Using malicious Google Ads or SEO poisoning to distribute malware has become a common tactic for cybercriminals. For example, in the Secureworks® 2022 State of the Threat report, Counter Threat Unit™ (CTU) researchers described legitimate web searches being hijacked by SEO poisoning to infect victims’ systems with Gootloader, and malicious Google Ads bundling infostealers like RedLine in trojanized installers for messaging apps such as Signal.
Recently, CTU™ researchers observed Bumblebee malware distributed via trojanized installers for popular software such as Zoom, Cisco AnyConnect, ChatGPT, and Citrix Workspace. Bumblebee is a modular loader, historically distributed primarily through phishing, that has been used to deliver payloads commonly associated with ransomware deployments. Trojanizing installers for software that is particularly topical (e.g., ChatGPT) or software commonly used by remote workers increases the likelihood of new infections.
One of the Bumblebee samples CTU researchers analyzed was downloaded from http: //appcisco . com/vpncleint/cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi. On or around February 16, 2023, a threat actor created a fake download page for Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.x (see Figure 1) on the appcisco . com domain. An infection chain that began with a malicious Google Ad sent the user to this fake download page via a compromised WordPress site.
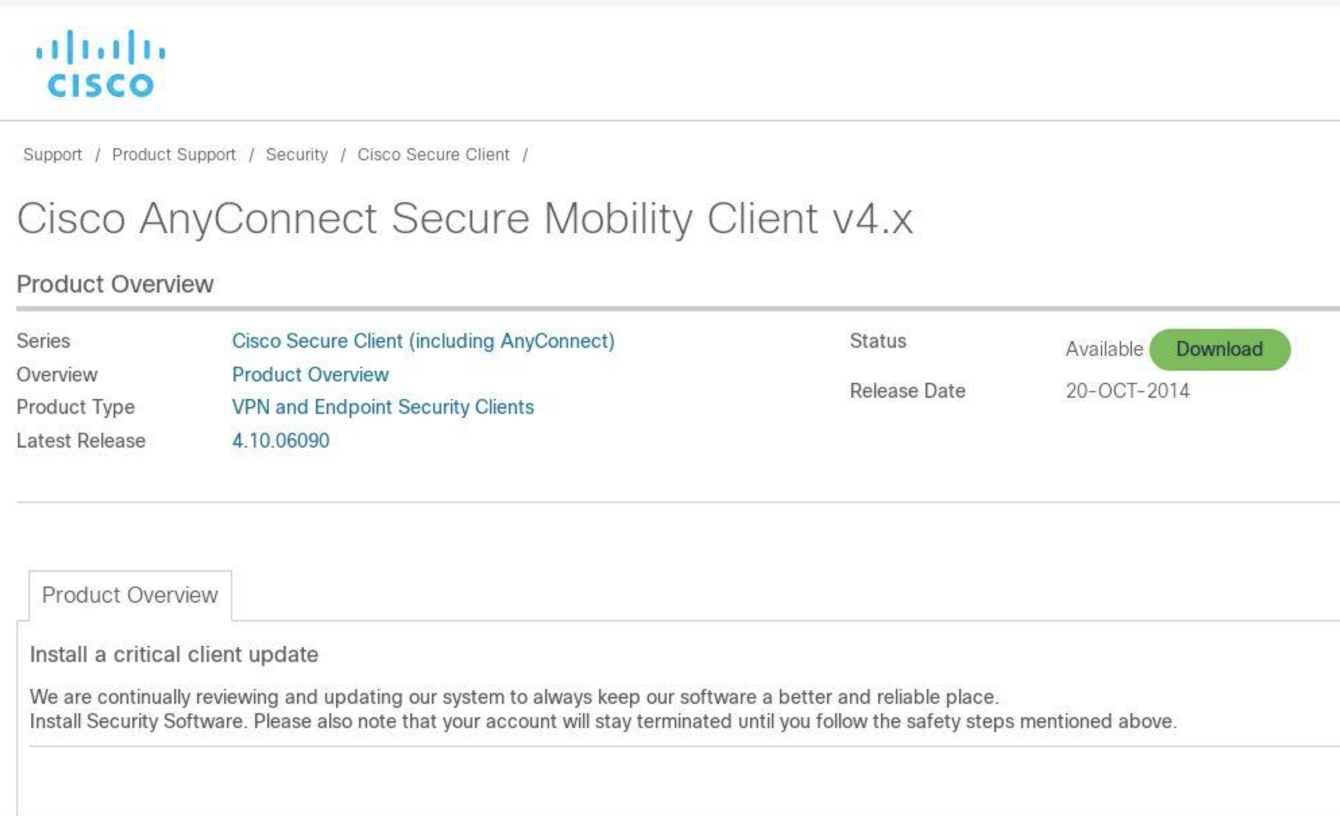
Figure 1. Malicious web page serving trojanized Cisco AnyConnect VPN installer. (Source: DomainTools)
The cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi file is an MSI installer that contains two files (see Figure 2).

