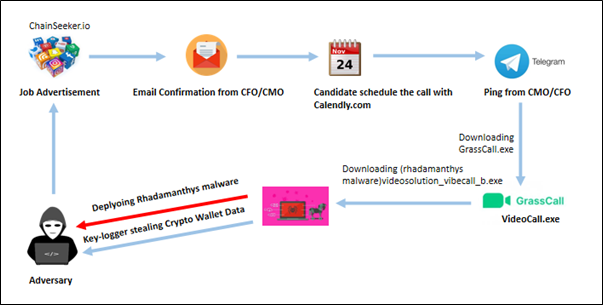
The “GrassCall” malware campaign is an advanced social engineering attack targeting job seekers in the cryptocurrency and Web3 sectors, orchestrated by the Russian cybercriminal organization “Crazy Evil.” Utilizing fake job interviews, the attackers compromise systems to steal cryptocurrency assets, resulting in hundreds of victims. Affected: cryptocurrency sector, job seekers
Keypoints :
- The GrassCall malware campaign is led by the Russian-speaking cyber-criminal organization “Crazy Evil.”
- Targets job seekers in cryptocurrency and Web3 sectors through fake job interviews.
- Prospective victims are lured with fake job ads on platforms like LinkedIn and Crypto Jobs List.
- Phishing communications occur via email and Telegram with impersonated company officials.
- Victims are directed to download malicious software disguised as a video conferencing application.
- GrassCall and its rebranded version Vibecall are central to the malware distribution.
- Windows users are infected by a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) combined with an information-stealing virus called Rhadamanthys.
- Mac users are affected by a macOS-specific stealer called Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS).
- The malware attempts to disable security features of Windows Defender to avoid detection.
MITRE Techniques :
- T1566.002 – Phishing: Spearphishing Link – Attackers utilize phishing emails to lure victims into downloading malicious software.
- T1071.001 – Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols – Malicious communications are conducted over web protocols.
- T1102.001 – Web Service: Social media – Job advertisements are prominently shared on social media platforms.
- T1199 – Trusted Relationship – Attackers exploit the trusted relationships between candidates and impersonated company officials.
- T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer – Malicious files are transferred to victim machines via social engineering tactics.
- T1059.001 – Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell/Windows Command Shell – The malware utilizes PowerShell commands to manipulate security settings.
- T1204.002 – User Execution: Malicious File – Victims are tricked into executing the downloaded malware.
- T1547.001 – Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder – Malware implements persistence mechanisms through registry changes.
- T1056.001 – Input Capture: Keylogging – The malware captures keystrokes to extract sensitive data.
- T1567 – Exfiltration Over Web Service – Data is exfiltrated over web services to the command-and-control server.
- T1566.001 – Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment – Attachments are used to deliver malicious payloads via phishing techniques.
Indicator of Compromise :
- [File Name] VibeCall.exe
- [Hash] b63367bd7da5aad9afef5e7531cac4561c8a671fd2270ade14640cf03849bf52
- [File Name] videosolution_vibecall_b.exe
- [Hash] 386b61ccdd4b785c835a064179d5fa58dc0d5fe34970a04487968e1ee0189ce6
- [File Name] contry_solution_vibecall_e.exe
- [Hash] 4b371777c2c638c97b818057ba4b0a2de246479776eaaacebccf41f467bb93c3
- [File Name] aisolution_vibecall_a.exe
- [Hash] f2e8f1f72abbc42f96c5599b8f27f620d91ae1680aa14b4f0bbf3daabd7bee30
Full Story: https://www.seqrite.com/blog/unmasking-grasscall-campaign-the-apt-behind-job-recruitment-cyber-scams/