Short Summary:
In 2024, the manufacturing sector has become a primary target for cyber attacks, particularly ransomware, leading to significant financial and operational disruptions. Key threat actors include various ransomware groups and hacktivist organizations, with the United States being the most targeted country. Manufacturers must enhance their cybersecurity measures to protect against evolving threats.
Key Points:
- The average cost of a data breach in manufacturing for small businesses is $105,000.
- It takes an average of 277 days to identify and contain a data breach.
- 1 in 5 breaches is caused by supply chain compromise.
- Ransomware groups like LockBit 3.0, Akira, and Black Basta are leading threats in the sector.
- The U.S. is the most targeted country, followed by France, India, and Italy.
- Manufacturers face risks from legacy systems and industrial control systems.
- Cybersecurity awareness and incident response plans are critical for manufacturers.
- SOCRadar offers tools for ransomware detection and supply chain intelligence.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs – created by AI
- Initial Access (TA0001)
- Phishing (T1566)
- Supply Chain Compromise (T1195)
- Execution (TA0002)
- Command and Scripting Interpreter (T1059)
- Persistence (TA0003)
- Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder (T1060)
- Privilege Escalation (TA0004)
- Exploitation for Client Execution (T1203)
- Defense Evasion (TA0005)
- Obfuscated Files or Information (T1027)
- Credential Access (TA0006)
- Credential Dumping (T1003)
- Discovery (TA0007)
- Network Service Scanning (T1046)
- Exfiltration (TA0008)
- Exfiltration Over Command and Control Channel (T1041)
- Impact (TA0009)
- Data Encrypted for Impact (T1486)
In 2024, the manufacturing sector will become a primary target for cyber attacks. According to data from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the average cost of a data breach in this industry for small businesses has reached $105,000, and it takes an average of 277 days to identify and contain such incidents. Furthermore, 1 out of 5 breaches is caused by supply chain compromise.

A depiction of a cyber attack targeting a high-tech manufacturing facility, highlighting ransomware and dark web threats. Designed by Dall-E.
With its critical role in global supply chains and reliance on legacy systems, manufacturing has become an attractive target for ransomware groups, hacktivist threat groups, and other cyber criminals. From data breaches to operational disruptions, these attacks have caused significant financial and reputational damage to some of the world’s largest manufacturers.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it’s crucial for manufacturers to stay ahead by understanding the tactics, techniques, and tools used by threat actors. This report will explore the major cyber attacks that have shaken the manufacturing industry in 2024, analyze the key actors behind them, and provide insights on how businesses can better protect themselves against these ever-increasing threats.
Cyber Threat Landscape in Manufacturing 2024: Key Actors and Targeted Regions
The manufacturing industry has become an increasingly attractive target for cybercriminals in 2024, with a variety of threat actors actively exploiting vulnerabilities in the sector. According to recent data, the most prominent threat actors targeting the manufacturing sector include a pro-Russian hacktivist threat group, People’s CyberArmy, and BreachForums’ admin IntelBroker, who stand out as the most active threat actors.
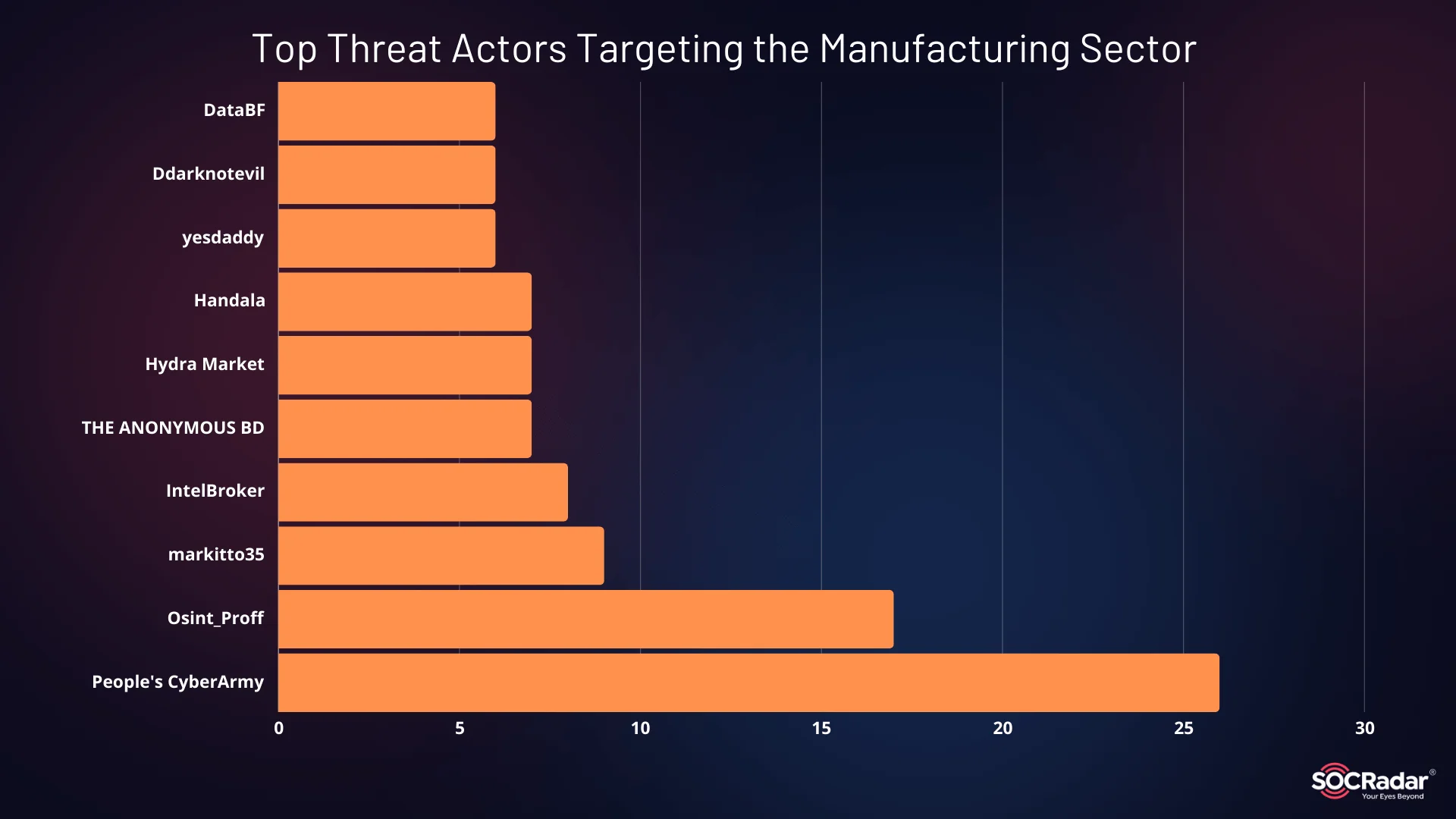
Top Threat Actors Targeting the Manufacturing Sector
In terms of ransomware groups LockBit 3.0 leads the pack, responsible for a significant number of attacks across the manufacturing industry. Other notable ransomware actors include Akira, Black Basta, and ALPHV (also known as BlackCat), all of which have been involved in major disruptions. These groups target critical systems, often leading to operational shutdowns and financial losses.