Figure 2. Contents of trojanized Cisco AnyConnect VPN installer. (Source: Secureworks)
When the MSI installer is executed, renamed versions of these two files are copied to the “%Temp%Package Installation Dir” folder (see Figure 3) and executed.
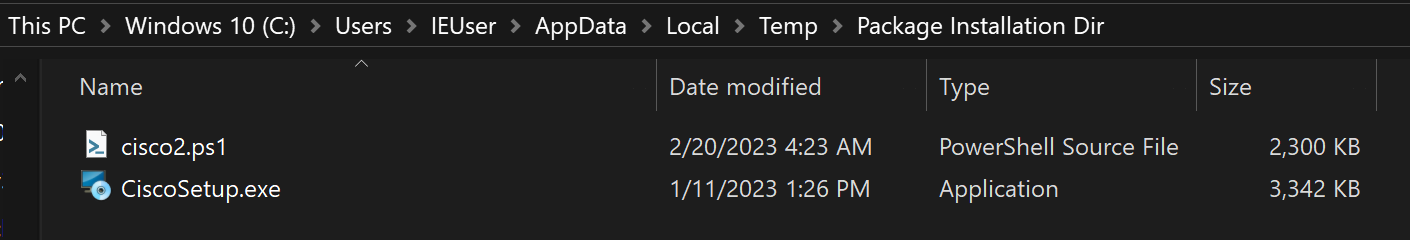
Figure 3. Renamed contents of trojanized Cisco AnyConnect installer. (Source: Secureworks)
FILE_InstallMeCisco (renamed to CiscoSetup.exe) is a legitimate installer for the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Secure Mobility Client application. FILE_InstallMeExe (renamed to cisco2.ps1) is a PowerShell script. CTU researchers identified other samples that used the same technique with a different software installer and related PowerShell script name, such as Zoom (ZoomInstaller.exe and zoom.ps1), ChatGPT (ChatGPT.msi and chch.ps1) and Citrix (CitrixWorkspaceApp.exe and citrix.ps1).
The PowerShell script contains a selection of renamed functions copied from the PowerSploit ReflectivePEInjection.ps1 script. It also contains an encoded Bumblebee malware payload that it reflectively loads into memory.
In one compromised environment, CTU researchers observed the threat actor moving laterally approximately three hours after infection, and deploying Cobalt Strike as well as the legitimate AnyDesk and DameWare remote access tools. The attacker used a Scheduled Task named WindowsSensor15 as a persistence mechanism for Cobalt Strike. Additional tools deployed by the threat actor included pshashes.txt, which is likely a script for conducting Kerberoasting attacks; a batch script to dump the contents of the Active Directory database; and a network scanning utility (netscanold.exe). These tools were dropped in the C:ProgramData directory. Network defenders detected the activity and disrupted access before the attacker achieved their objective, which was likely to deploy ransomware.
