Short Summary:
Kimsuky, a North Korean hacking group active since 2018, focuses on espionage and financially motivated cybercrime. They target various technologies and countries, employing sophisticated tactics and exploiting vulnerabilities to achieve their goals.
Key Points:
- Group Name: Kimsuky (also known as APT43)
- Motivation: Espionage and financial gain
- Target Technologies: Office Suites Software, Operating Systems, Web Applications
- Targeted Countries: South Korea, the United States, Japan, Vietnam, and NATO-affiliated European countries
- Recently Exploited Vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2024-21338
- CVE-2021-44228
- CVE-2017-17215
- CVE-2017-11882
- CVE-2020-0787
- CVE-2017-0199
- CVE-2017-0144
- Malware Used: RandomQuery, xRAT, Gold Dragon
- Recent Campaigns:
- Utilized a malicious Chrome extension (TRANSLATEXT) targeting South Korean academia.
- Deployed a Linux backdoor (Gomir) via trojanized software installers.
- Employed social engineering tactics such as spear-phishing and watering hole attacks.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs – created by AI
- Reconnaissance – T1594
- Gathering information about potential targets.
- Execution – T1053.005
- Executing malicious code on target systems.
- Defense Evasion – T1027
- Obfuscating malware to evade detection.
- Lateral Movement – T1550.002
- Moving within networks to access additional systems.
- Discovery – T1016
- Identifying network and system information.
- Collection – T1040
- Gathering sensitive information from compromised systems.
- Command and Control – T1071.001
- Establishing communication with compromised systems.
- Privilege Escalation – T1543.003
- Gaining elevated access to systems.
- Initial Access – T1190
- Gaining entry into victim networks.
- Credential Access – T1111
- Stealing user credentials for further access.
- Exfiltration – T1041
- Transferring stolen data out of the network.
Kimsuky is a North Korean hacking group identified as a moderately sophisticated cyber operator, active since at least 2018. This group primarily engages in espionage and financially motivated cybercrime to support its operations and align with the geopolitical interests of the North Korean government.
Alias:
Kimsuki APT43
Motivation:
Espionage
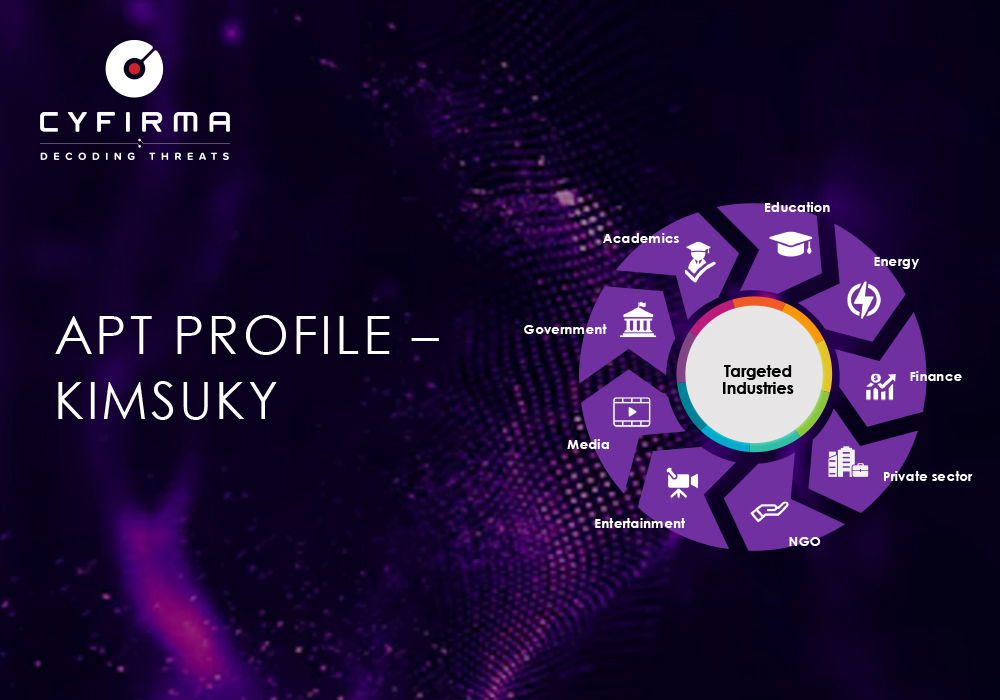
Target Technologies
Office Suites Software, Operating System, Web Application
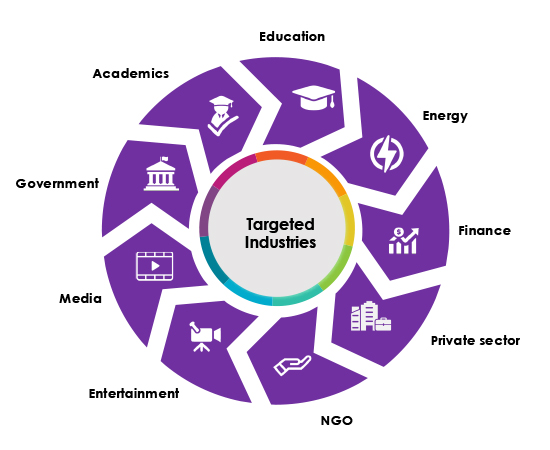
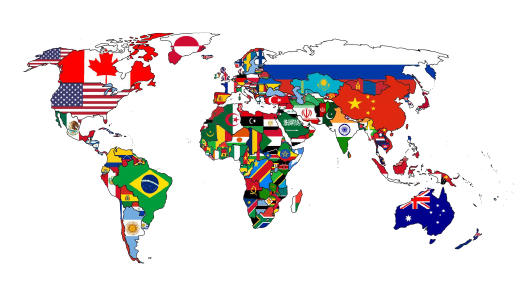
Targeted Countries
South Korea, the United States, Japan, Vietnam, and European countries (particularly those with ties to NATO)
Recently Exploited Vulnerabilities by Kimsuky
| CVE-2024-21338 | CVE-2021-44228 |
| CVE-2017-17215 | CVE-2017-11882 |