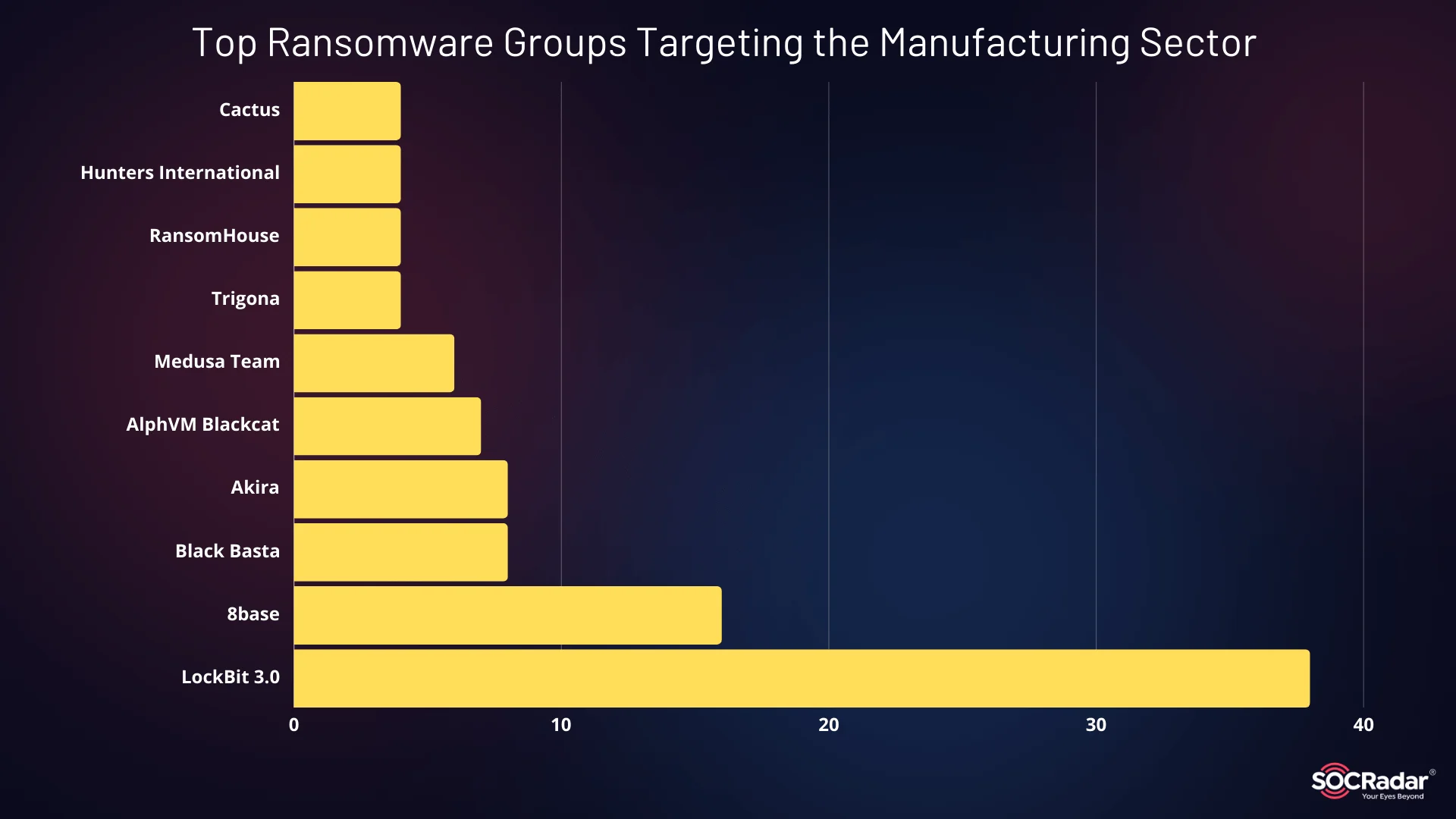
Top Ransomware Groups Targeting the Manufacturing Sector
When examining the global impact, the United States is by far the most targeted country, followed by France, India, and Italy. U.S.-based manufacturers have been hit particularly hard, with many facing ransomware attacks, data breaches, and service disruptions. This trend highlights the persistent focus on U.S. companies by cybercriminals, largely due to their high-value assets and critical role in global supply chains.
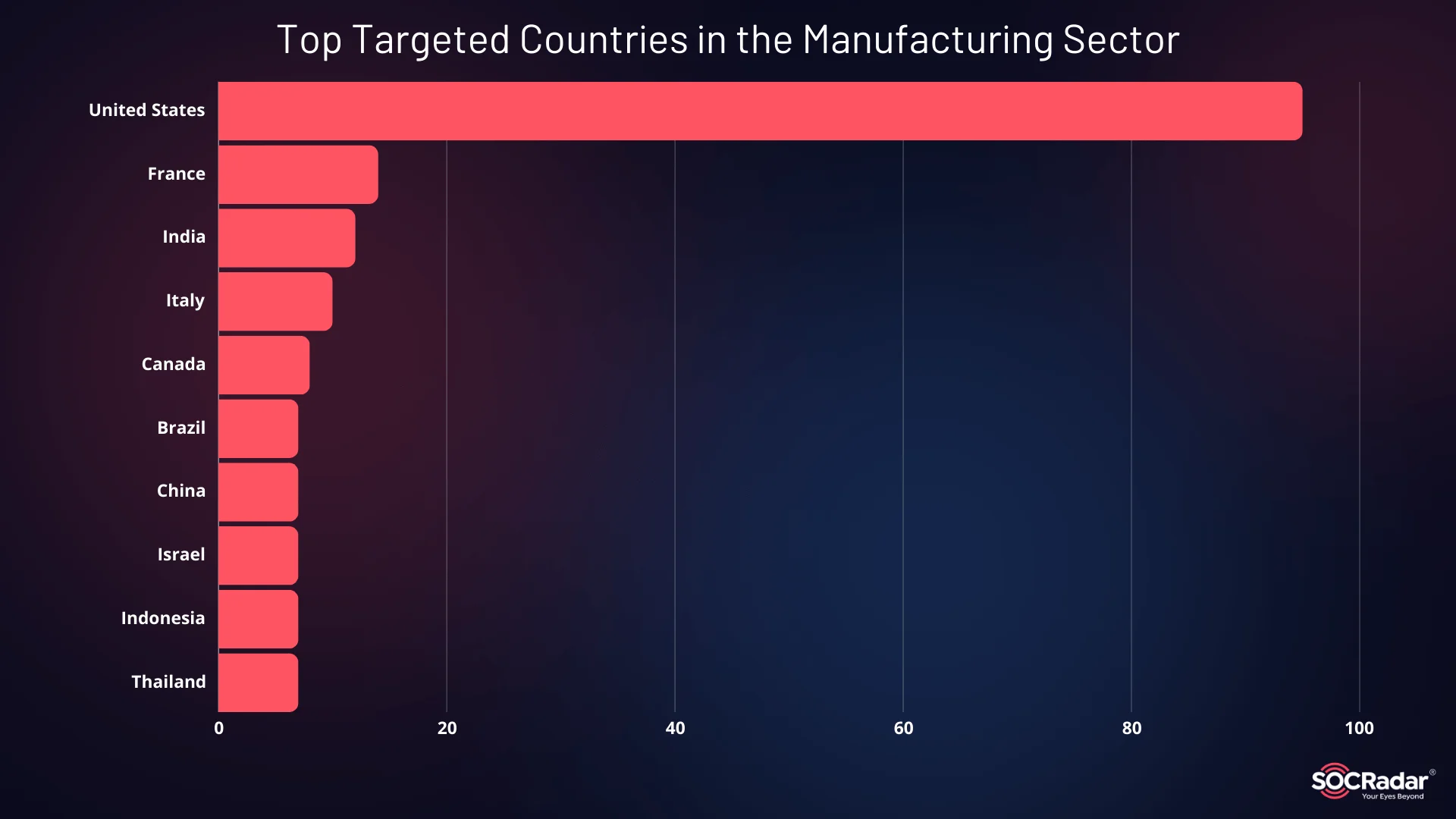
Top Targeted Countries in the Manufacturing Sector
Despite these rising threats, manufacturing is not the most mentioned sector on the Dark Web. Information, public administration, and retail trade sectors top the list, but manufacturing is steadily gaining attention from threat actors.