To mitigate this and similar threats, organizations should ensure that software installers and updates are only downloaded from known and trusted websites. Users should not have privileges to install software and run scripts on their computers. Tools such as AppLocker can prevent malware from being executed even if it is inadvertently downloaded.
CTU researchers identified numerous indicators associated with this threat (see Table 1). Due to the large number of C2 IP addresses extracted from the Bumblebee malware configuration data, the table only lists a subset. However, all identified indicators have been applied to Secureworks customer protections. Note that IP addresses can be reallocated. The IP addresses and domains may contain malicious content, so consider the risks before opening them in a browser.
| Indicator | Type | Context |
|---|---|---|
| appcisco.com | Domain name | Bumblebee malware staging server |
| e4a5383ac32d5642eaf2c7406a0f1c0f | MD5 hash | MSI file (cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
3e5637d253c40aefdb0465df15bc057e d5c26186 | SHA1 hash | MSI file (cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
d99b63e1740aa4f779b91d22f508a479 2f237f09413d24b51144e0694af5d34f | SHA256 hash | MSI file (cisco-anyconnect-4_9_0195.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
| 522c0b0d445c62cdeb0a80bcce645d57 | MD5 hash | MSI file (ProductCitrix.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
5dad52c67d114f7a3a5a1e7ae5b15b58 1054d468 | SHA1 hash | MSI file (ProductCitrix.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
957639998125a31c998b0104dba7f463 d0659716a0a5b62fcc82eb28a0c0477b | SHA256 hash | MSI file (ProductCitrix.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
| 6f7e07b84897cccab30594305416d36f | MD5 hash | MSI file (ChatGPT_Setup.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
6d1d531c921a17b36e792e2843311e27 b9aa77a4 | SHA1 hash | MSI file (ChatGPT_Setup.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
|
9982330ae990386cd74625f0eaa26ae6 97574694eb2ec330c2acac5e0149fdc0 | SHA256 hash | MSI file (ChatGPT_Setup.msi) containing Bumblebee malware |
| 711482ca4d5dcaf0aec4c7c4b3e1bef1 | MD5 hash | MSI file containing Bumblebee malware |
|
77b9050f2b974bc67996b6435520b557 a6ad1303 | SHA1 hash | MSI file containing Bumblebee malware |
|
e10dbd4a903b0fa82db9794df6496afe 17c98a166253d425f3535959110909a3 | SHA256 hash | MSI file containing Bumblebee malware |
| 173.44.141.131 | IP address | C2 server associated with Bumblebee malware activity (February 2023) |
| baveyek.com | Domain name | Cobalt Strike C2 server |
| 23.82.140.131 | IP address | Hosting Cobalt Strike C2 server (baveyak.com) (February 2023) |
| 172.93.193.3:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 23.81.246.22:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 95.168.191.134:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 104.168.175.78:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 172.93.193.46:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 157.254.194.104:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 37.28.157.29:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 23.106.124.23:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 194.135.33.182:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 54.38.139.94:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 192.119.65.175:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 107.189.8.58:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 205.185.114.241:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 104.168.171.159:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 103.144.139.159:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 91.206.178.204:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 198.98.58.184:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 172.241.27.120:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 23.106.223.197:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 23.108.57.83:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 54.37.131.232:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 23.82.128.11:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 160.20.147.91:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 103.175.16.10:443 | IP address:port | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (February 2023) |
| 45.61.187.225 | IP address | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (March 2023) |
| 91.206.178.68 | IP address | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (March 2023) |
| 193.109.120.252 | IP address | C2 server extracted from Bumblebee configuration data (March 2023) |
Table 1. Indicators for this threat.
If you need urgent assistance with an incident, contact the Secureworks Incident Response team.
Source: https://www.secureworks.com/blog/bumblebee-malware-distributed-via-trojanized-installer-downloads