| CVE-2020-0787 | CVE-2017-0199 |
| CVE-2017-0144 |
Malware used by Kimsuky: RandomQuery, xRAT, Gold Dragon
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques used by Kimsuky
| Reconnaissance | Execution | Defense Evasion | Lateral Movement | Discovery |
| T1594 | T1053.005 | T1027 | T1550.002 | T1016 |
| T1593.001 | T1059.003 | T1562.001 | T1021.001 | T1518.001 |
| T1593.002 | T1059.001 | T1112 | T1534 | T1057 |
| T1591 | T1204.001 | T1036 | T1012 | |
| T1589.002 | T1059.006 | T1055 | Collection | T1040 |
| T1598.003 | T1204.002 | T1078.003 | T1005 | T1082 |
| T1589.003 | T1059.007 | T1564.002 | T1114.003 | T1083 |
| T1059.005 | T1564.003 | T1074.001 | T1007 | |
| Resource Development | T1562.004 | T1114.002 | ||
| T1587 | Persistence | T1218.005 | T1560.001 | |
| T1585.002 | T1505.003 | T1218.011 | T1560.003 | |
| T1583.006 | T1543.003 | T1218.010 | T1056.001 | |
| T1608.001 | T1176 | T1036.005 | T1557 | |
| T1583.004 | T1133 | T1027.002 | ||
| T1588.002 | T1078.003 | T1553.002 | Command and Control | |
| T1584.001 | T1098 | T1550.002 | T1071.001 | |
| T1588.005 | T1053.005 | T1036.004 | T1102.002 | |
| T1587.001 | T1136.001 | T1140 | T1219 | |
| T1583.001 | T1547.001 | T1070.004 | T1071.003 | |
| T1586.002 | T1546.001 | T1070.006 | T1071.002 | |
| T1585.001 | T1055.012 | T1105 | ||
| Privilege Escalation | ||||
| Initial Access | T1543.003 | Credential Access | Exfiltration | |
| T1133 | T1055 | T1111 | T1567.002 | |
| T1566.001 | T1078.003 | T1555.003 | T1041 | |
| T1078.003 | T1053.005 | T1552.001 | ||
| T1566.002 | T1547.001 | T1040 | ||
| T1190 | T1546.001 | T1003.001 | ||
| T1055.012 | T1056.001 | |||
| T1557 |
Kimsuky’s Recent Campaign Highlights and Trends:
- In a recent campaign, Kimsuky utilized a malicious Google Chrome extension called TRANSLATEXT to target South Korean academia. This extension is capable of stealing sensitive information, such as email addresses, usernames, passwords, and cookies, while also capturing browser screenshots. The group uploaded this extension to an attacker-controlled GitHub repository but removed it shortly after to minimize exposure.
- In a recent campaign, Kimsuky has been observed deploying a new Linux backdoor named Gomir, a variant of the GoBear backdoor. This malware is delivered via trojanized software installers and features direct C2 communication, persistence mechanisms, and the ability to execute a wide range of commands on infected systems.
- The Kimsuky group employs various social engineering tactics, including spear-phishing and watering hole attacks, to gain initial access to victim networks. They have also been known to create social media accounts to monitor potential targets and news trends relevant to their operations.
Source: Original Post