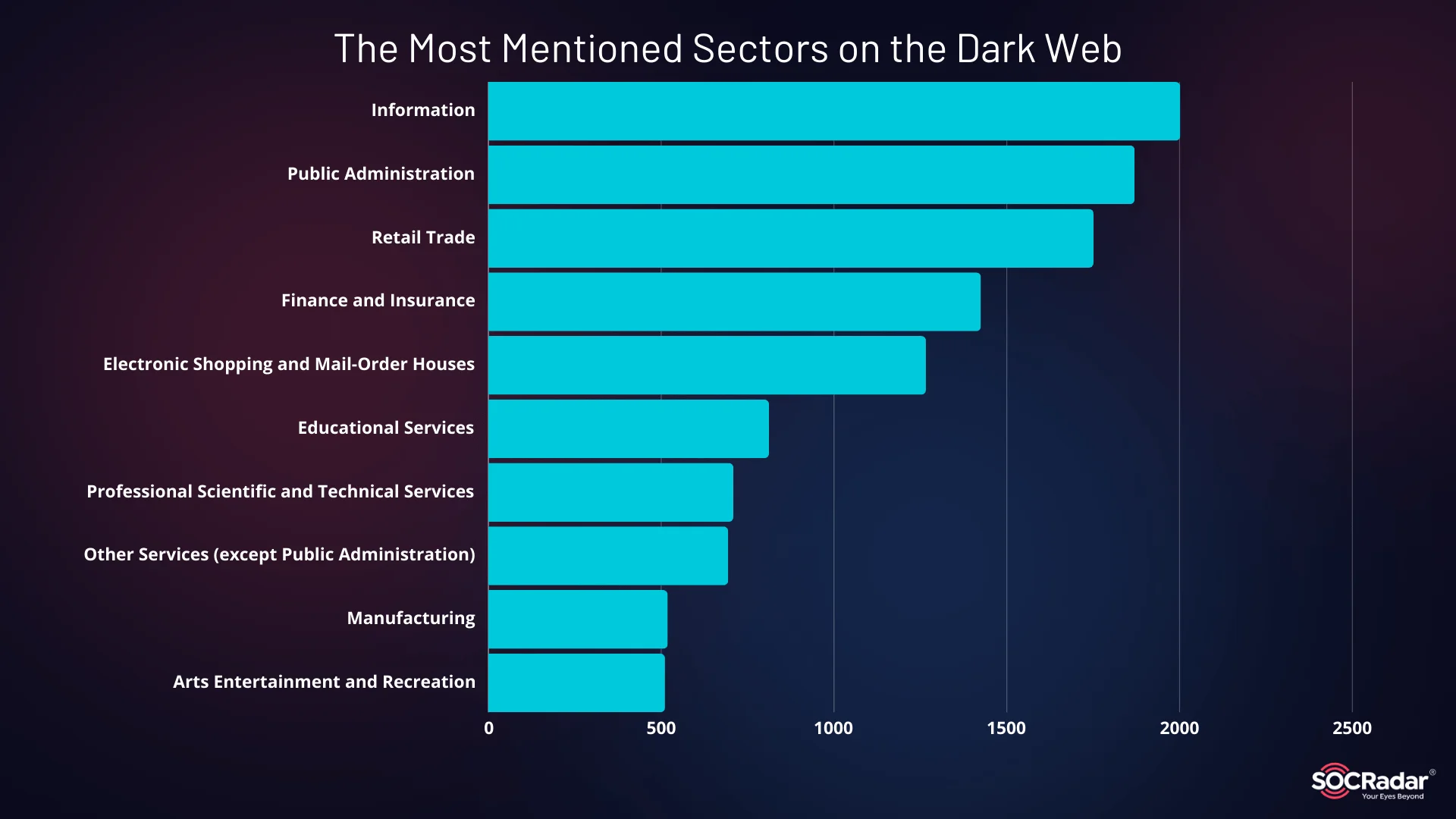
The Most Mentioned Sectors on the Dark Web (Hacker Forums, and Telegram)
However, although manufacturing isn’t the most frequently mentioned sector overall, the situation is different with ransomware groups. According to SOCRadar’s Ransomware Report, manufacturing is the sector most targeted by ransomware groups.
