
Summary: The Lazarus group has launched a new campaign targeting financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges by weaponizing the IPMsg installer to deliver backdoors and steal sensitive information. This sophisticated attack showcases their advanced social engineering tactics and evasion techniques.
Threat Actor: APT-C-26 (Lazarus) | Lazarus
Victim: Financial Institutions and Cryptocurrency Exchanges | financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges
Key Point :
- The attack begins with a weaponized version of the IPMsg installer, which deploys both a legitimate installer and a malicious DLL file.
- The malicious DLL initiates a multi-stage attack, ultimately establishing communication with a command-and-control (C2) server.
- Lazarus employs advanced evasion techniques, including stack-based checks to avoid detection in sandbox environments.
- Legitimate-looking domains, such as cryptocopedia[.]com, are used to host their C2 infrastructure, enhancing the credibility of the attack.
- The tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) align closely with previous Lazarus operations, indicating a consistent operational methodology.
- Organizations are urged to enhance their security measures and remain vigilant against such evolving threats.
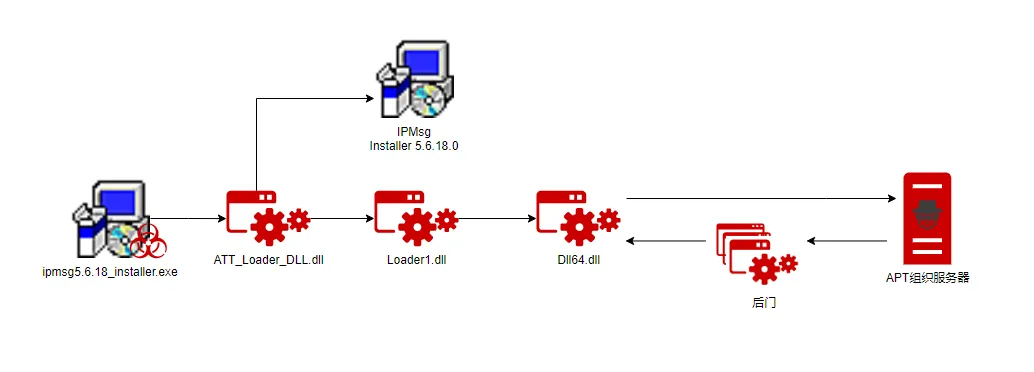
The notorious APT-C-26 (Lazarus) group, known for its advanced persistence and cyber espionage tactics, has resurfaced with a new campaign targeting financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges. In a recent analysis by the 360 Threat Intelligence Center, Lazarus was found to have weaponized the popular IPMsg installer, transforming it into a tool for delivering backdoors and stealing sensitive information.
The attack begins with a weaponized version of the IPMsg installer. Upon execution, the installer deploys two components:
- A legitimate IPMsg installer (version 5.6.18.0) to maintain credibility.
- A malicious DLL file that initiates a multi-stage attack, ultimately communicating with a command-and-control (C2) server.
This strategy reflects Lazarus’s expertise in social engineering, effectively tricking users into executing the malicious program.
The malicious DLL goes through several decryption and execution stages, culminating in a backdoor that allows the attackers to download further payloads and exfiltrate data.
Lazarus employed advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection. The DLL files include stack-based checks to ensure they cannot run independently in sandbox environments. Moreover, the group used legitimate-looking domains, such as cryptocopedia[.]com, to host their C2 infrastructure.
All executables involved, including the initial installer, are designed to appear legitimate, adding a layer of credibility that helps bypass traditional security measures.
The tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) observed in this campaign align closely with previous Lazarus operations. The use of cryptocopedia[.]com and similar URLs, combined with geopolitical targeting patterns, strongly suggests the involvement of this North Korean-linked threat group.
The similarities in domain usage and operational methods give us high confidence in attributing this campaign to the Lazarus group, stated the 360 Threat Intelligence Center.
As Lazarus continues to evolve its tactics, organizations must remain vigilant. The group’s ability to weaponize legitimate software highlights the importance of robust security measures and proactive threat intelligence.
Related Posts:
Source: https://securityonline.info/ipmsg-installer-weaponized-lazarus-group-targets-crypto-finance/
Views: 3