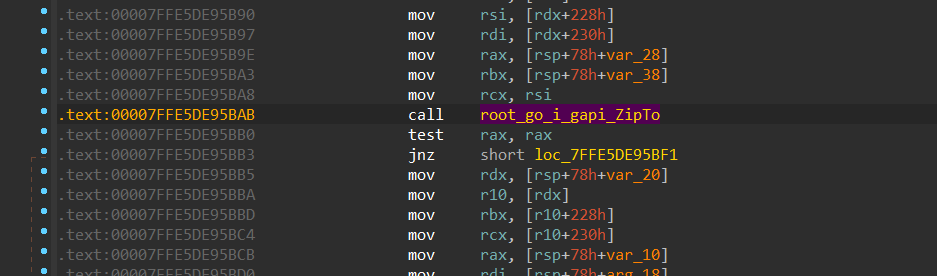
Figure 23- Data Compression
A Table for encrypted file names and it’s purpose
| Encrypted File Name | Purpose |
| gcfg@[timestamp].gte1 | Capturing software configuration data |
| tcd@[timestamp].gte1 | Logging data of an unidentified directory or file within the C drive |
| tfd@[timestamp].gte1 | Storing FileZilla directory information |
| tsd@[timestamp].gte1 | Recording SSH directory details |
| tnd@[timestamp].gte1 | Gathering data from Sticky Notes directory |
| tbd@[timestamp].gte1 | Saving browser-related information |
| ccmd@[timestamp].gte1 | Collecting data via cmd |
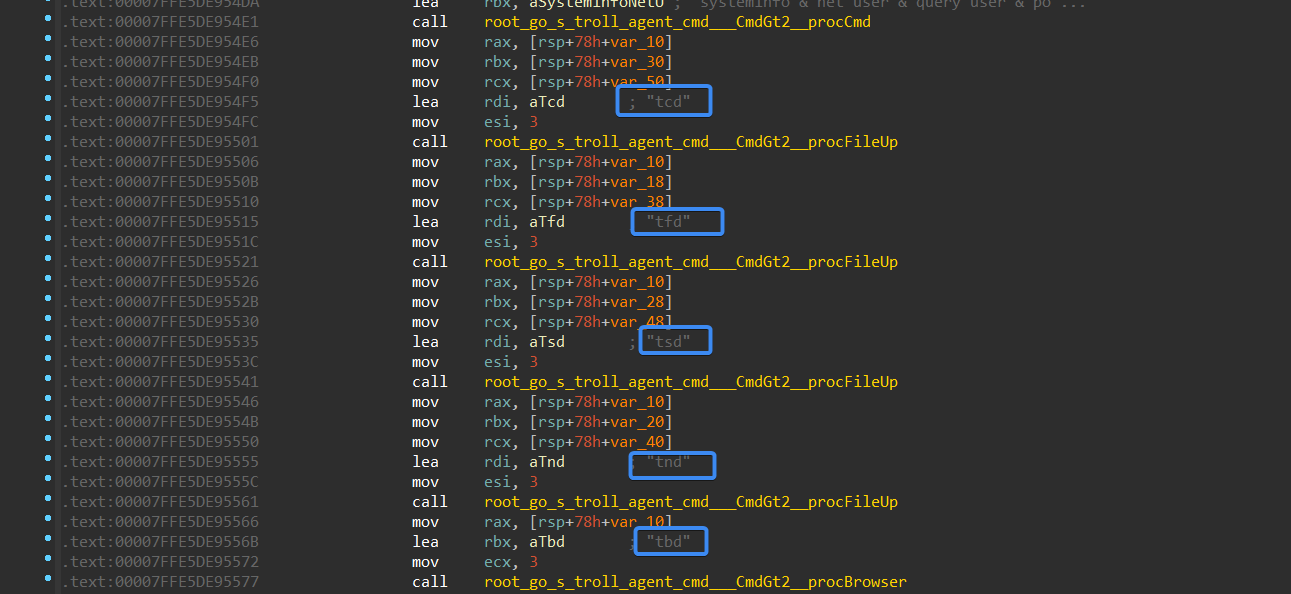
Figure 24- encrypted file names
Collecting Browser data
TrollAgent can harvest a wide range of browsers’ data like other stealers, its functionality is defined to collect credit card information, cookies, browsing history, and auto-login credentials, it has a dedicated function for each browser type like a function for handling all chromium browsers and another one for Firefox one.