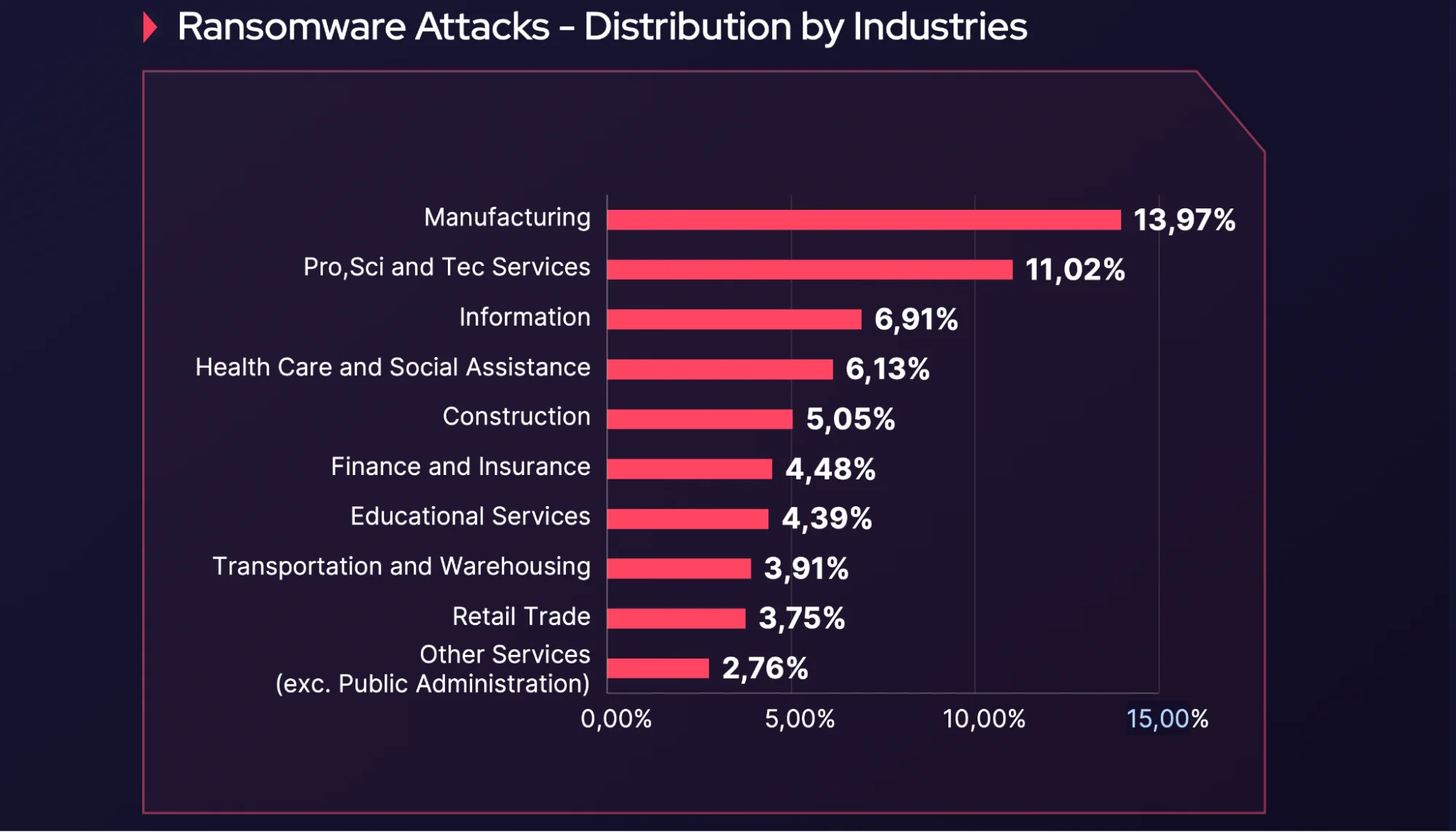
Ransomware Attacks – Distribution by Industries
These trends suggest a growing need for manufacturers to strengthen their cybersecurity measures, especially given the sophisticated tactics used by data brokers, hacktivist threat groups, and ransomware groups.

Essential Takeaways from 2024 Manufacturing Cyber Incidents
Increased Targeting by Ransomware: The manufacturing sector has become a prime target for ransomware attacks. Cybercriminals are exploiting the critical nature of manufacturing operations, knowing that downtime can cost millions, pushing companies to pay ransoms quickly.
SOCRadar Ransomware Intelligence
SOCRadar helps detect and prevent ransomware through several key features. Its Credentials & Data Leak Detection monitors the deep, dark, and surface web for stolen credentials and leaks, providing real-time alerts. The Asset Discovery feature identifies vulnerabilities and open ports in your internet-facing assets, enabling timely remediation. Additionally, the Ransomware Intelligence suite offers custom IoC collections and feeds that integrate with your security tools to block ransomware-related traffic. These capabilities empower organizations to stay ahead of ransomware threats.
Vulnerable Industrial Control Systems (ICS): Many manufacturers rely on legacy systems and industrial control systems that were not designed with cybersecurity in mind. These systems are vulnerable to attacks, and their exploitation can cause significant disruptions in production.
SOCRadar External Attack Surface Management
SOCRadar’s External Attack Surface Management helps secure your digital footprint by monitoring vulnerable software, exposed assets, and SSL certificates in real-time. It provides alerts on critical vulnerabilities and detects Shadow IT, enabling proactive threat protection and keeping your systems secure.
Supply Chain Threats: Manufacturers are highly reliant on their supply chain, and cyber attacks on suppliers or vendors can have cascading effects. Securing the entire supply chain is essential to mitigate the risks of data breaches or malware propagation.
SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence provides visibility into over 50 million companies, helping you monitor cyber risks and third-party vulnerabilities. With dynamic scoring and customizable alerts, you can prioritize and secure high-risk suppliers, ensuring a more resilient supply chain.
Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness: Many organizations in the sector lag behind in cybersecurity maturity. Regular training and awareness programs are crucial to ensure that employees understand common threats like phishing or social engineering.
IoT and Smart Manufacturing Risks: As manufacturers adopt more IoT devices and smart technologies, they are also increasing the attack surface. These devices often have security vulnerabilities that can be exploited if not properly secured.
Need for Incident Response Plans: Given the critical nature of manufacturing, having a robust incident response plan is essential. Quick and effective responses to cyber incidents can help limit the damage and restore operations faster.
Regulatory Compliance: Manufacturers must ensure compliance with evolving cybersecurity regulations and standards, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, to avoid penalties and improve their security posture.
Top Manufacturing Cyber Attacks 2024
1. Akira Threatened to Leak 110GB of Data Stolen from UK Cosmetics Giant Lush
In January 2024, the SOCRadar Dark Web Team detected a claim by the Akira ransomware group, alleging the theft of 110 GB of data from Lush, a UK-based cosmetics company. According to Akira’s statement, the stolen data includes accounting records, financial documents, and client details.
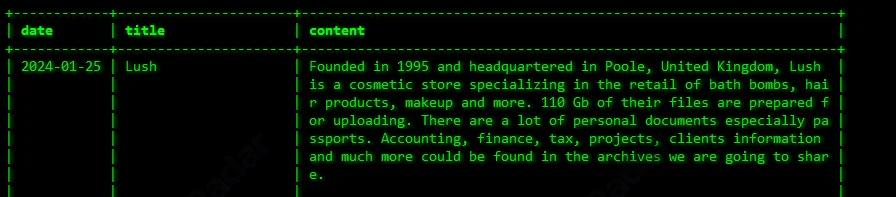
Akira’s claims to have breached Lush
A significant portion of the stolen data allegedly includes passport scans collected during Lush’s recruitment process for identity verification. This suggests that the attackers may have accessed sensitive employee information.
2. Schneider Electric Targeted by Cactus Ransomware Group in 1.5TB Data Breach
In January 2024, the Cactus ransomware group claimed to have breached Schneider Electric, a global leader in energy and automation, stealing approximately 1.5TB of data. The breach primarily affected Schneider Electric’s Sustainability Business division, leading to disruptions on the Resource Advisor cloud platform.

Cactus’ claims to have breached Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric confirmed the breach but assured that other divisions were not impacted. The Cactus group supported their claim by publishing 25MB of allegedly stolen data on their Tor leak site, which included passport images and company documents.

For further details on the Cactus Ransomware group’s tactics and operations, explore SOCRadar’s Dark Web Profile.
