Summary: A recent alert from Sophos X-Ops MDR highlights a surge in ransomware attacks exploiting the critical CVE-2024-40711 vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication software. Attackers have been leveraging this flaw to create unauthorized accounts and deploy ransomware variants, emphasizing the urgent need for enterprises to patch their systems and enhance remote access defenses.
Threat Actor: Ransomware Operators | ransomware operators
Victim: Enterprises using Veeam Backup & Replication | enterprises using Veeam Backup & Replication
Key Point :
- Exploitation of CVE-2024-40711 allows attackers to execute remote code without authentication, leading to unauthorized account creation.
- Recent attacks have involved deploying Fog and Akira ransomware, with attackers also exfiltrating sensitive data using rclone.
- Organizations are urged to update to Veeam Backup & Replication version 12.2.0.334 or later and strengthen their VPN security measures.
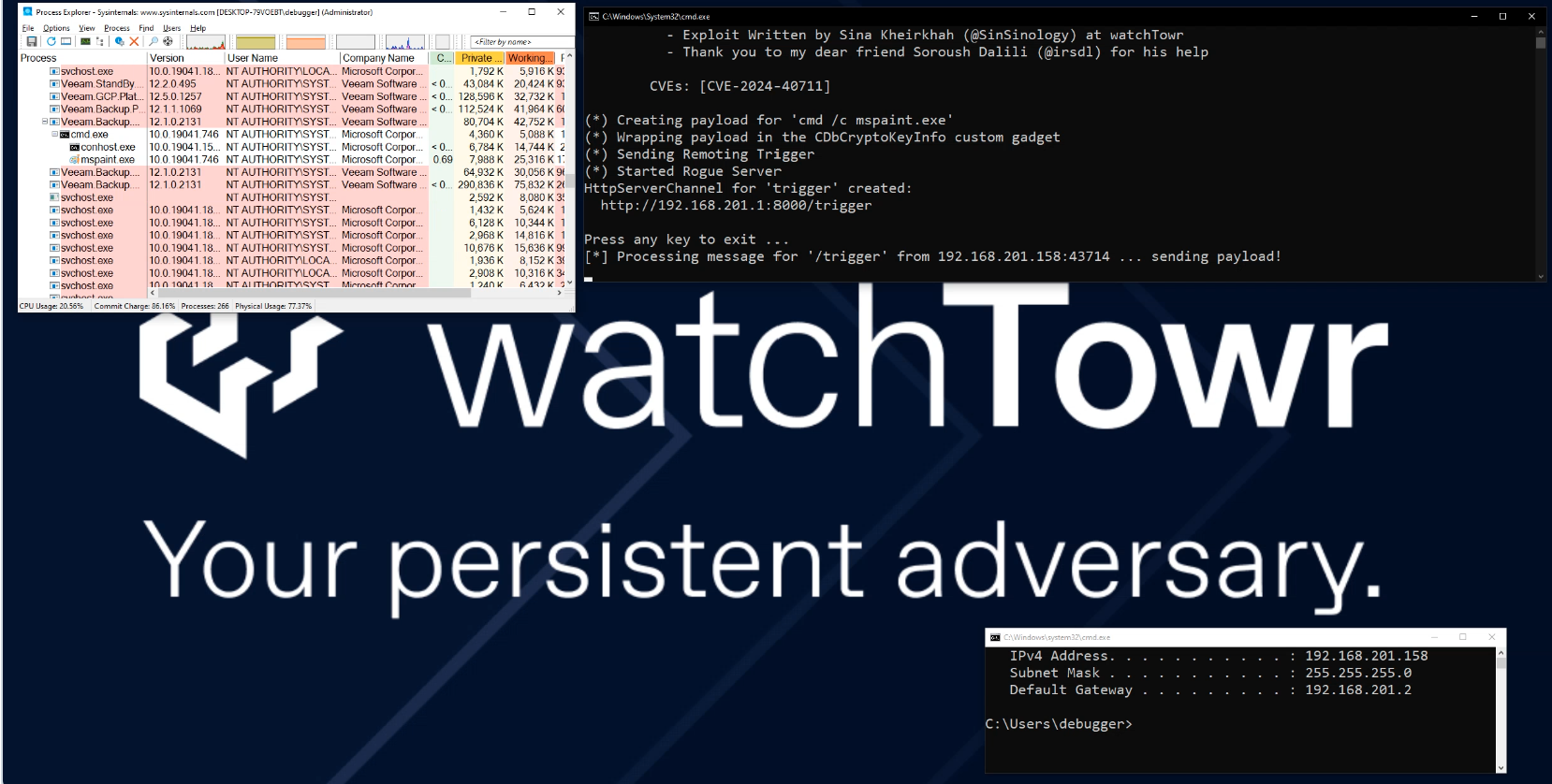
In a recent alert, Sophos X-Ops MDR and Incident Response revealed a surge in ransomware attacks exploiting a critical vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication software, CVE-2024-40711. Over the past month, attackers have leveraged this flaw, along with compromised credentials, to create unauthorized accounts and attempt to deploy ransomware variants, including Fog and Akira. Enterprises relying on Veeam Backup & Replication are strongly advised to patch their systems and strengthen remote access defenses immediately.
The CVE-2024-40711 vulnerability, assigned a CVSS score of 9.8, represents a deserialization of untrusted data flaw that allows attackers to execute remote code without authentication. This critical vulnerability was analyzed by security researcher Sina Kheirkhah (@SinSinology) of watchTowr, who published a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit, bringing it to the attention of the wider cybersecurity community.
Attackers can exploit this flaw through a specific URI /trigger on port 8000, causing the Veeam.Backup.MountService.exe to spawn a process that can lead to the creation of a new local account named “point”, which is then added to both the Administrators and Remote Desktop Users groups. This gives attackers privileged access to the system, a crucial step toward executing further malicious actions like deploying ransomware.
Sophos X-Ops revealed several cases where attackers exploited the CVE-2024-40711 vulnerability in unpatched versions of Veeam Backup & Replication software. In one of the tracked incidents, the attackers deployed Fog ransomware on an unprotected Hyper-V server, while another attack in the same timeframe attempted to deliver the Akira ransomware. These cases were traced back to unauthorized access via compromised VPN gateways that were either running outdated versions or had multifactor authentication (MFA) disabled.
In the Fog ransomware attack, the attackers didn’t stop at deploying ransomware. They also used a utility called rclone to exfiltrate sensitive data from the compromised system, highlighting the dual threat of encryption and data theft faced by victims of modern ransomware attacks.
Sophos emphasized that these incidents underline the necessity for organizations to maintain updated and fully supported VPN gateways, apply patches for known vulnerabilities, and implement multifactor authentication (MFA) to secure remote access points. The initial access in all cases was achieved via compromised VPN gateways, which underscores how critical these access points are to network security.
Enterprises using Veeam Backup & Replication are strongly urged to update to version 12.2.0.334 or later to ensure full protection.