Inside root_go_s_troll_agent_cmd___CmdGt2__procBrowser there is a call to root_go_s_troll_agent_internal_browser_PickBrowser and this function wraps calls to the functions responsible for gripping and collecting data, the function that handles chromium stuff is called root_go_s_troll_agent_internal_browser_pickChromium. The function responsible for Firefox is called root_go_s_troll_agent_internal_browser_pickFirefox
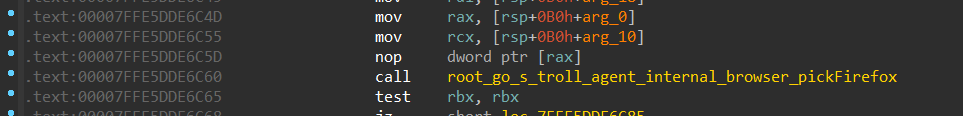
Figure 25- functions to collect browsers data
The function that initializes the file path and type of data collected is called root_go_s_troll_agent_internal_browser_init, it contains all browser configurations for Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Brave, Yandex, OperaX, and many other browsers.
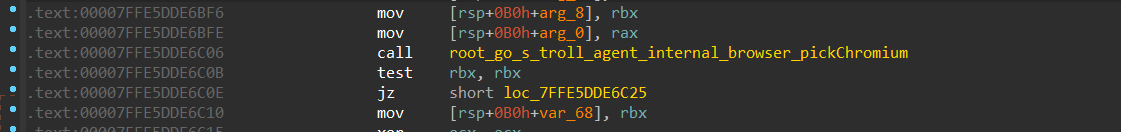
Figure 26- Browsers file configuration
TrollAgent has multiple code blocks for each browser to handle the collection part. Each data type has a dedicated function, such as one for retrieving passwords and another for parsing credit cards. This differentiation is necessary because each browser’s database structure is different, leading to variations in the executed SQLite queries across browsers. Let’s provide an overview of this.
Yandex Browser
For Yandex, it has a function for parsing passwords and another function for parsing credit cards.
The type of database is Sqlite3:
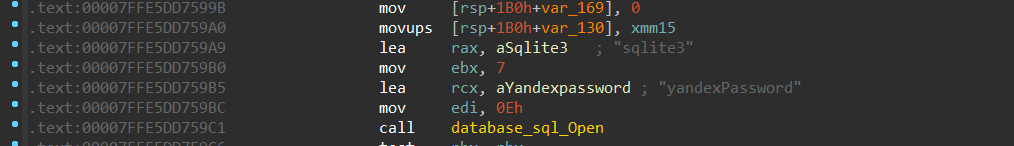
Figure 27- Yandex passwords Database
for parsing the database, it executes a SQLite query

Figure 28- password parsing SQL query
Uninstall and Config Deletion
After sending all data to the C2, TrollAgent clears its configuration and uninstalls itself.
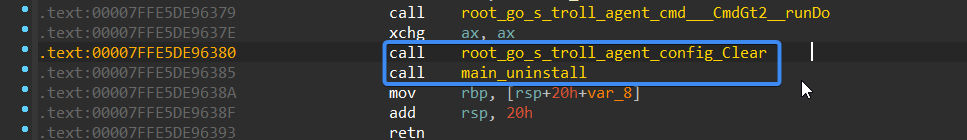
Figure 29 – Clearing Config
Inside the main-uninstall function, it does the same as it did in the main_anti function by deleting a scheduled task with the same name “ChromeUpdateTaskMachineUAC”
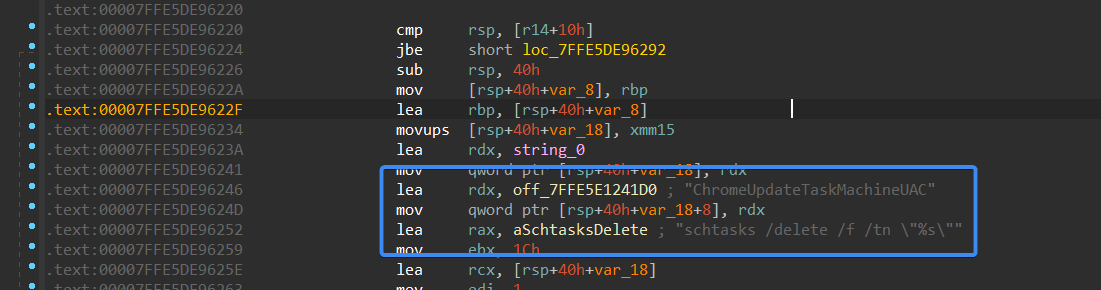
Figure 30 – Task Deletion
| Tactic | Technique | MITRE ATT&CK ID | Description (In Context of TrollAgent) |
| Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell | T1059.003 | Kimsuky drops PowerShell (PS) and batch (BAT) files to potentially perform tasks on the compromised machine |
| Defense Evasion | Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing | T1027.002 | TrollAgent DLL protected using VMProtect3, a packer that obfuscates code to hinder analysis. |
| System Binary Proxy Execution: Rundll32 | T1218.011 | Kimsuky abuses rundll32.exe, a legitimate Windows program, to execute the malicious TrollAgent DLL | |
| Masquerading | T1036 | Kimsuky creates files inside user directory | |
| Indicator Removal: File Deletion | T1070.004 | Kimsuky checks for a file dropped by the initial infection stage. If the file doesn’t exist, it terminates itself and deletes its own files to avoid detection. | |
| Credential Access | Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers | T1555.003 | Kimsuky targets browser databases to collect usernames and passwords stored by the user |
| Steal Web Session Cookie | T1539 | Kimsuky steals cookies from web browsers to maintain or hijack active sessions | |
| Discovery | System Information Discovery | T1082 | Kimsuky uses commands such as: systeminfo, hotfixes to gather information about the infected machine |