3. Nissan Data Breach Led to Exposure of Over 53,000 Employees’ Information
Last year, Nissan North America suffered a significant data breach when a threat actor targeted the company’s external VPN, resulting in a ransomware attack that forced systems to shut down. The breach, discovered in early November 2023, has since exposed the personal data of more than 53,000 current and former employees.
In a notification to those affected, Nissan explained that the cyber attack was detected on November 7, 2023, and immediately reported to law enforcement. The company quickly initiated an investigation and containment measures, working with external cybersecurity experts to eliminate the threat.
The investigation revealed that the attacker had accessed files stored on local and network shares, containing business-related information. However, it wasn’t until February 28, 2024, that Nissan identified the exposure of personal data, including Social Security numbers. The company reassured that no financial information had been compromised.
While there is no evidence of misuse of the exposed data, Nissan has offered affected individuals free 24-month credit monitoring and identity theft protection through Experian to minimize potential risks
4. Cencora Data Breach Exposed Sensitive Patient Data from Major Pharmaceutical Companies
In February 2024, Cencora, formerly known as AmerisourceBergen, experienced a serious data breach that compromised the data of several major pharmaceutical companies. The breach, reported in a filing with the SEC, allowed unauthorized access to personal information from Cencora’s systems.

Cencora’s 8K report filed with the SEC
Initially, the details of the breach and its impact on clients were not fully disclosed, and no ransomware group was linked to the incident.
By late May 2024, the California Attorney General’s office made notifications from pharmaceutical firms such as Novartis, Bayer, AbbVie, and GlaxoSmithKline public, revealing the full extent of the breach. Exposed data included personal information such as names, addresses, medical diagnoses, medications, and prescriptions.

5. ShinyHunters Allegedly Leaked Data of High-Profile Individuals from Neiman Marcus
In July 2024, ShinyHunters claimed to have stolen 193 million barcodes, including Taylor Swift tickets, valued at nearly $23 billion. They demanded $8 million and hinted at future leaks involving 30 million more tickets.
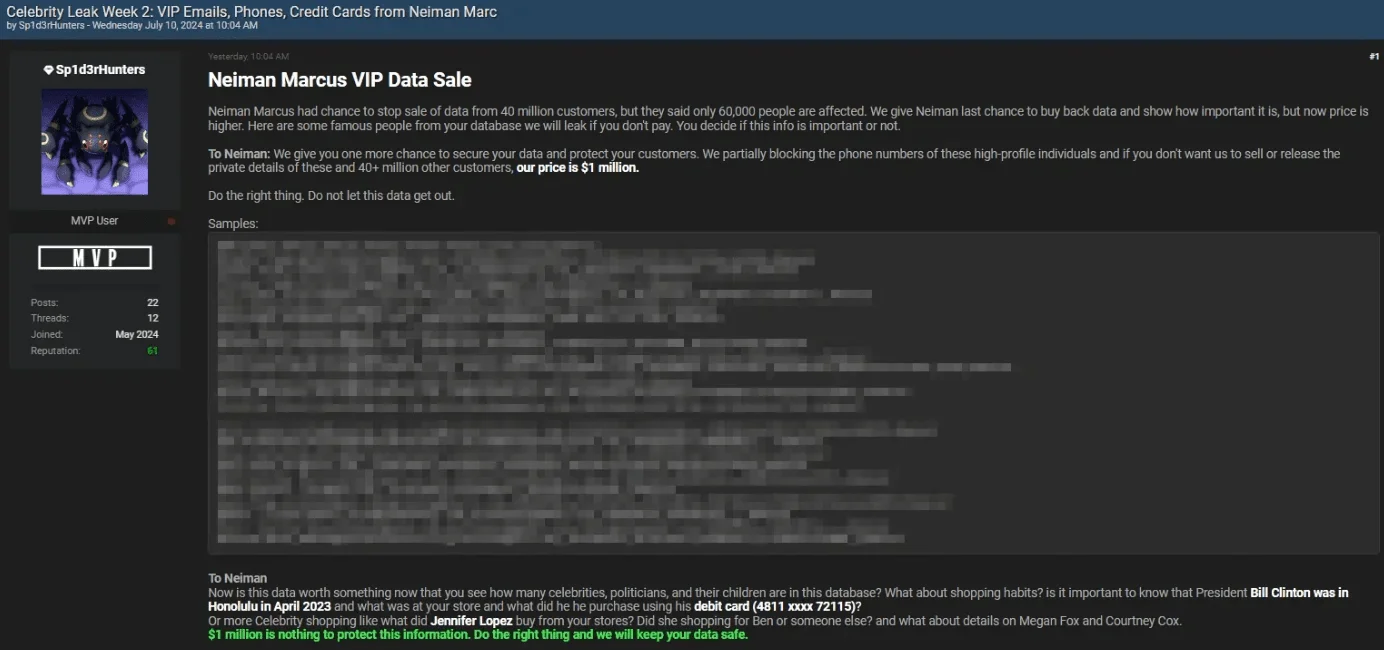
Threat actor’s post: Exclusive Neiman Marcus VIP Data Leaked in Week 2 of Celebrity Breach
On July 5, 2024, Sp1d3rHunters escalated by releasing 170,000 Taylor Swift barcodes during “Celebrity Leak Week 1” and demanded $2 million from Ticketmaster to prevent further exposure of 680 million users’ data, including tickets for major events like P!nk, F1, and NFL.
During “Celebrity Leak Week 2,” Sp1d3rHunters leaked additional Neiman Marcus data, involving high-profile figures like Biden, Trump, and Elon Musk.
Earlier in June, ShinyHunters had leaked a Neiman Marcus database containing data from 40 million customers, demanding $1 million to prevent more releases.
6. Halliburton Hit by RansomHub Cyber Attack, Disrupting Operations
In late August 2024, Halliburton, a global leader in energy and oil services, experienced a major cyber attack, forcing the shutdown of critical systems. The breach, reported in a U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filing, involved unauthorized access to the company’s IT infrastructure.

Halliburton’s 8K report filed with the SEC
Upon discovery, Halliburton immediately disabled affected systems and launched an investigation with external cybersecurity experts. Law enforcement was also contacted to support the response.
The breach disrupted essential operations, preventing customers from processing invoices and purchase orders. Halliburton is working to restore systems and assess the broader impact of the attack.
The RansomHub ransomware group claimed to be behind the attack. This incident is part of a broader wave of attacks targeting U.S. critical infrastructure, with over 200 entities affected by RansomHub since February 2024.
7. Toyota Responds to Alleged Data Breach Involving Third-Party Vendor
In August 2024, Toyota addressed reports of a data breach involving 240GB of stolen information. The company clarified that its own systems were not compromised, but the breach occurred through a third-party vendor linked to the automaker.
Details surrounding the breach remain limited, with Toyota emphasizing that the incident affected a small scope and did not pose a system-wide threat. Toyota Motor North America confirmed that its internal systems were unaffected, dispelling rumors of a direct attack on its network.
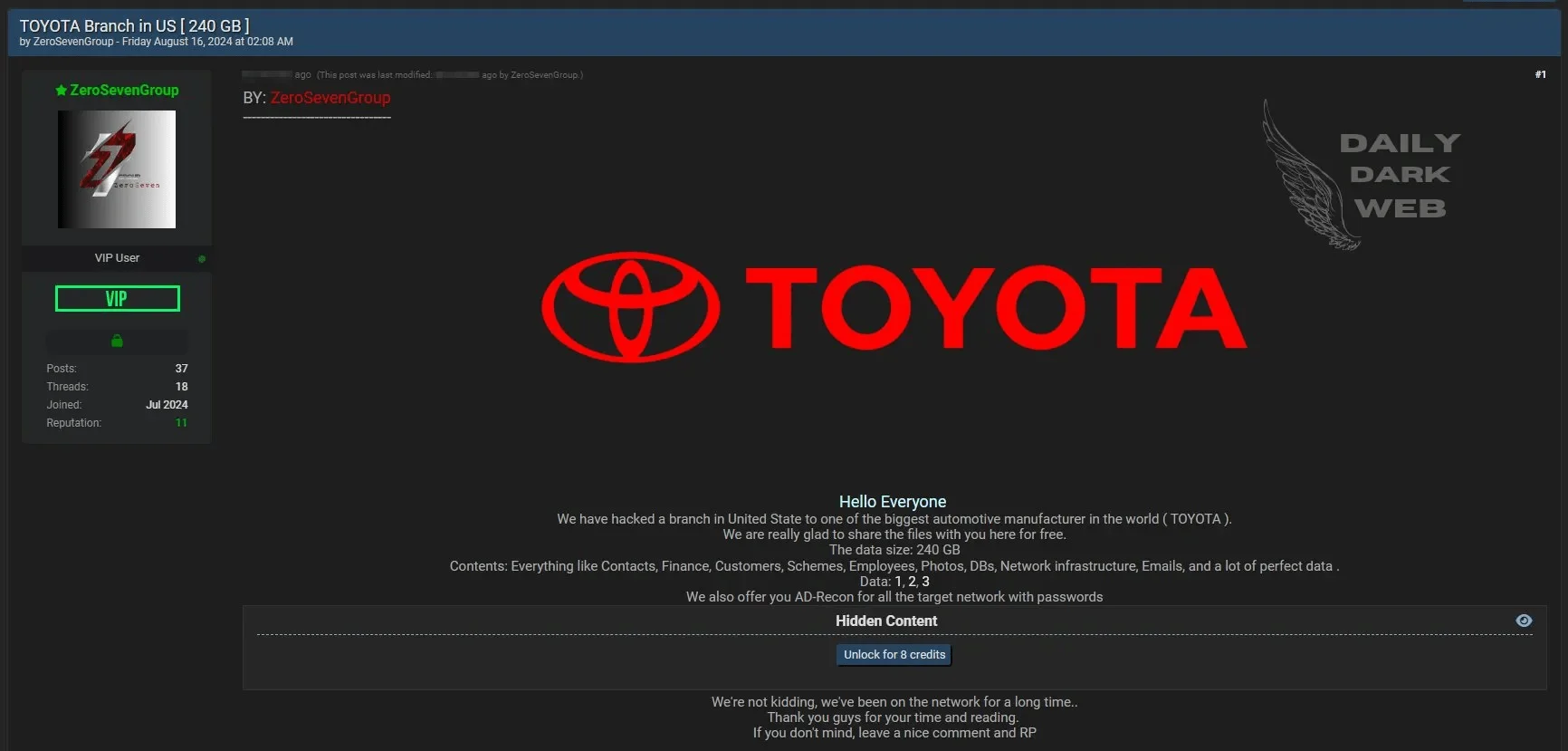
Threat actor’s post regarding the Toyota data breach
ZeroSevenGroup, the threat actor behind the breach, claimed to have obtained sensitive information about Toyota’s employees, customers, contracts, and financial records. They also alleged access to network infrastructure details using the ADRecon tool, potentially broadening the impact of the breach.
8. Alleged Bausch Health Breach Exposes 1.6 Million DEA Numbers
On July 30, 2024, Sp1d3rHunters posted claims of a major data breach involving Bausch Health, a global pharmaceutical company. The threat actor alleged that they had acquired 1.6 million DEA numbers, which are assigned to healthcare providers for writing prescriptions. The total volume of stolen data, including detailed prescriber information, was said to be 3TB.
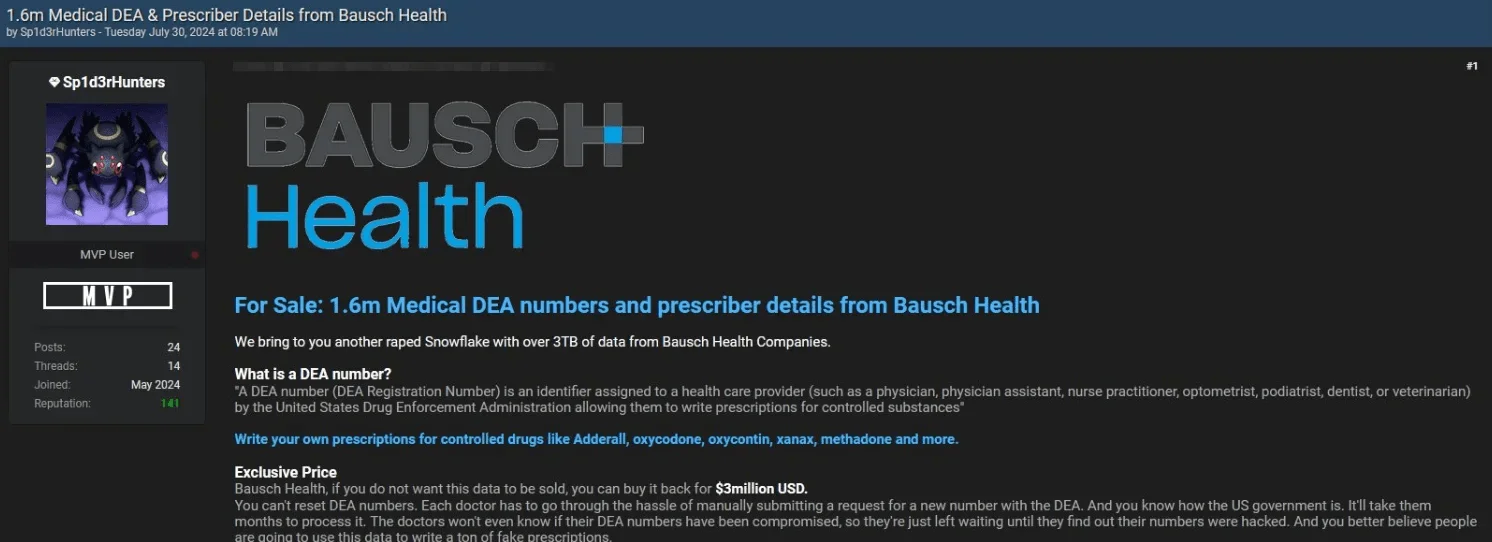
Bausch Health data breach post
The breach puts Bausch Health, which operates in over 90 countries, under significant pressure. The attackers demanded a $3 million ransom to prevent the sale of the stolen data. To back up their claims, Sp1d3rHunters shared samples of prescriber numbers with partially redacted DEA numbers, adding credibility to the breach.