| Process Discovery | T1057 | Kimsuky uses the tasklist and wmic process get Capture, CommandLine commands to gather the processes running on the system | |
| Account Discovery: Local Account | T1087.001 | Kimsuky uses the commands net user to find accounts on the system | |
| Network Information Gathering | T1016 | Kimsuky has used ipconfig/all , arp -a and route print to gather network configuration information | |
| File and Directory Discovery | T1083 | Kimsuky has used commands such as: dir "%programdata%MicrosoftWindowsStart MenuPrograms" and dir /s "%userprofile%desktop" to enumerate all files and directories on an infected system | |
| Software Discovery: Security Software Discovery | T1518.001 | Kimsuky checks for the presence of antivirus software with powershell Get-CimInstance -Namespace root/securityCenter2 – classname antivirusproduct | |
| Collection | Data from Local System | T1005 | Kimsuky might collect SSH keys and FileZilla FTP sessions stored on the compromised system |
| Screen Capture | T1113 | Kimsuky uses kbinani/screenshot Go library to take screenshot of the victim machine | |
| Command and Control | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | T1071.001 | Kimsuky uses HTTP GET and POST requests for C2 |
| Exfiltration | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | T1041 | Kimsuky exfiltrates data over its C2 channel |
Indicators of Compromise
| Indicator | Type | Description |
| 9e75705b4930f50502bcbd740fc3ece1 | MD5 | Initial installer |
| 27ef6917fe32685fdf9b755eb8e97565 | MD5 | Initial installer |
| 7b6d02a459fdaa4caa1a5bf741c4bd42 | MD5 | Initial installer |
| 7457dc037c4a5f3713d9243a0dfb1a2c | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| c8e7b0d3b6afa22e801cacaf16b37355 | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| 2e5f2a154e1b67cd0d6a2f6b5feb6de7 | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| 045f28a479ba19a95c0407a663e2f188 | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| a67cf9add2905c11f5c466bc01d554b0 | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| 3b596ca429cf1b733f1ff3676189e44a | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| 88f183304b99c897aacfa321d58e1840 | MD5 | TrollAgent DLL |
| hxxp://ar.kostin.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
| hxxp://dl.netup.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
| hxxp://qi.limsjo.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
| hxxp://ol.negapa.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
| hxxp://ai.negapa.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
| hxxp://sa.netup.p-e[.]kr/index.php | URL | C2 Server |
rule TrollAgent_Kimsuky_Stealer
{
meta:
description = "Detect TrollAgent Stealer"
author = "Dark Atlas Squad"
date = "2024-07-14"
strings:
$ex1 = "rollbackHookTrampoline" wide ascii
$ex2 = "preUpdateHookTrampoline" wide ascii
$ex3 = "compareTrampoline" wide ascii
$ex4 = "doneTrampoline" wide ascii
$ex5 = "authorizerTrampoline" wide ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5a4d and
pe.characteristics & pe.DLL and
all of them and
pe.number_of_exports > 11 and
for any i in (0 .. pe.number_of_sections) : (
pe.sections[i].name == ".vmp0" or
pe.sections[i].name == ".vmp1"
)
}Source: https://darkatlas.io/blog/kimsuky-apt-the-trollagent-stealer-analysis