9. RansomHub Claims Ransomware Attack on Nissan Dubai Branches, Exfiltrating Over 500,000 Client Records
SOCRadar Dark Web Team detected a claim by the RansomHub group regarding a ransomware attack on Nissan’s Dubai branches on August 31, 2024.
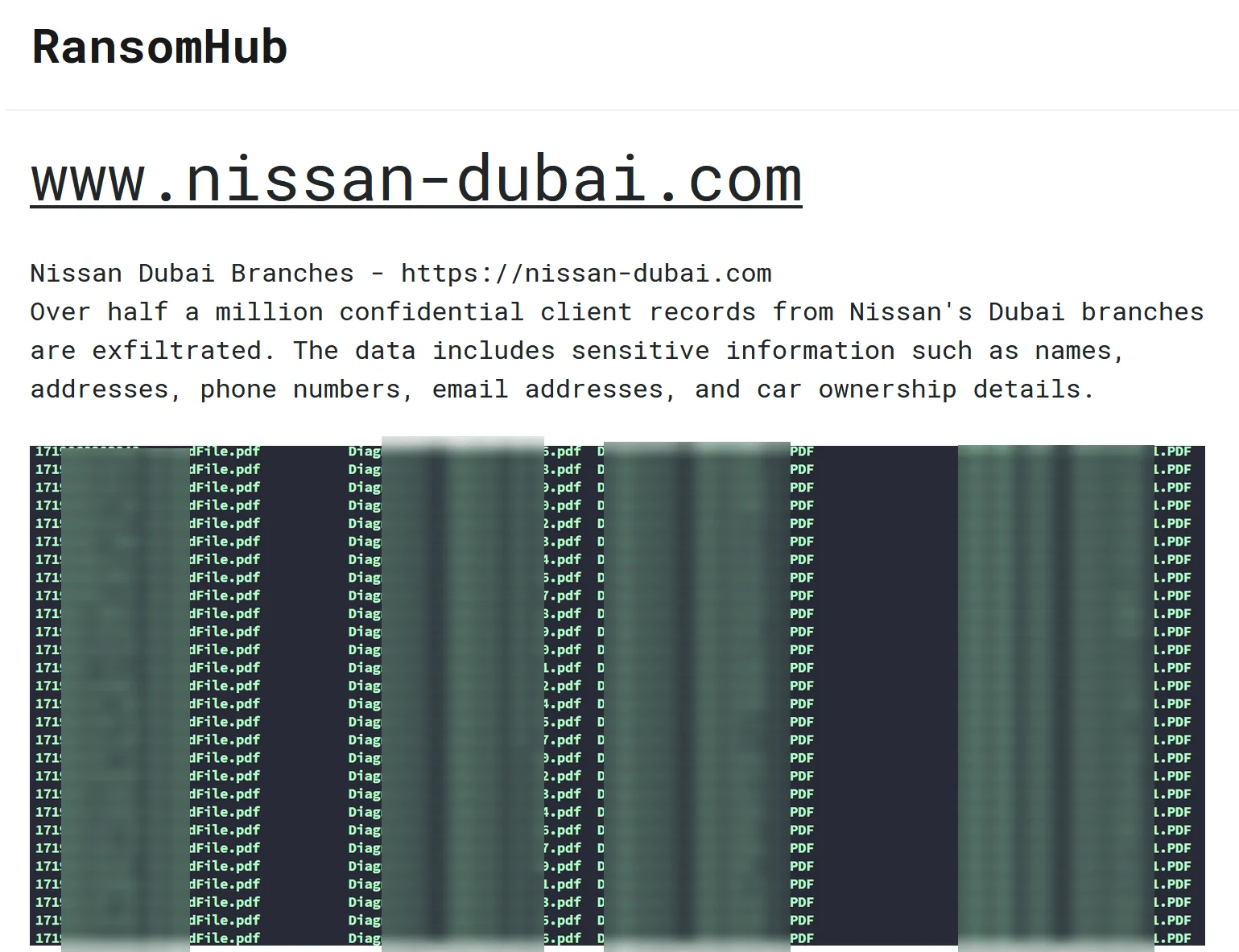
RansomHub’s claims to have breached Nissan
According to the threat actor’s claims, they have exfiltrated over 500,000 confidential client records from nissan-dubai.com, including sensitive information such as names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and car ownership details.
This alleged breach, dated August 31, 2024, could pose significant risks to Nissan’s clients, exposing personal information and potentially leading to further security concerns.
10. IntelBroker Shares Two Alleged Breaches of AMD Data on the Dark Web
The SOCRadar Dark Web Team has uncovered two separate posts from the threat actor
IntelBroker, both involving claims of breaches targeting AMD (Advanced Micro Devices).
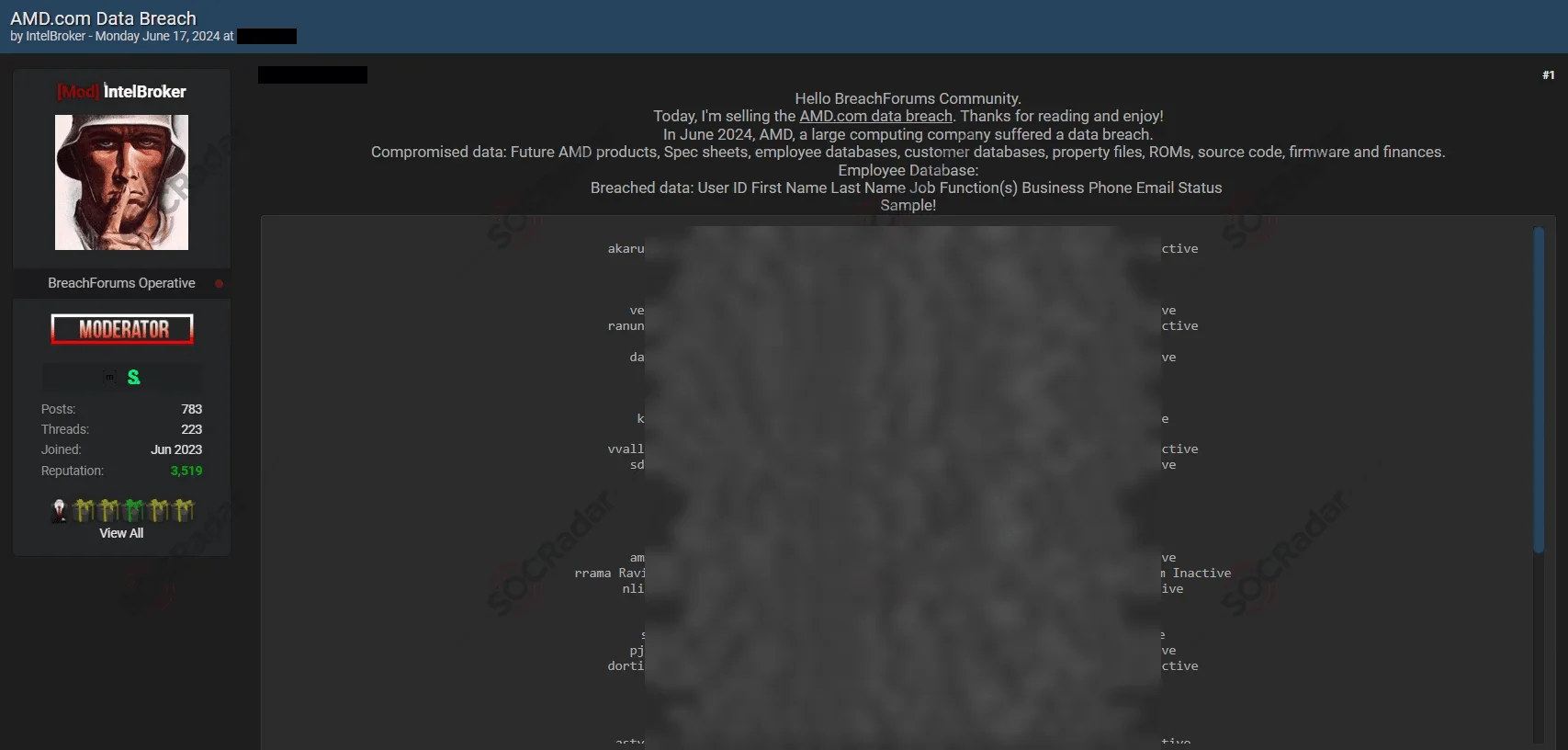
Below is the screenshot of IntelBroker’s first post on June 17, 2024, detailing the alleged breach of AMD’s database
On June 17, 2024, IntelBroker claimed to have infiltrated AMD’s database and listed the stolen data for sale. The allegedly compromised information includes highly sensitive details such as future AMD products, spec sheets, customer databases, property files, ROMs, source code, firmware, financial records, and personal information of AMD employees, including user IDs, full names, job functions, phone numbers, and emails.
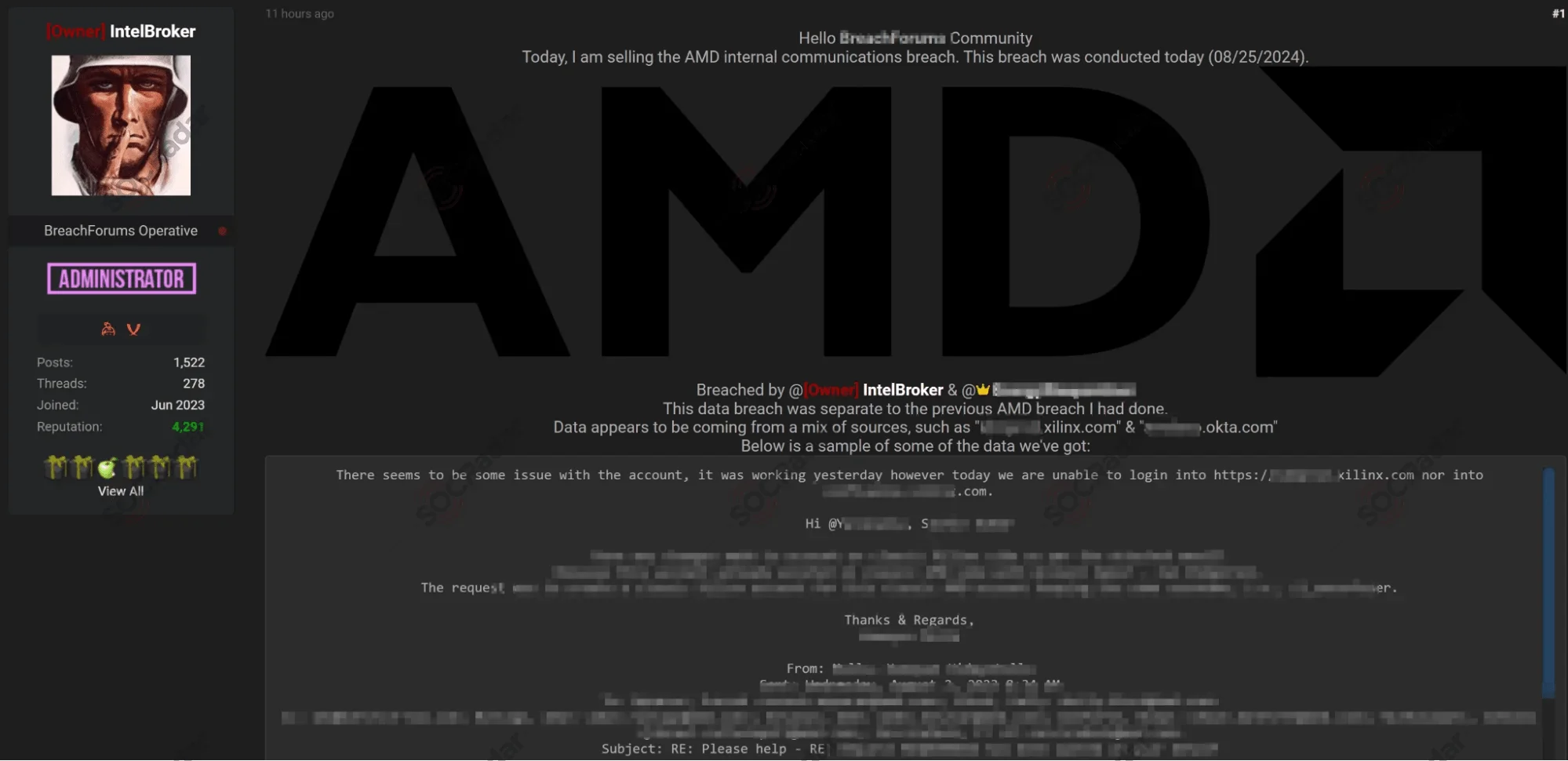
The second screenshot, from August 25, 2024, showcases IntelBroker’s claim regarding the breach of AMD’s internal communications
On August 25, 2024, IntelBroker made a second claim, asserting that they had breached AMD’s internal communications. This new breach, according to the threat actor, differs from the first and purportedly contains sensitive internal conversations related to AMD’s operations.
Conclusion
In 2024, the manufacturing sector has faced a growing wave of cyber attacks, especially ransomware incidents, leading to severe operational disruptions and financial losses. Throughout the years, cybercriminals have increasingly exploited vulnerabilities in outdated systems, industrial control networks, and supply chains.
Threat actors, often active on the Dark Web and hacker forums, continue to adapt their tactics. This makes it critical for manufacturers to implement effective cybersecurity strategies. SOCRadar provides real-time threat detection and prevention, helping businesses protect their sensitive data and maintain operational resilience.
As we approach the end of 2024, manufacturers must remain vigilant and continuously improve their defenses to stay ahead of the constantly evolving threat landscape.

Source: Original Post
Views: 1